China's response to 100% US tariffs: The trade conflict between the US and China reaches a new, explosive level
Language selection 📢
Published on: October 12, 2025 / Updated on: October 12, 2025 – Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

China's response to 100% US tariffs: The trade conflict between the US and China reaches a new, explosive level – Image: Xpert.Digital
Nothing works without them: How China controls the global economy with rare earths
Is the collapse of global supply chains now imminent? 100% tariffs on Chinese goods in the US
The US is toughening its tone by threatening drastic 100 percent tariffs on Chinese imports, but Beijing isn't intimidated. China's response is as strategic as it is effective: targeted control over the export of rare earths. These obscure raw materials are the secret heart of our modern world—essential for smartphones, electric cars, wind turbines, and sophisticated weapons systems.
But the dispute is far more than just an economic war. It is a bitter struggle for technological supremacy, national security, and control over the global supply chains of the future. While the US seeks to protect its industry with tariffs and export bans on semiconductors, China is using its quasi-monopoly on rare earths as a powerful lever. This article sheds light on the background to the escalation, explains why rare earths are China's most powerful asset, and analyzes the far-reaching consequences for the global economy, industry, and ultimately for consumers in Europe.
Suitable for:
- Escalation in the US-China trade conflict: 100 percent tariffs, export controls on software, and the shaky Trump-Xi meeting in South Korea
The tariff dispute between China and the USA: Questions and answers from a neutral person
In the ongoing trade conflict between China and the United States, the dynamics have intensified again. The US is threatening new, comprehensive tariffs on Chinese goods, while Beijing is responding with countermeasures and export restrictions on rare earths. This Q&A text lets a neutral person pose the key questions to illuminate the background, the measures, the economic and political impacts, and the technical details of the dispute, providing a comprehensive overview for the reader.
What is the current reason for the new escalation in the trade dispute between China and the USA?
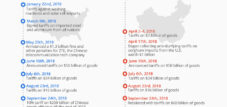
The current trigger is a new tariff threat from the US government. President Donald Trump announced that he would impose additional tariffs of 100 percent on imports from China starting November 1. This affects a wide range of Chinese goods and is part of a longer series of trade measures that have been in place between the two countries for several years. The Chinese government responded promptly with an official statement accusing the US side of double standards and nationalistic economic protectionism.
How does China justify its criticism of the US measures?
China accuses the US of generalizing the principle of national security and using it as a pretext to tighten export controls. The Chinese Ministry of Commerce criticizes the United States for applying discriminatory measures against Chinese companies and products. According to Beijing, Washington is unilaterally extending its right to control international trade, particularly in the semiconductor and computer chip sectors. This is leading to disruption of global supply chains and undermining the results of previous trade talks.
What are China's main accusations against the US in the current trade conflict?
China sees itself as disadvantaged by the US measures and calls on the US government to abandon its "wrong approach." The accusation of double standards refers in particular to the fact that, on the one hand, the US promotes free trade, while, on the other, it seals off large sectors of the economy with tariffs and export controls in the name of national security. Beijing urges the US to respect the results of past trade talks and resolve bilateral issues through dialogue. Otherwise, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce has threatened decisive countermeasures to protect its own legitimate rights and interests.
What concrete countermeasures does Beijing plan to take in response to the US tariffs?
In direct response to the new US tariffs, the Chinese government plans to expand its export controls on rare earths, which are considered strategic raw materials for industry and especially the military. This affects not only the mining, but also the processing and export of these minerals. Beijing emphasizes that this is not a blanket export ban; applications for civilian purposes will continue to be approved. The measure is primarily intended to further develop the domestic export control system and secure international competitive advantages.
What are rare earths – and why do they play such a central role in the conflict?
Rare earths are a group of 17 chemical elements essential for the production of a wide variety of modern technology products. The best known examples are neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium, yttrium, and others. Their unique magnetic, electronic, and optical properties make them key components in the manufacture of electric motors, turbines, semiconductors, and various high-tech and defense products.
Although the term "rare" is misleading, these elements are not necessarily rare, but often only occur in low concentrations in the Earth's crust. Their extraction is technically challenging, as they are often bound in complex mineral mixtures. The separation of the elements and subsequent processing are environmentally and technologically intensive. Over the past decades, China has built a specialized industry that is a world leader in mining and processing.
Suitable for:
- Rare earths: China's raw material dominance-with recycling, research and new mines out of raw material dependency?
What is the economic and geopolitical significance of rare earths?
Economically, rare earths are a crucial factor for many industrial and future technologies. Their uses range from mobile phones and wind turbines to OLED displays, electric vehicles, and precision weapons. Due to their key role, control over their mining and processing is considered a strategic resource.
Geopolitically, China's dominant market position gives it strong leverage to exert pressure on other countries—especially the US and the EU—in trade negotiations. More than 60 percent of global production and well over 80 percent of processing take place in China. Other countries that mine rare earths often bring them to China for processing, as the country possesses unique know-how and numerous patents, which make it significantly more difficult for competitors to establish their own industries.
How does China's dominant position in rare earths affect the global supply chain?
China's central role in extraction and processing means that a significant portion of the world's permissible raw materials and intermediate products find their way to China. A global network has been established in which Chinese companies and authorities virtually monopolize key processing and final manufacturing. Because China holds many technical patents on extraction and processing, other nations are often forced to transport their raw materials to China for final processing. This gives Beijing extraordinary leverage over the supply of strategic raw materials in trade conflicts, such as the current tariff dispute with the United States.
Why are US measures against Chinese technology products particularly sensitive for Beijing?
China sees US export controls and tariffs on semiconductors, computer chips, and other high-tech components as motivated not only by economic but also by security interests. The US often justifies its measures with the protection of national security, for example, in the control of technologies that can be used for military purposes. For China, interfering in advanced industrial sectors and restricting Chinese companies constitutes interference in economic development and global competition.
Beijing emphasizes that such measures disrupt global supply chains and impair international trade. At the same time, China seeks to secure its own technological development by expanding its innovation capacity and increasing patenting. The US, in turn, fears that its dependence on Chinese rare earths and technological components could jeopardize its own security and competitiveness.
What role do patents play in the processing of rare earths?
In recent decades, China has successfully filed numerous patents relating to the technological development and efficient processing of rare earths. This intellectual property poses a significant hurdle for other countries, as they are denied access to certain processes and technologies or are only granted in return for high licensing fees.
These patents protect Chinese innovations and give the domestic industry a significant advantage. Countries like the United States or members of the European Union that are striving to build their own processing capacities encounter not only technical difficulties but also legal restrictions. The consequence: raw materials are exported to China, processed there, and then sold to the global market as refined products.
Are there international efforts to reduce dependence on China for rare earths?
Several countries have begun to strategically protect themselves in the event of a trade escalation. The US, Japan, and the EU, in particular, are investing in developing their own extraction and processing capacities, developing new deposits, and promoting recycling methods. They are also working on international cooperation to reduce technological dependence.
So far, success has been limited, as China has a technological and economic advantage in many processing fields. The development of alternative processes and the exploration of new deposits require significant investment and a development phase lasting several years. The market structure will therefore remain Chinese-dominated in the medium term, continuing to give China a privileged position in trade conflicts.
Our global industry and economic expertise in business development, sales and marketing

Our global industry and business expertise in business development, sales and marketing - Image: Xpert.Digital
Industry focus: B2B, digitalization (from AI to XR), mechanical engineering, logistics, renewable energies and industry
More about it here:
A topic hub with insights and expertise:
- Knowledge platform on the global and regional economy, innovation and industry-specific trends
- Collection of analyses, impulses and background information from our focus areas
- A place for expertise and information on current developments in business and technology
- Topic hub for companies that want to learn about markets, digitalization and industry innovations
Rare earths as a geopolitical weapon: China's leverage in high-tech markets
How have trade talks between China and the US developed in the past?
Trade talks between the two countries have been characterized by varying degrees of success since the current trade conflict began in 2018. Phases of détente, such as the so-called "Phase 1 Deal," alternated with new sanctions and tariff packages. The negotiating partners repeatedly managed to make some progress, for example, by clarifying issues regarding agriculture or market liberalization. Nevertheless, key points of contention, such as access to high-tech markets or the control of key technologies, remained unresolved.
The new round of tariff negotiations and the renewed expansion of export controls have made it clear that both sides are currently neither willing to compromise nor interested in a quick solution. The tone has become harsher; China and the US are emphasizing in their official communications that they do not want a trade war—but are also not afraid of one.
Suitable for:
What impact would additional tariffs of 100 percent on imports from China have on the United States?
The introduction of additional tariffs would drastically increase the prices of Chinese goods in the US. This would affect consumer goods, electronics, machinery, and numerous intermediate products that are further processed in US industries. For end consumers, this could mean an immediate price increase for everyday products, from smartphones to household appliances.
US industry faces a risk of a deterioration in competitiveness, as intermediate products are often unavailable and cannot be obtained from other sources at short notice. Companies would have to bear higher costs or relocate production abroad. Jobs could also be affected if companies close or relocate parts of their production operations.
What economic and political motives lie behind the US course?
The US is pursuing several goals with these tariff measures. On the one hand, it is intended to protect its own industry from unfair, subsidized competition; on the other, it is intended to prevent US technology companies from becoming dependent on Chinese suppliers and service providers. At the same time, the measures are often justified on grounds of national security, particularly in the area of military-relevant technologies.
Politically, populist motives play a role. Trade conflicts can be used in domestic political discourse to strengthen one's own position and as leverage in international competition. Especially in the run-up to elections, protective measures against China are often cited as evidence of decisive action.
How does China justify its countermeasures and controls?
China justifies the expansion of export controls with the goal of improving its own export control system and further developing it in accordance with the law. The government points to the importance of rare earths for military goods and recurring conflict situations around the world. Applications for peaceful, civilian use will continue to be approved, and a general export ban is not planned. Beijing opposes a trade war but simultaneously emphasizes that it is not afraid of escalation and will resolutely defend its own interests.
The accusation of double standards against the United States plays a central role in the argument. They see themselves as victims of unilateral, discriminatory protective measures and call for respect for free trade and the resolution of disputes through dialogue.
What role does the aspect of national security play in the trade conflict?
National security interests have become the dominant argument in transatlantic and transpacific trade in recent years. The US justifies many measures as protection against technology misuse by foreign powers. China, on the other hand, sees the expansion of export controls as a self-protection measure, especially in light of military developments and geopolitical uncertainties.
Both states use the argument of national security to defend their protective measures against foreign criticism and to declare them legally legitimate. This leads to a further sharpening of the political and economic dividing lines and complicates the resolution of the trade conflict based on a purely economic model.
What role does US jurisdiction play in international technology products?
The United States is increasingly applying the principle of extraterritorial jurisdiction, particularly for products containing sensitive technologies or components. This means that not only products manufactured in the United States, but also international goods containing US technology may be subject to American export control laws.
This often affects semiconductors and computer chips; companies in Europe, Asia, and elsewhere may be required to comply with American regulations and obtain approvals from US authorities. This practice creates additional uncertainty and complications in global trade, as companies must adapt to different legal systems and conduct complex compliance checks.
How are global companies reacting to increasing uncertainty?
Many internationally operating companies have begun to rethink and diversify their supply chains and production processes. The "China Plus One" strategy, for example, envisions establishing production sites near China in order to be able to react flexibly to trade conflicts. Others are investing in developing their own technologies and patents to avoid legal risks.
At the same time, interest in new recycling methods and the development of alternative materials, especially for rare earths and high-tech components, is growing. Companies are setting up compliance departments, training staff on international export regulations, and seeking legal advice to prepare for various scenarios.
Are there historical parallels to current export controls and customs measures?
Past trade conflicts, for example, between Japan and the United States in the 1980s, show similar patterns: tariffs, export restrictions, legal disputes, and the debate over national security. Technology was also a central point of conflict back then.
The unique nature of the current dispute lies in the global interdependence and strategic importance of rare earths. While previous trade conflicts were often limited to individual sectors, the current dispute affects broad areas of industry and technology. Global dependence on China is unprecedented and gives Beijing an additional power-political tool.
How might trade relations develop in the medium term?
The prognosis is difficult. Further escalation is likely in the short term, as both sides are acting decisively and lacking a willingness to compromise. In the medium term, alternative supply chains and new technological solutions could emerge to reduce dependencies.
In the long term, a path back to multilaterally coordinated international trade is possible if both states recognize that protectionist measures endanger global prosperity and innovation in the long term. This would require intensive negotiations, mutual concessions, and a return to constructive dialogue.
What impact does the conflict have on German and European industry?
German and European industry also faces major challenges. Many high-tech products and industrial goods require rare earths and other raw materials, which predominantly come from China. Uncertainty about customs measures and export controls complicates planning and increases costs. Companies are developing contingency strategies, seeking alternative sources, and investing in research and development.
At the same time, opportunities for innovation and cooperation in the field of raw material extraction and recycling arise. The EU is working on funding programs to expand technological sovereignty and reduce the gap in patents and processing technologies.
Suitable for:
- A high song in Germany and the EU - why they need themselves to be able to survive against the USA and China
What are the global impacts of the trade dispute on developing countries?
For many developing countries, the current situation presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Countries with their own rare earth deposits could benefit from the increased demand. However, there is a risk that they will become dependent on price fluctuations and political pressure from major economic powers.
The global interconnectedness of supply chains also means that shortages of rare earths could impact the industrial sectors of numerous emerging economies. Many of these countries are not yet sufficiently capable of independently driving technological innovations in the raw materials sector. International development policy and technological cooperation could help reduce dependence on China and the US and open up new prospects.
How can the current tariff dispute between China and the USA be classified?
The current tariff dispute between China and the United States represents a complex mix of economic, political, and technological interests. At its core are key strategic resources such as rare earths and future-oriented industrial goods such as semiconductors and computer chips.
Both sides are using the dispute to assert their own interests and secure their technology sectors. China benefits from its dominant market position in rare earths and patented processes, while the US is attempting to protect its own industry and exert geopolitical influence through tariffs and export controls.
The dispute poses considerable uncertainty for the global economy and international relations, potentially leading to price fluctuations, supply bottlenecks, and innovations in response to trade-related restrictions. There is currently no end in sight to the conflict – developments in the coming months and years will show whether constructive negotiations and technological diversification can lead to a long-term easing of tensions.
Your global marketing and business development partner
☑️ Our business language is English or German
☑️ NEW: Correspondence in your national language!
I would be happy to serve you and my team as a personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) . My email address is: wolfenstein ∂ xpert.digital
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development / Marketing / PR / Trade Fairs
B2B support and SaaS for SEO and GEO (AI search) combined: The all-in-one solution for B2B companies

B2B support and SaaS for SEO and GEO (AI search) combined: The all-in-one solution for B2B companies - Image: Xpert.Digital
AI search changes everything: How this SaaS solution is revolutionizing your B2B rankings forever.
The digital landscape for B2B companies is undergoing rapid change. Driven by artificial intelligence, the rules of online visibility are being rewritten. It has always been a challenge for companies to not only be visible in the digital masses, but also to be relevant to the right decision-makers. Traditional SEO strategies and local presence management (geomarketing) are complex, time-consuming, and often a battle against constantly changing algorithms and intense competition.
But what if there were a solution that not only simplifies this process, but makes it smarter, more predictive, and far more effective? This is where the combination of specialized B2B support with a powerful SaaS (Software as a Service) platform, specifically designed for the needs of SEO and GEO in the age of AI search, comes into play.
This new generation of tools no longer relies solely on manual keyword analysis and backlink strategies. Instead, it leverages artificial intelligence to more precisely understand search intent, automatically optimize local ranking factors, and conduct real-time competitive analysis. The result is a proactive, data-driven strategy that gives B2B companies a decisive advantage: They are not only found, but perceived as the authoritative authority in their niche and location.
Here's the symbiosis of B2B support and AI-powered SaaS technology that is transforming SEO and GEO marketing and how your company can benefit from it to grow sustainably in the digital space.
More about it here: