Artificial intelligence as a growth engine: How enterprise AI platforms are redefining the American economy
Language selection 📢
Published on: December 12, 2025 / Updated on: December 12, 2025 – Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Artificial intelligence as a growth engine: How enterprise AI platforms are redefining the American economy – Image: Xpert.Digital
A $109 billion lead: How the US is outperforming China in the global AI race
Forget ChatGPT or Gemini: The new “Blueprint approach” automates companies in days instead of months.
The American economy is facing its biggest transformation since electrification: As billions are flowing, the decision is now being made as to who will make the leap from hype to real value creation.
The United States emphatically cemented its position as the undisputed superpower of artificial intelligence in 2024. With private investments exceeding $109 billion and an innovation rate that far surpasses even China, the stage seems set for an AI-dominated future. However, the glittering tech facades of Silicon Valley sometimes mask the harsh reality in the wider corporate landscape. While giants like Microsoft and Alphabet are upgrading their infrastructures with hundreds of billions of dollars, "Main Street"—the industrial backbone of America—is grappling with a dangerous implementation gap.
The figures are both alarming and promising: While almost 90 percent of large companies already use AI, a staggering 95 percent of all generative AI pilot projects fail due to the complex integration into existing systems. It is precisely within this tension between technological feasibility and operational hurdles that a new class of enterprise solutions is currently emerging. Platforms based on the so-called "blueprint approach" promise to reduce development time, which can last for months, to just a few days and to break through the barriers of legacy IT.
This article delves into how the US economy is reinventing itself through autonomous agents, edge computing, and radical process automation. We analyze why companies with successful AI strategies significantly outperform the S&P 500, what cultural resistance needs to be overcome, and why the Fourth Industrial Revolution will redefine not only technology but also the labor market and America's global competitiveness for decades to come.
When Silicon Valley meets Main Street: The revolution doesn't wait for the hesitant.
The American economy is at a technological turning point, redefining competitiveness and economic viability. While major tech companies in Silicon Valley are already investing billions in artificial intelligence, the wider American business community is still struggling with the practical implementation of this technology. With $109.1 billion in private AI investments in 2024 alone, the United States is leading the global AI revolution, exceeding China's investments twelvefold. However, an implementation gap exists between technological leadership and operational reality, a gap that only a few companies have successfully closed.
In this tension between innovation and implementation, platforms like Unframeare emerging, promising to realize complex enterprise AI projects within days instead of months. The so-called blueprint approach transforms traditional development cycles and makes AI-powered automation accessible, something that previously required months of implementation. While American companies are still grappling with the integration of isolated AI solutions, pioneers like Fortune 500 corporations are already demonstrating how comprehensive automation solutions can have an operational impact in a very short time.
The figures speak for themselves: 87 percent of large companies with more than 10,000 employees have already implemented AI, representing a 23 percent increase since 2023. However, current studies also reveal the downside: 95 percent of generative AI pilot projects in companies fail, primarily due to integration problems, a lack of expertise, and inadequate strategy. This discrepancy between adoption and successful implementation highlights the central challenge of modern enterprise automation.
The American AI landscape in a global context
The United States has established itself as the undisputed superpower in artificial intelligence. With cumulative private investments exceeding $470 billion between 2013 and 2024, the US surpasses the investments of all EU countries combined by a factor of nine. This dominance manifests itself not only in capital but also in the speed of technological development and the willingness to disrupt established business models.
The American AI market differs fundamentally from other economic regions due to its risk appetite and the close integration of venture capital, university research, and industrial application. The four largest tech companies alone—Amazon, Alphabet, Microsoft, and Meta—plan to invest $364 billion in AI infrastructure in 2025, a dramatic increase from $325 billion the previous year. These investments generate far-reaching multiplier effects: Every dollar directly invested generates an additional $2.53 in economic activity and supports a total of 2.7 million jobs across the American economy.
The impact on gross domestic product is already measurable. AI-related investments contributed 1.1 percentage points to GDP growth in the first half of 2025, surpassing consumer spending as a growth driver for the first time. Technically speaking, investments in information processing equipment and software accounted for only four percent of US GDP, yet they were responsible for 92 percent of the growth during this period. This concentration of growth on AI-related investments is unprecedented and underscores the transformative power of this technology.
The industry distribution of AI adoption reveals interesting patterns. While 30 percent of companies in the information sector are using AI, followed by professional services at 23 percent and financial services at 17 percent, traditional sectors such as hospitality and construction lag significantly behind at only three percent each. In the manufacturing sector, approximately 29 percent of American manufacturers will adopt AI or machine learning for smart manufacturing by 2025, with 87 percent stating that a regulatory understanding of AI technologies is important for industrial development.
The historical dimension of the fourth industrial revolution
The history of industrial transformation in the United States is characterized by waves of innovation, each resulting in fundamental changes to the production landscape. From mechanization through the steam engine, through electrification and assembly line production, to computerization, every industrial revolution has reshaped the American economy. However, the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by artificial intelligence and cyber-physical systems, is unfolding at an unprecedented pace.
ChatGPT's breakthrough in November 2022 marked a turning point. Within just five days, the platform reached one million users, triggering a wave of investment across all industries. This development highlighted for the first time the potential of generative AI for practical applications and led to a fundamental reassessment of AI technologies in industrial contexts. The cost of AI queries decreased 280-fold between November 2022 and October 2024, accelerating adoption and stimulating further technological development.
Unframe.AI emerged in 2024 in this dynamic environment, founded in Cupertino by former Noname Security founder Shay Levi. The company identified a key market gap: While AI technologies were becoming increasingly mature, companies lacked practical ways to quickly implement these technologies into their existing systems. In its first year of operation, Unframe generated millions of US dollars in recurring revenue and began collaborating with Fortune 500 companies.
The accelerated pace of innovation is also evident in the spread of AI in the American business landscape. While previous industrial revolutions took decades to become widespread, AI adoption among US companies doubled in just two years, from 3.7 percent at the end of 2023 to 9.7 percent in August 2025. The adoption rate is significantly higher among Fortune 500 companies: 78 percent of these organizations were using AI in 2024, compared to 55 percent the previous year.
Technological architecture and core mechanisms
The technological foundation of modern enterprise AI platforms is based on a modular architecture that differs fundamentally from traditional software development approaches. At its core is the blueprint approach, an innovative method for transforming business requirements into functional AI solutions. This approach eliminates the traditional phases of requirements analysis, software architecture, and implementation, replacing them with an automated generation process.
Modern enterprise AI platforms have four key technical building blocks. First, they include advanced search and reasoning capabilities that transform unstructured enterprise data into searchable, structured information. This functionality allows American companies to access decades of accumulated domain knowledge that was previously hidden in emails, reports, and legacy systems.
The second component focuses on automation and AI agents. These autonomous systems execute complex workflows and make proactive decisions based on real-time data. In industrial environments, for example, these agents can optimize maintenance intervals, perform quality control checks, or make supply chain decisions without requiring human intervention. The development of such autonomous agents is a key focus in 2025, with 64 percent of companies expecting fully autonomous business processes by 2027.
The abstraction and data processing component forms the third technical building block. Platforms transform unstructured content such as sensor data, machine logs, or production documentation into usable structured formats. This capability is particularly relevant for American industrial companies, which often have heterogeneous IT landscapes with various data formats and legacy systems. A study shows that 83 percent of US executives believe that a stronger data infrastructure would accelerate AI adoption in their organizations.
The fourth component comprises modernization functions that transform legacy systems into AI-native software. This functionality addresses one of the biggest challenges facing American companies: integrating modern AI technologies into existing production environments without requiring disruptive system changes. In fact, 80 percent of American companies identified integration with legacy systems as one of their biggest AI implementation hurdles.
Edge computing is playing an increasingly central role in enterprise AI architecture. Industrial applications often require real-time processing with sub-millisecond latency. More than 14 million industrial sites are being transformed, or are on the verge of transformation, by the emergence of AI-dependent applications. Edge computing brings data processing closer to sensors and production equipment, enabling critical decisions to be made without delays caused by network transmissions. For example, Tesla is rolling out private 5G at scale in its Gigafactories, while Airbus has announced plans to replace Wi-Fi with private 5G in all its factories within the next five years.
Security architecture is increasingly following a zero-trust principle. Customer data should never leave the secure corporate environment, as platforms can be deployed both in private clouds and on-premises. This architectural decision is particularly relevant for American companies, which are subject to strict data protection regulations and must protect sensitive production data. The threat from AI-powered cyberattacks is increasing dramatically: 90 percent of companies currently lack the necessary maturity to effectively combat today's advanced, AI-driven threats.
Practical application and operational transformation
The practical application of enterprise AI technology in the American business landscape is already showing measurable results. Companies that invest heavily in AI, with $10 million or more across all business units, are significantly more likely (71 percent) to report substantial AI-related productivity gains in the past year than companies with smaller investments (under $10 million), of which only 52 percent report such gains.
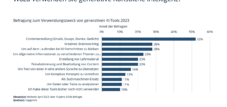
IT operations have established themselves as the dominant application area. A comprehensive survey of 235 decision-makers in large companies identified IT operations as the most impactful AI application, cited by 50 percent of respondents. Enterprise AI platforms automate complex IT service management workflows that previously required manual processing. Emails are automatically converted into tickets, service level agreements are assigned and routed to the appropriate teams, while executives receive real-time insights into the processing status.
Process automation leads the way in concrete use cases with a 76 percent adoption rate, followed by customer service chatbots at 71 percent and data analytics at 68 percent. The impact is significant: Process automation reduces processing times by 43 percent, while customer service chatbots shorten response times by 67 percent. Predictive maintenance, with a 52 percent adoption rate, reduces downtime by 29 percent.
A concrete example illustrates the transformation of quotation processes. A global technology distributor fully automated its sales quotation process with AI, reducing processing time from 24 hours to just a few seconds. This increase in efficiency allows the company to handle significantly more customer inquiries and react more quickly to market changes.
Quality assurance benefits significantly from AI-supported image processing systems. Modern production lines operate at speeds that overwhelm human quality control. AI systems continuously analyze camera images and identify microscopic defects or deviations in real time. This technology enables American manufacturers to raise their quality standards while simultaneously reducing scrap and rework.
Predictive maintenance represents another key area of successful AI implementation. The National Science Foundation supported the development of MaVila, an AI model specifically designed for manufacturing that learns directly from visual and speech-based data in factory environments. The tool can see and communicate by analyzing images of parts, describing defects in simple language, suggesting solutions, and even communicating with machines to make automatic adjustments. This technology could be particularly accessible to small and medium-sized businesses that cannot afford expensive AI tools or the expertise required to operate them.
The speed of implementation fundamentally distinguishes modern enterprise AI platforms from traditional IT projects. While classic AI implementations take months or years, blueprint-based solutions can be deployed productively in just a few days. This time saving results from an approach that eliminates or drastically shortens the lengthy phases of requirements analysis, system design, and programming.
🤖🚀 Managed AI Platform: Faster, safer & smarter to AI solutions with UNFRAME.AI
Here you will learn how your company can implement customized AI solutions quickly, securely, and without high entry barriers.
A Managed AI Platform is your all-round, worry-free package for artificial intelligence. Instead of dealing with complex technology, expensive infrastructure, and lengthy development processes, you receive a turnkey solution tailored to your needs from a specialized partner – often within a few days.
The key benefits at a glance:
⚡ Fast implementation: From idea to operational application in days, not months. We deliver practical solutions that create immediate value.
🔒 Maximum data security: Your sensitive data remains with you. We guarantee secure and compliant processing without sharing data with third parties.
💸 No financial risk: You only pay for results. High upfront investments in hardware, software, or personnel are completely eliminated.
🎯 Focus on your core business: Concentrate on what you do best. We handle the entire technical implementation, operation, and maintenance of your AI solution.
📈 Future-proof & Scalable: Your AI grows with you. We ensure ongoing optimization and scalability, and flexibly adapt the models to new requirements.
More about it here:
America's AI race: Why speed, governance, and culture now determine the lead
The economic dimension of AI transformation
The economic impact of AI adoption in the United States is already clearly measurable and promises fundamental changes in the long term. Companies using productivity AI outperformed the S&P 500 by 29 percent year-over-year from July 2024 to July 2025, with share price growth of 17.2 percent compared to 13.3 percent for the overall index. Even more impressive are the revenue gains: These companies reported an average year-over-year revenue increase of 13.1 percent in their 10-Q filings, compared to the index-weighted average of the S&P 500 of just 5.1 percent.
The productivity gains from AI are already visible in aggregated economic data. Estimates from Anthropic show that current AI systems could increase annual labor productivity in the US by 1.8 percent over the next ten years, nearly doubling the current long-term growth rate. The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis reports that the share of work hours using generative AI increased from 4.1 percent in November 2024 to 5.7 percent in 2025, suggesting a productivity increase of up to 1.3 percent since the introduction of ChatGPT.
Long-term projections from the Wharton School estimate that AI will boost productivity and GDP by 1.5 percent by 2035, by almost 3 percent by 2055, and by 3.7 percent by 2075. These estimates are based on the assumption that about 15 percent of current GDP will be impacted by AI over time, with this share growing over the next two decades as more exposed sectors grow faster than the rest of the economy.
Investments in AI infrastructure have far-reaching multiplier effects. The $364 billion in investments by large tech companies in 2025 are expected to support $923 billion in total economic output, create 2.7 million jobs, generate $297 billion in labor income, contribute $469 billion to GDP, and generate $105 billion in tax revenue.
AI offers unique opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Ninety-eight percent of American small businesses use AI-powered tools, with 91 percent convinced these tools will help their businesses grow. The use of generative AI tools, such as chatbots and image generation, nearly doubled among small businesses, rising from 23 percent in 2023 to 40 percent in 2024. Most notably, small businesses that fully embrace technology not only outperform their competitors but also demonstrate greater optimism about the future. Four out of five small businesses report that using technology has helped them avoid raising prices for consumers, despite ongoing inflation.
Challenges and implementation barriers
Despite its promising potential, American companies face significant challenges in implementing AI. Cultural resilience is one of the most underestimated barriers. Large organizations have often developed cultures that reward stability, predictability, and established ways of working. AI inherently introduces uncertainty and change.
Employees who have built their careers on specific expertise may feel threatened by AI systems that can perform some of their tasks more efficiently. Middle managers may worry that AI will make their roles obsolete. Executives are concerned about the risks of making decisions based on algorithms they don't fully understand. This resistance manifests itself in subtle but powerful ways: employees may formally comply with AI implementation directives but find ways to circumvent the new systems. Managers may support AI in principle but create bureaucratic hurdles that slow implementation.
Technological integration complexity presents another massive hurdle. Large organizations typically have hundreds or thousands of different software applications, each with its own APIs, data formats, and integration requirements. Adding AI capabilities to this environment requires careful planning to ensure that AI systems can access the necessary data while maintaining the security and performance requirements of the entire technology ecosystem.
Data availability and quality are particularly problematic. Two-thirds of executives acknowledge that inadequate infrastructure is an obstacle to AI implementation in their companies. AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on, and many companies struggle with fragmented, inconsistent, or low-quality datasets.
The skills shortage is further exacerbating the situation. The AI talent market is highly competitive, and large organizations often struggle to compete with tech companies and startups for the best AI professionals. According to a survey by SnapLogic, 93 percent of US and UK organizations report that AI is a business priority, yet more than half acknowledge that they lack the right mix of skilled AI talent to implement their strategies. Only one in ten employees reports having everyday AI skills.
Compliance and regulatory requirements add further complexity. The US pursues a multi-layered regulatory approach to AI, combining federal executive orders, agency guidance, and various state laws, creating a complex compliance landscape for companies. State legislation such as the Colorado AI Act and the California AI Transparency Act lead the regulatory efforts by focusing on high-risk AI systems, transparency, and consumer protection.
The Colorado AI Act requires developers and operators of AI systems that make consequential decisions in areas such as employment, education, financial services, healthcare, housing, insurance, and legal services to conduct comprehensive impact assessments 90 days prior to deployment. These requirements create significant administrative burdens and necessitate specialized legal and technical expertise.
Shadow AI poses a particularly insidious risk. Business units frequently deploy unauthorized AI tools and applications without the security team's knowledge, creating massive visibility gaps. The financial impact of this governance gap is substantial: According to IBM's 2025 report, data breaches involving shadow AI cost organizations an average of $670,000 more than breaches without unauthorized AI. The root cause is governance failure: A staggering 97 percent of all AI-related security incidents occurred in systems lacking adequate access controls, governance policies, and security oversight.
The changing world of work
The impact of AI on the American labor market is complex and multifaceted. On the one hand, studies show that AI increases productivity and, in most cases, helps to close skills gaps in the workforce. On the other hand, American manufacturers face a massive labor shortage: almost two million jobs, half of all newly created positions, could remain unfilled by the end of the decade.
Many companies have turned to artificial intelligence and automation to close this gap. Robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning have become key tools for US manufacturers to combat labor shortages. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the number of collaborative robots deployed in the US manufacturing industry has grown by 25 percent annually over the past three years.
The White House AI Action Plan emphasizes the need to empower the workforce for the AI era. The Department of Labor was urged to direct workforce development funds toward training, education programs, and other skills-based initiatives that prioritize the development of AI capabilities. By 2025, education and workforce opportunities provided by the Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation are expected to add more than 500 new researchers at all career levels to the national AI workforce across various critical basic research and enabling technology development areas.
However, reality shows that 67 percent of jobs today require AI skills, while training capacity lags far behind. Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) funding is increasingly encouraged to be used to develop AI workforce development programs. State and local governments are expected to work with industry to create industry-driven training programs and expand early exposure and pre-training programs.
It is important to emphasize that automation should augment human capabilities, not replace people. If a production environment is struggling to find skilled workers, implementing the right CNC machines to automate repetitive and labor-intensive tasks allows current employees to focus on higher-value activities such as design refinement, process optimization, and strategic decision-making.
Future trends and technological convergence
The development of AI-powered enterprise automation is facing fundamental transformations that go beyond isolated improvements and will reshape entire industries. Edge computing will become the dominant architecture for industrial AI applications. While current solutions still rely heavily on cloud computing, data processing is increasingly shifting directly to production facilities.
The convergence of digital twins and AI will revolutionize industrial simulations. The American digital twin market is projected to grow from $3.90 billion in 2025 to $29.79 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 33.7 percent. Nearly one-third of organizations are investing over $10 million in digital twin technology, with manufacturing leading adoption. Over 40 percent of manufacturing companies are piloting digital twin technology, with full rollouts continuing.
Of the organizations that have used digital twin technology, 65 percent report reduced downtime and operating costs. More than half report improved predictive maintenance, while 40 percent have achieved better collaboration. This combination makes it possible to train and test AI models in secure virtual environments before deploying them in critical production systems.
Prescriptive maintenance will replace predictive maintenance and mark the next evolutionary step. While current systems forecast maintenance needs, future AI systems will generate concrete recommendations for action and implement them automatically. An intelligent production plant will not only warn that a warehouse might fail in three days, but will automatically order spare parts, schedule maintenance technicians, and adjust production plans accordingly.
Explainable AI is becoming a regulatory necessity, particularly in the US with increasing compliance requirements. The black-box nature of current AI systems is unsustainable in the long run, as businesses and regulators will demand transparent decision-making processes. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework remains a highly influential, voluntary framework and is widely regarded as best practice, making it a cornerstone of any effective AI governance program.
The integration of quantum computing will find its first practical applications in enterprise automation starting in 2028. This technology will enable revolutionary improvements, particularly in solving complex scheduling problems and optimizing supply chains.
Autonomous production systems are gradually becoming a reality. American automakers like Tesla are already experimenting with factories that can operate entirely without human intervention. These lights-out factories use AI for all production decisions, from material planning to quality control.
The democratization of AI development will empower American companies to create their own AI solutions. Low-code and no-code platforms will enable engineers without programming skills to build AI applications. This development will significantly accelerate the pace of innovation in American companies.
The strategic importance for the American economy
The strategic importance of AI for the United States as a business location is considerable. With 87 percent of large companies already using AI and another 78 percent of all organizations using some form of AI, America is in a favorable position. Investments of $109.1 billion in AI planned for 2024 will exceed China's investments twelvefold, underscoring its technological leadership.
At the same time, there is a risk that the slow pace of implementation will lead to competitive disadvantages. While 95 percent of manufacturers are either investing in AI or plan to invest within five years, 95 percent of generative AI pilot projects fail. This implementation gap could be closed by platforms like Unframe, which would enable American companies to realize their AI ambitions more quickly.
The economic implications extend beyond individual companies. The projected productivity increases of 1.8 percent annually over the next ten years could nearly double the current long-term growth rate. This could be crucial in compensating for the challenges of demographic change and the shortage of skilled workers.
The Trump administration's America's AI Action Plan emphasizes improving America's global dominance in AI by reducing regulatory barriers to foster innovation. In December 2025, President Trump issued an executive order to ensure a national policy framework for artificial intelligence, aiming to prevent government regulations that would create a patchwork of 50 different regulatory regimes, making compliance more challenging.
Differentiated assessment
Analyzing the enterprise AI landscape in the United States reveals a complex picture of technological disruption, presenting both extraordinary opportunities and significant risks. The fundamental innovation of the blueprint approach and similar platforms lies not in the underlying AI technology, but in the radical acceleration of implementation cycles, compressing traditional IT project durations from months to days.
The technological strengths of modern enterprise AI platforms are undeniable: their modular architecture, universal integration capabilities, and the ability to leverage existing enterprise data without complex data migration address key pain points for American companies. The productivity gains already achieved at Fortune 500 companies demonstrate their practical potential. Companies using productivity AI outperformed the S&P 500 by 29 percent and more than doubled their revenue gains.
Nevertheless, the identified risks have the potential to undermine the promised benefits. The lack of traceability in AI-driven decisions clashes with American compliance requirements and quality standards. The speed of implementation can lead to hasty decisions that carry operational risks. Cybersecurity risks increase with each additional networked AI system, with AI-related cybercrime projected to cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
The assessment yields a nuanced conclusion: Enterprise AI platforms represent a significant technological advancement with the potential to accelerate American business automation. However, the technology is not a panacea and requires careful strategic planning, appropriate risk management, and responsible implementation. American companies should view the technology as one component of their digital transformation, not as a complete solution.
Success will ultimately depend on how well American companies manage to harmonize technological opportunities with their specific requirements for quality, safety, and compliance. The United States, with its massive investments, technological expertise, and culture of innovation, has a unique opportunity to lead the global AI revolution. But this leadership position requires more than just capital investment: it demands strategic thinking, cultural transformation, investment in education and workforce development, and a balanced regulatory approach that fosters innovation while adequately addressing risks.
The coming years will be crucial. Companies that invest in AI automation today, taking both the technological possibilities and the organizational and cultural challenges seriously, are positioning themselves for the technological convergence of the future. Enterprise AI platforms like Unframecould serve as an integration base, seamlessly combining various technologies and bridging the implementation gap between ambition and reality. Ultimately, however, success will not be determined by technology alone, but by the ability of American companies to use these tools responsibly, strategically, and with a focus on long-term value rather than short-term efficiency gains.
Download Unframe ’s Enterprise AI Trends Report 2025
Click here to download:
Advice - planning - implementation
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
contact me under Wolfenstein ∂ Xpert.digital
call me under +49 89 674 804 (Munich)
Our global industry and economic expertise in business development, sales and marketing

Our global industry and business expertise in business development, sales and marketing - Image: Xpert.Digital
Industry focus: B2B, digitalization (from AI to XR), mechanical engineering, logistics, renewable energies and industry
More about it here:
A topic hub with insights and expertise:
- Knowledge platform on the global and regional economy, innovation and industry-specific trends
- Collection of analyses, impulses and background information from our focus areas
- A place for expertise and information on current developments in business and technology
- Topic hub for companies that want to learn about markets, digitalization and industry innovations