New parking space with solar panels – looking for a roof with photovoltaics: Planning a solar carport or building a system in Düren, Ratingen, Lünen or Marl?
Language selection 📢
Published on: October 17, 2021 / Updated on: October 18, 2021 – Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
Solar carports for all requirements and needs
Solar carports are available in various sizes and for all requirements. Single carports, double carports, and from single to double-row carports.
They protect against rain, wind, and even the sun! A solar carport also generates electricity. In addition, it offers plenty of space for vehicles, and optionally, energy storage systems and charging stations can be integrated. Furthermore, a solar carport pays for itself in a short time.
Depending on the starting point, a solar carport can be erected relatively quickly. Especially with large, covered solar parking areas, it's important that they are stable and durable. They should require little maintenance and not be rendered unusable after every minor collision, potentially requiring complete repairs.
They must therefore be able to withstand a lot and suffer virtually no damage in accidents. They have to be indestructible.
Then again, there are solar carports that need to have a prestigious design, whether for municipalities, hotels, or events and functions. Transparent glass-glass solar modules are the ideal solution for such a solar carport.
Our solar carport solutions for covering open parking areas are modular and scalable:
- Quick and easy assembly
- Individually customizable design (color, materials, surface, size, etc.)
- Installation of charging stations and inverters is possible at any time
- Scalable & modular: Available as a single, double or arbitrarily scalable row carport
- Suitable for use even in the standard version for very high wind and snow loads
- …and much more
📣 Open parking areas: Photovoltaic solutions for industry, retail and municipalities
Everything from a single source, specially designed for solar solutions for large parking areas. You refinance or counterfinance into the future with your own electricity generation.
🎯 For solar engineers, plumbers, electricians and roofers
Advice and planning including a non-binding cost estimate. We bring you together with strong photovoltaic partners.
👨🏻 👩🏻 👴🏻 👵🏻 For private households
We are positioned across regions in German-speaking countries. We have reliable partners who advise you and implement your wishes.
With over 1,000 specialist articles, we cannot present all topics here. Therefore, you will find a small excerpt from our work here and we would be pleased if we have piqued your interest in getting to know us better:
Our Solar PDF Library
Large PDF library: Market monitoring and market intelligence on the topic of photovoltaics.
Data is viewed at regular intervals and checked for relevance. This usually brings together some interesting information and documentation, which we combine into a PDF presentation: our own data analyzes and marketing intelligence as well as external market observations.
More about it here:
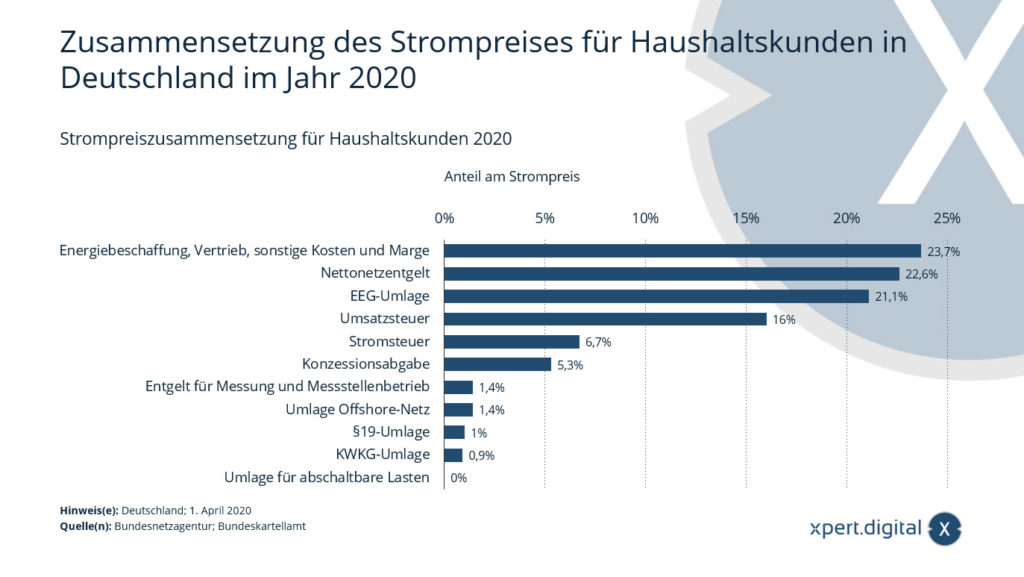
Electricity price composition for residential customers
The statistic shows the composition of the electricity price for household customers in Germany in 2020. In 2020, the item “net network charge” amounted to approximately 23 percent of the total electricity price for household customers.
Composition of the electricity price* for household customers in Germany in 2020
- Energy procurement, distribution, other costs and margin – 23.7%
- Net network charge – 22.6%
- EEG surcharge – 21.1%
- Value Added Tax – 16%
- Electricity tax – 6.7%
- Concession fee – 5.3%
- Fee for measurement and meter operation – 1.4%
- Offshore grid levy – 1.4%
- Section 19 levy – 1%
- CHP levy – 0.9%
- Levy for interruptible loads – 0%
Average composition of commercial electricity prices according to the Federal Network Agency (2016)
- Energy supplier's performance – 24%
- Government taxes and levies – 48%
- Network operator's network charges – 28%
* Volume-weighted averages across all tariffs (standard contract with the basic supplier, special contract with the basic supplier, contract with an energy supplier other than the basic supplier) as of April 1, 2020.
EEG = Renewable Energy Sources Act; KWKG = Combined Heat and Power Act.
Composition of the electricity price for household customers in Germany
The statistic shows the development of the composition of the electricity price for household customers in Germany in the years 2020 and 2021. In 2021, the electricity tax for private households in Germany was 2.05 euro cents per kilowatt hour.
Composition of the electricity price for residential customers in Germany in 2020
- Network charge (incl. measurement, billing, meter operation) – 7.75 cents
- Procurement, sales – 7.51 cents
- EEG surcharge – 6.76 cents
- Value added tax – 5.08 cents
- Electricity tax – 2.05 cents
- Concession fee – 1.66 cents
- §19 levy NEV levy – 0.36 cents
- Offshore network levy* – 0.42 cents
- CHP surcharge – 0.23 cents
- Surcharge for switchable loads – 0.01 cents
Composition of the electricity price for household customers in Germany 2021
- Network charge (incl. measurement, billing, meter operation) – 7.80 cents
- Procurement, sales – 7.70 cents
- EEG surcharge – 6.50 cents
- Value added tax – 5.09 cents
- Electricity tax – 2.05 cents
- Concession fee – 1.66 cents
- §19 levy NEV levy – 0.43 cents
- Offshore network levy* – 0.40 cents
- KWKG surcharge – 0.25 cents
- Surcharge for switchable loads – 0.01 cents
* Offshore liability levy until 2018.
The figures are based on a 3-person household with an annual consumption of 3,500 kilowatt hours. Some values are rounded. The concession fee is based on the average; it varies depending on the size of the municipality.
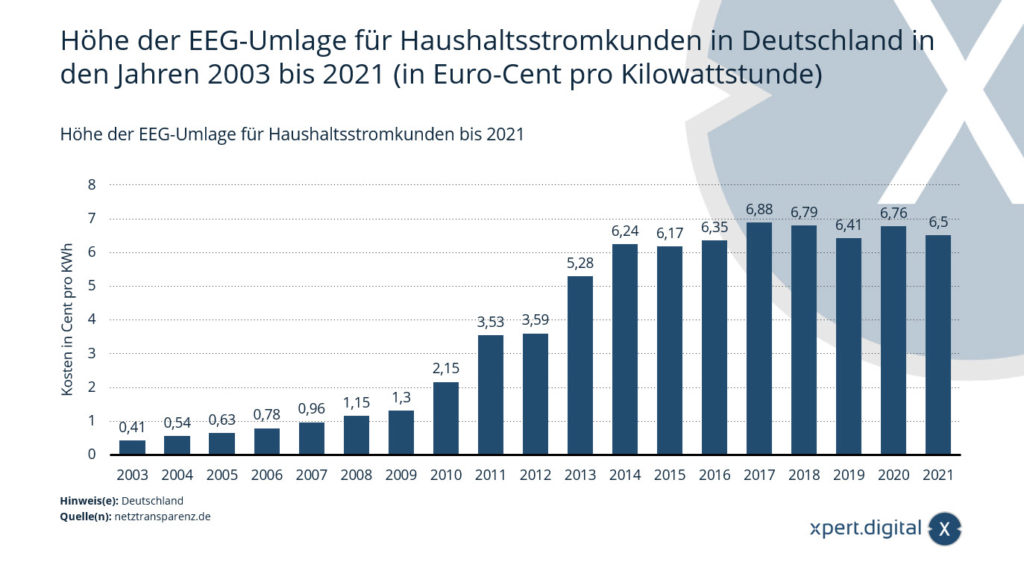
Amount of the EEG surcharge for household electricity customers
Amount of the EEG surcharge for household electricity customers in Germany in the years 2003 to 2021 (in euro cents per kilowatt hour)
The figures for the years from 2019 onwards were taken from the same publications of the previous year. The figures for the years 2010 to 2018 are taken from the reports of the four transmission system operators. The figures for the years before 2010 are taken from the publication “Exemption of energy-intensive industries in Germany from energy levies”, published in 2012.
In 2021, private households in Germany paid 6.5 cents per kilowatt-hour of electricity for the EEG surcharge. The EEG surcharge is used to promote renewable energies under the Renewable Energy Sources Act. It is part of the electricity price and represents the difference between the market price for electricity and the feed-in tariff for renewable energy sources.
Composition of the electricity price
In 2019, residential customers in Germany paid an average of 31.94 cents per kilowatt-hour of electricity under the basic supply tariff. The electricity price in Germany is composed of various components. The EEG surcharge, network charges, and the "procurement and distribution" factor make up the largest share of the total price.
Industrial electricity prices
Electricity prices for industry in Germany have tended to rise since the turn of the 20th century. However, if prices are considered without taking the levied electricity tax into account, a price decrease can be observed in Germany. As with private households, the electricity price for industry is mainly composed of network charges, procurement and distribution costs, and the EEG surcharge. In a European comparison, Malta, Ireland, and Cyprus have the highest industrial electricity prices.
Review: How is the renewable energy market developing in South Korea?
When the nuclear disaster occurred in Fukushima, Japan, on March 11, 2011, there was great horror in South Korea, 1000 km away. And the violent earthquake on November 15, 2017, triggered by geothermal drilling in the southeast of the country, where four nuclear reactors are located just a few kilometers from the epicenter, still has an impact today.
“In South Korea, nuclear power has been supported by the government for over 40 years, primarily because we lack natural resources.” With this statement, Daum Jang of Greenpeace aptly describes South Korea’s dilemma. He further mentions in an interview that he is annoyed by how industry-friendly newspapers use Germany’s energy transition as a negative example, emphasizing the costs of German climate policy but not its benefits. Now, since Fukushima, the situation has changed, and President Moon Jae-in has reaffirmed his plans for a nuclear phase-out. He faces a powerful lobby, however, but public sentiment in South Korea leaves him with no other choice.
More about it here:
What measures can make the energy transition a success?
The Austrian Ministry for Climate Action (BMK) plans to simplify subsidies for rooftop photovoltaic systems with the upcoming Renewable Energy Expansion Act (EAG). Climate Action Minister Leonore Gewessler presented details of the planned measures on Thursday, September 10th: Starting in 2021, the new Renewable Energy Expansion Act (EAG) will make subsidies for photovoltaics (PV) significantly more efficient. The focus will be on additional approaches, greater transparency, and a clearer and more accessible subsidy system.
Photovoltaic systems should primarily be installed on buildings or structures (e.g., parking lots, noise barriers, industrial facilities). The major advantage lies in the existing infrastructure, such as grid connections. However, many roof surfaces are not yet suitable for PV. Therefore, a corresponding support program is planned to improve the mobilization of rooftop systems. In addition, a funding program for innovative systems (roof-integrated systems, building-integrated systems, etc.) will be available starting next year.
More about it here:
How can artificial intelligence be useful in the field of renewable energies?
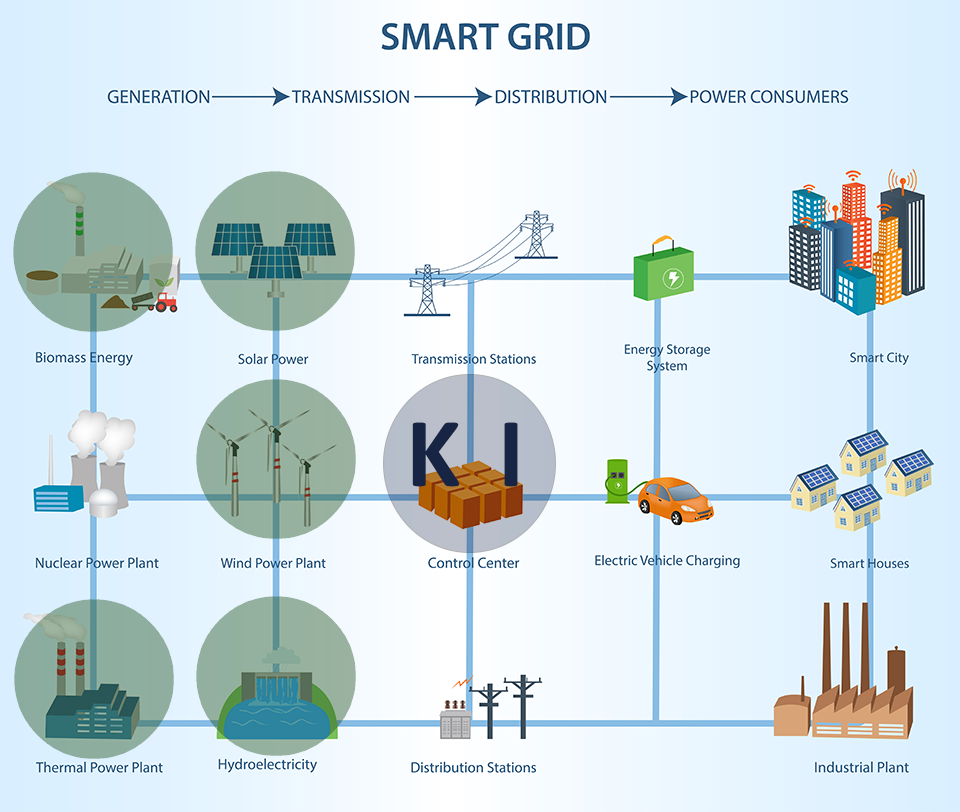
While centralized power generation has dominated electricity grids to date, the trend is shifting towards decentralized generation facilities. This is particularly true for renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic systems, solar thermal power plants, wind turbines, and biogas plants. This leads to a significantly more complex structure, primarily in the areas of load control, voltage regulation in the distribution network, and maintaining grid stability. Smaller, decentralized generation facilities, unlike medium to large power plants, also feed directly into lower voltage levels such as the low-voltage or medium-voltage networks.
An intelligent power grid integrates all actors into an overall system through the interaction of generation, storage, network management and consumption. Power plants (including storage) are already controlled in such a way that the same amount of electrical energy is always produced as is consumed. Intelligent power grids include consumers as well as decentralized small energy suppliers and storage devices in this control, so that, on the one hand, consumption is balanced in time and space (smart power/intelligent power consumption) and, on the other hand, non-disposable generation systems (e.g. wind energy and PV Systems) and consumers (e.g. lighting) can be better integrated.
With the increasing share of renewable energies, it is becoming more important to align fluctuations in energy production with fluctuations in energy consumption. Besides the possibility of storing electrical energy using energy storage systems or pumped-storage power plants, demand-driven electricity generation (e.g., through hydroelectric power plants or bioenergy), and the expansion of electricity grids for rapid distribution over large areas, there is also the option of adjusting electricity consumption to the electricity supply.
More about it here:
Is photovoltaics a billion-dollar business?
The share of photovoltaics in electricity generation from renewable energy sources is steadily increasing. A key reason for this is the comparatively low investment costs for the design and implementation of new systems. This often makes it possible to install the modules on existing roofs or buildings, thereby minimizing the land area required by the systems.
The booming solar energy market benefits not only energy producers and the environment, but also hardware manufacturers. There are now over half a dozen companies worldwide that generate revenues exceeding one billion US dollars each from solar technology. Leading the pack is the Chinese corporation Jinko Solar, which recorded revenues of 4.3 billion USD in 2019.
German companies are also playing in the game of major suppliers. For example, SMA Solar Technology AG from Niestetal in northern Hesse broke the one billion dollar revenue mark for the first time last year, thus establishing itself among the world's leading producers.
More about it here:
- Warehouses, production halls and industrial halls with their own power source from a photovoltaic roof system - Image: NavinTar|Shutterstock.com
- Industrial plant with its own power source from an outdoor photovoltaic system - Image: Peteri|Shutterstock.com
- Plan solar systems with photovoltaic solutions for freight forwarding and contract logistics
- B2B solar systems and photovoltaic solutions & advice
- Plan photovoltaics for warehouses, commercial halls and industrial halls
- Industrial plant: Plan a photovoltaic open-air system or open-space system
- Plan solar systems with photovoltaic solutions for freight forwarding and contract logistics
- B2B solar systems and photovoltaic solutions & advice
Photovoltaic system solutions: Xpert.Solar for planning and consulting in the area of solar carports, solar systems on roofs and photovoltaic systems in general for Düren, Ratingen, Lünen and Marl
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus