What do you understand by digitalization?
Language selection 📢
Published on: April 8, 2019 / Update from: April 8, 2019 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
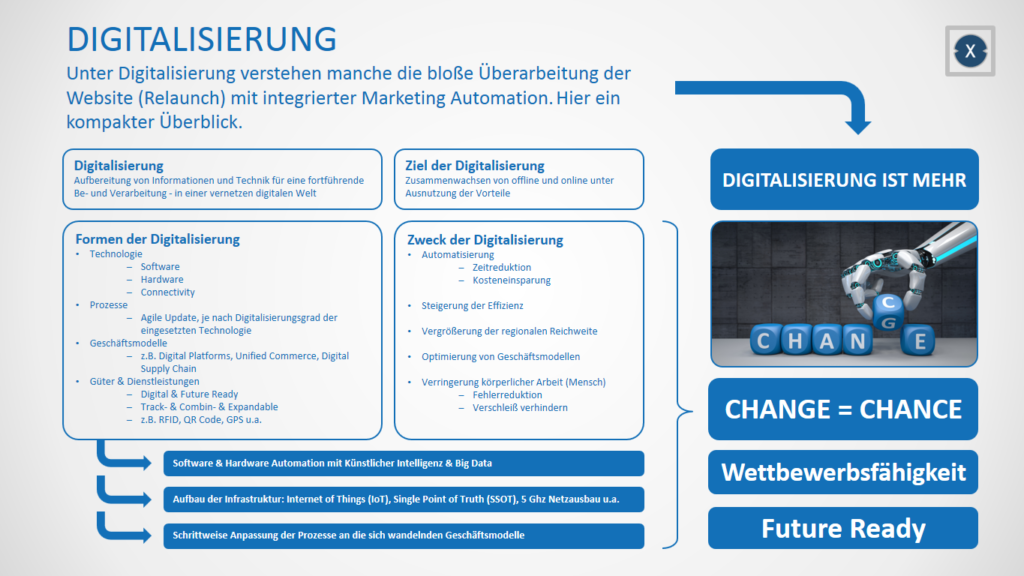
Some people understand digitalization as simply revising the website (relaunch) with integrated marketing automation.
However, this assumption is insufficient and falls short. In its original sense, the term digitization refers to the conversion of analog values into digital formats. Digitalization has come a long way here.
The original purpose of digitalization was to store information digitally and make it available for electronic data processing. Historically, it usually began with an analog medium (e.g. tape recording, vinyl record).
In science, however, digitalization in the sense of changing processes ( process digitalization ) and procedures due to the use of digital technologies (digital revolution, digital transformation) has become a cross-cutting topic in many disciplines.
Interfaces into the physical world
With regard to process digitalization, interfaces to the outside world are particularly crucial: Digital information is output on analog devices or attached to physical goods so that it can be read again by people or by the same machine with a time delay, or by other machines.
In addition to classic techniques such as the output of digital information on carrier materials such as paper using human-readable letters and numbers (and their reconversion using OCR), this also includes specialized techniques such as barcodes, 2D codes (e.g. QR codes) or wireless, without visual contact electrical connection readable information carriers (e.g. RFID, “radio-frequency identification”).
The digitalization of traffic and logistics includes, for example, digitally controlled warehouse technology, driverless transport systems, autonomous driving, navigation systems and digital traffic control systems.
Whether digitalization in measurement technology, healthcare or production technology (e.g. with the help of CNC machines or 3D printing), the fundamental advantages of digitalization lie in the speed and universality of information dissemination. Due to inexpensive hardware and software for digitalization and ever-increasing networking via the Internet, new opportunities are emerging at a rapid pace.
Reasons for digitalization
- Digital data allows the use, processing, distribution, indexing and reproduction in electronic data processing systems
- Digital data can be processed, distributed and reproduced more quickly by machines
- They can be searched (also word by word).
- The storage space requirement is significantly lower today
- Even over long transport routes and after multiple processing, errors and distortions (e.g. noise overlays) are minimal or can be completely eliminated compared to analog processing
- Long-term archiving
The more you look at digitalization, the more the complexity of the entire topic becomes clear. The big challenge is to capture and implement digitalization as a whole => digital transformation . If only partial areas of digitalization are taken into account or left out, then in reality no real digital transformation will take place and its positive effects as well as its advantages can evaporate.
Without questioning the existing business models, without planning processes (degree of digitization of the respective areas) and not completely thought-out steps in the digitization of goods and services, digital technology will not be able to manage the digital transformation on its own.
To return to the example from the beginning: Without further search engine optimization and other marketing measures, you will not generate any additional leads with a new website and marketing automation! It helps to simplify the process, make it faster and easier for third parties to process. Without further measures and integrations, such as in a merchandise management system, it will still be a dry run and everything will remain the same.
Digital business transformation
Digital transformation (also “digital change”) refers to an ongoing process of change , which, as a digital revolution, affects the entire society and, from an economic point of view, especially companies. The basis of digital transformation are digital technologies that are being developed at an ever-increasing pace, paving the way for new digital technologies.
In the narrower sense, digital transformation is often the change process within a company triggered by digital technologies or customer expectations based on them (digital business transformation). But digital transformation goes much further and beyond that. It is a process of change that affects a variety of aspects of our society and does not end with companies.
Through the possibilities and potential of digital media and the Internet, digital business transformation sustainably changes the foundation of every company in its strategy, structure, culture and processes. It affects the organization via change management (is a topic from the IT Infrastructure Library – ITIL) . With Digital Business Transformation, companies are responding to the changes of the digital age. As a conceptual development, Digital Business Transformation is derived from the English term “Business Transformation”, the development of new business opportunities and the implementation of new business models by a company.
Digital Business Transformation also deals with the planning, control, optimization and implementation of a company's value chain in the digital era. The focus is on identifying the effects of digitalization on existing business models, sales, revenue streams and differentiating features of a company in the market.
There is no uniform definition for digital business models. In the broadest sense, they are business models whose value-adding activities rely on digital technologies. Oliver Gassmann defines it more narrowly as “internet-based value propositions based on intelligent value chains”. Due to constant progress in digital technologies and/or due to changing expectations, possible digital business models are also constantly changing.
These increasingly rapid and ongoing changes in business models and their processes, including the respective levels of digitalization, make it necessary to rely on experts with comprehensive know-how in the digital management of tomorrow (or: industry know-how).