Why actually? Duty-free imports from China lead to distortions of competition and tax losses - and then there are safety and quality concerns
Language selection 📢
Published on: September 27, 2024 / Update from: September 27, 2024 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Duty-free imports from China lead to distortions of competition and tax losses - Image: Xpert.Digital
🤔📦 Distortions of competition through duty-free imports from China: Impact on the economy and consumers
📈 In recent years, the rise of duty-free imports from China has caused a stir, particularly in Europe and the US. At first glance, duty-free imports seem to be a boon for consumers as they offer a wide range of affordable products. But a closer look reveals significant disadvantages that go far beyond the supposed advantages. These imports not only lead to massive distortions of competition, but also to significant tax losses and threats to the safety and quality of the products that enter the market.
📉🏭 Distortions of competition: The domestic industry under pressure
One of the biggest challenges posed by duty-free imports from China is distortion of competition. In many countries, especially in Europe, local companies are subject to strict regulations and regulations regarding product safety, labor law and environmental standards. These requirements inevitably lead to higher production costs. In contrast, companies in China, which are often subject to less stringent regulations, can produce their products at significantly lower costs and then offer them to international markets at unbeatable prices.
It is almost impossible for many local companies to compete with the prices of Chinese products. Even established companies with high quality and strong brands are under pressure to reduce their production costs or adjust their prices in order to remain competitive. In the long term, this can lead to a downward spiral in which the quality of the products suffers and jobs in the affected regions are put at risk.
📊💰 Tax losses: A problem for the state budget
Duty-free imports from China also mean significant tax losses for the affected countries. Normally, imports would be taxed through tariffs and duties, which make an important contribution to the national budget. This income is now missing, which leads to financial bottlenecks. This forces states to develop other sources of revenue, which often leads to an increased tax burden for citizens and companies at home.
Another problem arises from the so -called “goods value limit”, in which goods can be imported duty -free up to a certain value. Especially in the case of smaller products that are offered massively by Chinese online marketplaces, these duty-free purchases quickly add up to enormous sums. This practice is used by many consumers to import products such as electronic items, clothing or household appliances at no additional costs. In the long term, however, this creates considerable loss of income for the state, which must be compensated for elsewhere.
⚠️🔍 Safety and Quality Concerns: Dangers to Consumers
In addition to the economic impact, there is another serious problem: the safety and quality of imported goods. Products imported from China are often not subject to the same strict safety and quality controls as goods manufactured within the European Union or other Western countries. This means that inferior or even dangerous products can end up on the market.
An example of this is electronic devices that do not meet safety standards and, in the worst case, can cause fires or injuries. There are also repeated reports of pollutants in toys and household items that are well above the permissible limits. This represents a significant risk for the consumer, as when purchasing these cheap products they often do not know which standards - if any - have been met.
🌍🏭 Environmental and social standards: The dark side of global trade
Another aspect that is often overlooked when it comes to duty-free imports from China are environmental and social standards. In many cases, products are manufactured under conditions that are far from international standards. Workers in China, often including children, work in factories under sometimes inhumane conditions and receive wages that are far below the subsistence level. At the same time, the production processes used in many Chinese factories place a heavy burden on the environment. Pollution of water and air as well as the immense CO2 emissions are direct consequences of mass production for export.
While the low prices of these products seem attractive to consumers, the hidden costs for the environment and social conditions in the producing countries are enormous. In an increasingly globalized world, not only the price of a product, but also its origin and the conditions under which it is produced should play a role.
💻📦 The role of online marketplaces and the difficulty of regulation
A crucial factor in the boom in duty-free imports from China is the increasing importance of online marketplaces such as Temu, Shein, Alibaba, Wish and AliExpress. These platforms allow Chinese companies to sell directly to international customers, often at prices that local retailers cannot beat. This not only leads to more intense price pressure on local companies, but also makes it more difficult for national regulators to keep track of the imported products and their quality.
Another challenge is that many of these products, particularly in the electronics or fashion sectors, are offered as so-called “white label products”. This means that the products are sold without brand names and are therefore difficult to trace. If there is a problem with the quality or safety of such a product, it is often almost impossible to hold the manufacturer responsible or make any claims.
🛠️🏛️ Possible solutions: measures and strategies
Given these challenges, the question arises as to what measures can be taken to counteract the negative effects of duty-free imports from China. One possibility would be to reintroduce or tighten customs regulations for certain product groups in order to protect local companies and create fair competition conditions. However, this could lead to countermeasures from China and put a strain on international trade.
Another approach would be to tighten controls on imported products and ensure that they meet the same standards as domestic products. This could be done through stricter import checks or by requiring online marketplaces to comply with safety and quality standards. There are already moves in the EU to increase the liability of platforms such as Amazon or eBay for the safety of the products sold, which could be a step in the right direction.
⚖️🌐 The need for a balanced trading system
At first glance, duty-free imports from China offer many advantages, especially for price-conscious consumers. But the negative impact on the domestic economy, the national budget and the safety and quality of products should not be underestimated. There is an urgent need to create a balanced trading system that promotes a level playing field while ensuring that consumers are protected from substandard or dangerous products.
An open global economy can only be successful if it is based on fair rules that both promote free trade and protect the interests of consumers, businesses and governments alike. Dealing with duty-free imports from China will be one of the central challenges of the next few years.
📣 Similar topics
- 📉 Distortions of competition through duty-free imports from China: A look at the domestic industry
- 💰 Tax losses due to duty-free imports from China: Impact on national budgets
- ⚠️ Safety and quality risks with duty-free imports from China
- 🌍 Environmental and social standards for duty-free imports from China: The hidden costs
- 💻 Online Marketplaces: The Difficulty of Regulating Duty-Free Imports from China
- 🔍 Distortions of competition in detail: How duty-free imports burden domestic companies
- 📉 State budget in crisis: tax losses due to duty-free imports
- ⚠️ Consumers at risk: safety and quality problems with products from China
- 🌍 Global Production and Local Impact: The Truth About Duty-Free Imports
- 💻 Online marketplaces and their role in duty-free imports: A challenge for regulation
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Duty-free imports #Distortion of competition #Security risks #Environmental standards #State budget
🌏📈 Interesting to know: According to the definition of the OECD Development Committee, China is still considered a developing country
🔍 Duty-free or preferential trade with China was actually an aspect of development aid in the past, but the situation has changed significantly in recent years:
🌟 China's changing status
For a long time, China was considered a developing country and in this role benefited from trade facilitation:
- According to the OECD definition, China is still classified as a developing country based on per capita income.
- However, China today has enormous political, economic and technological resources that far exceed those of a typical developing country.
🔄 Change in development cooperation
Relations with China have changed fundamentally:
- Germany stopped traditional bilateral development cooperation with China in 2010.
- effectively no longer treated as a developing country by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development ( BMZ
- Instead, China is expected to take on more international responsibilities and help solve global problems.
🚀 China's new role
China has transformed from a recipient to a donor of development aid:
- The People's Republic has now become an important lender to countries in Africa and Asia.
- China provides loans for development aid and export financing through its state banking system.
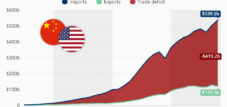
📈 Current trade relationships
Today, trade relations between China and other countries are based less on development aid and more on mutual economic interests:
- China has become the most important trading partner for several Latin American countries.
- New regional trade agreements such as RCEP in Asia promote economic integration and strengthen China's position as a regional economic center.
Although tariff-free trade from China was once an aspect of development aid, this is no longer the case due to China's economic rise and changing global role. Instead, China now faces the challenge of redefining its own role in international development cooperation and taking on more responsibility.
📦🌐 The question of duty-free limits for online shops from China
🌐🚢 The question of duty-free borders for online shops from China is a complex and current issue that has both economic and political dimensions. In order to better understand the problem and possible solutions, it is important to look at the background, effects and different perspectives.
📜 Duty free border background
The duty-free limit, also known as the de minimis limit, is a threshold below which no customs duties and import sales tax are levied on imported goods. In the European Union, this limit is currently 150 euros for customs duties and 22 euros for import sales tax. This regulation was originally introduced to facilitate international trade and reduce the administrative burden on customs authorities.
Historical development
The idea of the duty-free border emerged at a time when cross-border trade still consisted mainly of traditional business relationships. However, with the emergence of e-commerce and especially the growth of Chinese online shops, the situation has changed drastically. Platforms such as AliExpress, Wish, Temu, Shein and others have created the opportunity to order products directly from China at very low prices.
Current situation
The current tariff-free limit is seen by many as problematic because it gives Chinese traders an unfair competitive advantage. European companies have to pay tariffs and taxes on their products, while Chinese suppliers can often avoid these costs by declaring the value of their goods below the duty-free limit.
🌍🔍 Problems and challenges
The existence of the duty-free border for online shops from China brings with it several problems that affect both economic and legal aspects.
Distortion of competition
One of the main criticisms of the current regulation is the distortion of competition in favor of Chinese providers. European companies, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, are finding it difficult to compete with the extremely low prices of Chinese products. This creates an uneven playing field in global e-commerce.
Tax losses
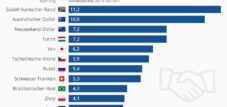
By circumventing customs duties and import sales tax, European countries suffer significant tax losses. It is estimated that these losses amount to several billion euros annually. This missing revenue could be used elsewhere for important public spending.
Safety and quality concerns
Another aspect that is often overlooked is the question of product safety and quality. Many goods imported below the duty-free limit are not subject to strict European safety and quality standards. This can lead to risks for consumers and undermines the EU's efforts to ensure high product standards.
**Environmental aspects
The ability to order very cheap products from China often encourages excessive consumption of inferior goods. This contradicts the EU's efforts to promote sustainability and the circular economy. In addition, the increased shipping of individual products leads to greater environmental impact through transport and packaging.
💬👍 Arguments for abolishing the duty-free border
In view of the problems mentioned, there are strong arguments for abolishing or at least significantly adjusting the duty-free limit for online shops from China.
Fair competition conditions
The abolition of the duty-free border would lead to fairer conditions of competition for European companies. This could strengthen the local economy and secure jobs in the EU. Small and medium-sized companies in particular, which often suffer the most from competition from China, could benefit from this.
Increase in tax revenue
By levying customs duties and import sales tax on all imported goods, the tax revenue of the EU states could be significantly increased. These additional funds could be invested in important areas such as education, infrastructure or environmental protection.
Improving product safety
Tighter controls on imports could help reduce imports of products that do not meet EU standards. This would strengthen consumer protection and improve the quality of products available on the European market.
Promoting sustainability
The abolition of the duty-free border could curb the excessive consumption of cheap, often inferior products. This would be in line with EU goals to promote a more sustainable economy and could lead to a reduction in waste and resource consumption.
🔧📝 Challenges in implementation
Despite the convincing arguments for abolishing the duty-free border, there are significant challenges in practical implementation.
Administrative costs
One of the biggest challenges would be the increased administrative burden on customs authorities. Processing a significantly larger number of shipments could lead to delays and increased costs. Efficient systems would have to be developed to cope with this additional effort.
Technological requirements
Implementation would require significant investment in technological infrastructure. Automated systems for recording, assessing and clearing shipments would need to be developed or expanded to handle the increased throughput.
International Relations
The abolition of the tariff-free border could lead to tensions in trade relations with China. It would be important to take a diplomatic approach and possibly conduct negotiations at the international level to minimize any negative impact on trade relations.
Consumer resistance
Many consumers have become accustomed to the ability to order very cheap products from China. A price increase through tariffs and taxes could face resistance. It would be important to inform the public about the reasons and benefits of the change.
💡🔧 Possible solutions
There are various possible approaches to abolish or adjust the duty-free limit for online shops from China:
Gradual lowering
Instead of an immediate complete abolition, the duty-free limit could be gradually reduced. This would give the parties involved time to adapt and gradually increase the administrative burden.
Digitalization and automation
Investments in digital technologies and automated processes could cope with the increased administrative burden. For example, artificial intelligence and blockchain technology could be used to process and monitor shipments more efficiently.
International cooperation
Close cooperation with Chinese authorities and e-commerce platforms could help reduce fraud and misdeclarations. Shared databases and information sharing could facilitate enforcement.
Consumer education
A comprehensive information campaign could explain to consumers the reasons for the change and the long-term benefits for the European economy and environment.
Adjustment of legislation
EU legislation would have to be adapted to implement the new regulation. This could also include measures to simplify customs clearance for small businesses in order to maintain their competitiveness.
🎯👥 Impact on various stakeholders
The abolition of the duty-free border would affect different interest groups differently:
European companies
For European companies, especially small and medium-sized businesses, the change could lead to fairer conditions of competition. They would have a better chance of competing with Chinese suppliers, which could lead to growth and job creation.
consumer
Consumers may initially face higher prices for products from China. However, in the long term this could lead to a greater choice of high quality and safe products. In addition, awareness of sustainable consumption could be increased.
Customs authorities
The change would mean an increased workload for customs authorities. However, this could be offset by investments in technology and human resources, financed by the additional revenue.
Logistics company
Logistics companies would have to adapt their processes to meet the new requirements. This could lead to investments in new technologies and potentially higher shipping costs.
Chinese traders
Chinese online shops and retailers would be most affected. They would have to adapt their business models and possibly charge higher prices, which could affect their competitiveness in the European market.
💬📈 Strong arguments for abolishing the duty-free limit for online shops from China
The abolition of the duty-free border for online shops from China is a complex issue with far-reaching effects. While there are strong arguments for such a measure, particularly in terms of fair competition and tax revenue, the challenges of implementation cannot be underestimated.
A balanced solution could be a gradual adjustment of the duty-free border, accompanied by investments in technology and international cooperation. It would also be important to inform consumers about the reasons and long-term benefits of the change.
Ultimately, it is about finding a balance between the benefits of global e-commerce and protecting the European economy, consumers and the environment. The discussion on this topic will certainly become more important in the coming years as cross-border online commerce continues to grow and develop.
The EU institutions and Member States are faced with the challenge of developing policies that promote innovation and competition, while also protecting the interests of the European economy and society. Abolishing or adjusting the tariff-free border could be an important step in this direction, but requires careful planning and implementation to achieve the desired goals.
📣 Similar topics
- 🌟 The question of the duty-free limit for online shops from China
- 📜 Duty free border background
- 📈 Historical development of the duty-free border
- 📊 Current situation of the duty-free border
- ⚖️ Distortion of competition due to the duty-free border
- 📉 Tax losses due to bypassing the duty-free border
- 🛡️ Safety and quality concerns with imported goods
- 🌍 Environmental aspects of the duty-free border
- 🤝 Arguments for abolishing the duty-free border
- 💼 Challenges in implementing the duty-free border change
#️⃣ Hashtags: #tariff-free border #competition #tax losses #product safety #environmental aspects
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Industry expert, here with his own Xpert.Digital industry hub with over 2,500 specialist articles
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus