Industry & Service Robotics in South Korea: Challenges and global comparison with China, USA, Japan, Germany and the EU
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: January 3, 2025 / update from: January 3, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Industry & Service Robotics in South Korea: Challenges and global comparison with China, USA, Japan, Germany and the EU - Image: Xpert.Digital
Automation in Focus: How South Korea is redefining the robotics industry
South Korea is a world leader in automation and robot density. However, the rapid development of the robotics industry in the country also brings challenges. This report examines the challenges facing robotics in South Korea and compares the country's automation to other leading nations.
The robotics industry in South Korea
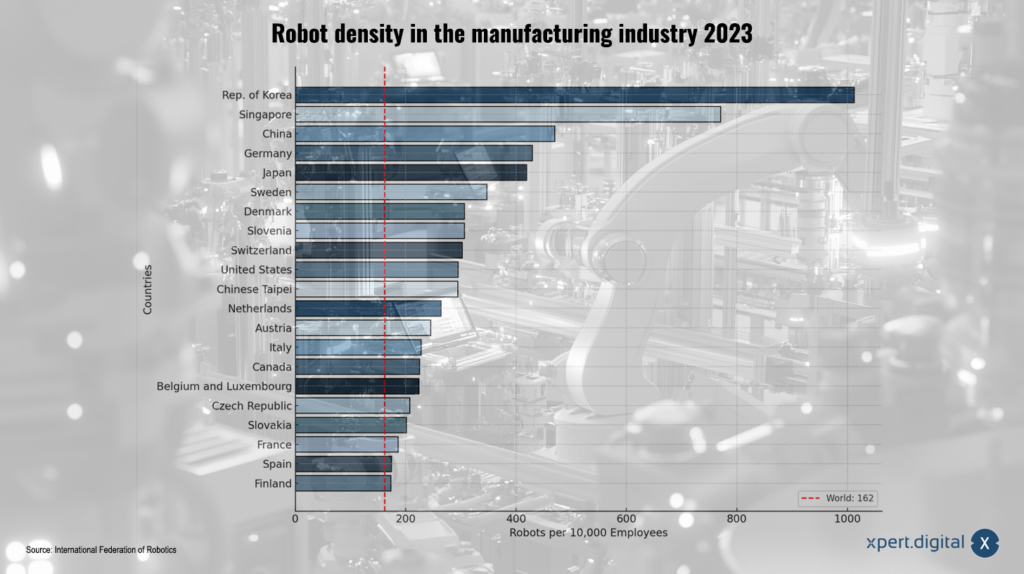
South Korea has the highest robot density in the world, with 1,012 robots installed per 10,000 manufacturing workers - more than six times the global average. South Korea's industrial robot market was valued at US$894.97 million in 2024 and is expected to grow to US$1,874.65 million by 2033, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.9% during the forecast period (2025– 2033). This trend is driven by machine learning, advances in artificial intelligence (AI), and sensing technologies. The South Korean government plans to quadruple the country's robot market to 20 trillion won from 2021 to 2023 to address labor shortages in South Korea, which has one of the lowest birth rates in the world.
The most important companies in the industry include
- Industrial robots: HD Hyundai Robotics, Hyundai WIA, Doosan Robotics, Hanwha Robotics, Higen Motor
- Service robots: LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics
- Other important players: Neuromeka, T-Robotics, Koh Young Technology, Robostar
In 2023, an estimated 3,000 service robots were deployed in restaurants in South Korea, up from just 50 in 2019.
Areas of application
Robots are used in a variety of industries in South Korea, including:
- Manufacturing: automotive industry, electronics, metal and mechanical engineering, plastics and chemical industries
- Services: healthcare, catering, retail, logistics
- Agriculture, defense and social security:
Challenges for the robotics industry
Despite rapid growth, the robotics industry in South Korea faces various challenges:
High investment costs
The acquisition, integration and maintenance of robotic systems is expensive, which is particularly a hurdle for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). According to KIET, around 40% of SMEs in South Korea are hesitant to adopt robotic technologies due to financial constraints. A 2024 Korea Industrial Complex Corporation survey of small manufacturers in Changwon found that 40.7% cited financing difficulties as a barrier to automation. Another 25.9% said government support was inadequate, while 20.4% cited long payback periods.
Lack of qualified workers
Although automation is replacing jobs, demand is increasing for new jobs that require technical and engineering skills, particularly in robotics, automation and artificial intelligence. There is a need to retrain and upskill the workforce to manage, maintain and improve these systems.
acceptance in society
Increasing automation raises questions about job losses, ethical concerns and regional development. There is a need to promote the acceptance of robots in society and educate the public about the benefits of automation.
Safety concerns
Industrial robots pose risks to human workers, particularly in the event of malfunctions or improper programming. In 2023, a man in South Korea was killed by a robot at a vegetable packing plant. Strict safety precautions must be taken to avoid accidents. In South Korea, risk assessment is required before implementing robotic tasks to increase safety by eliminating and reducing hazards.
Global comparison
South Korea has a significantly higher robot density compared to other countries. South Korea's robot density, or the number of robots per 10,000 employees, is seven times higher than the global average of 141 robots per 10,000 employees.
More about it here:
Strengthen
- Early adoption of robots: South Korea invested early in robotics and built a strong industry.
- Government funding: The government supports the robotics industry through funding programs and initiatives.
- Technological Innovation: South Korea is a leader in the development of new robotic technologies.
Weaken
- Dependence on key industries: The South Korean economy is heavily dependent on the electronics and automotive industries, which are the largest buyers of industrial robots.
- Social inequality: Automation can increase social inequality between generations and regions. Ethical concerns: Increasing automation raises ethical questions that need to be resolved.
- Low acceptance among SMEs: The acceptance of new technologies such as robotics and AI is significantly higher among large companies (24.5%) than among small and medium-sized companies (12.1%).
Comparison with Japan
South Korea has overtaken Japan in terms of robot density. In 2022, there were 1,000 robots installed per 10,000 manufacturing workers in South Korea, compared to 399 in Japan. A possible reason for the higher robot density in South Korea compared to Japan could be the faster response to demographic changes and associated challenges such as labor shortages.
Comparison with China
Although China has invested heavily in industrial robotics in recent years, its robot density is still well below that of South Korea. South Korea has 2.5 times as many robots per 10,000 employees as China. This could be due to earlier and more consistent promotion of the robotics industry in South Korea.
Comparison with the USA
The USA has a significantly lower robot density than South Korea. South Korea has almost seven times as many robots per 10,000 employees as the United States. A possible reason for this difference could be the higher priority that the South Korean government gives to automation compared to the US.
Comparison with Germany
South Korea has more than twice as many robots per 10,000 employees as Germany. This shows South Korea's more aggressive approach to integrating automation. One factor for the higher robot density in South Korea could be the greater focus on the electronics industry, which has a high level of automation.
Further insights into global comparison
Despite high robot density and active investment in research and development, South Korea lags behind the United States, Japan and the European Union in the competitiveness of its robotic technology. This suggests that South Korea needs to increase its efforts in developing innovative robotic technologies to maintain its global competitiveness.
State initiatives and funding programs
The South Korean government is promoting robotics and automation through various initiatives:
Promoting research and development
Fourth Intelligent Robot Basic Plan (2024-2028): Investing over $2.24 billion in the public and private sectors by 2030. The goal is to increase the local production rate of robot parts from 44% to 80% by 2030. The government also plans to deploy one million robots in various sectors by 2030.
Support for companies
Promoting specialized robotics clusters
The government supports 11 regions as specialized centers for robotics companies and projects.
Regulation and Legislation
Approval of mobile robots outdoors
In 2023, Korea approved the use of outdoor mobile robots for new business areas such as delivery services and patrols.
Training of specialists
Training programs: Training programs for robotics experts are offered.
Opportunities and risks
opportunities
Growing Market: The robotics market in South Korea is expected to continue growing.
- New jobs: Automation is creating new jobs in robot maintenance, software development and data analysis.
- Increase productivity: Robots can increase productivity in various industries.
Risks
- Job loss: Automation can lead to job losses, especially among low-skilled workers.
- Safety risks: Robots pose safety risks for human workers.
- Ethical concerns: Increasing automation raises ethical questions.
South Korea is a pioneer in robotics and automation
The high density of robots and government funding have led to a strong robotics industry. However, there are also challenges such as high investment costs, lack of skilled labor and safety concerns. South Korea must overcome these challenges to fully realize the benefits of automation and maintain its position as a global leader in robotics.
The future of robotics in South Korea depends on the country's ability to drive innovation, promote social acceptance and overcome the challenges of automation. This also includes the question of how the workers made redundant by automation can be retrained and integrated into new professions. South Korean society needs to prepare for the changes in the world of work and discuss the ethical and social issues raised by increasing automation.
South Korea has the potential to play a leading role in the global robotics landscape. By combining technological innovation, government support and social acceptance, the country can seize the opportunities of automation and overcome the challenges.
Our recommendation: 🌍 Limitless reach 🔗 Networked 🌐 Multilingual 💪 Strong sales: 💡 Authentic with strategy 🚀 Innovation meets 🧠 Intuition
At a time when a company's digital presence determines its success, the challenge is how to make this presence authentic, individual and far-reaching. Xpert.Digital offers an innovative solution that positions itself as an intersection between an industry hub, a blog and a brand ambassador. It combines the advantages of communication and sales channels in a single platform and enables publication in 18 different languages. The cooperation with partner portals and the possibility of publishing articles on Google News and a press distribution list with around 8,000 journalists and readers maximize the reach and visibility of the content. This represents an essential factor in external sales & marketing (SMarketing).
More about it here:
Short version: South Korea is at the forefront of global robotics and automation, but it also faces some challenges
Leading position of South Korea
South Korea leads the world in robot density in industry:
- With 1,012 robots per 10,000 employees, South Korea has by far the highest robot density in the world.
- This exceeds the global average by more than eight times.
- South Korea has maintained this top position continuously since 2010.
In comparison, Germany ranks third with 415 robots per 10,000 employees, Japan ranks fourth with 397, and China ranks fifth with 392.
Drivers of automation
Several factors favor high automation in South Korea:
- A strong electronics industry and a strong automotive industry as the main users.
- Massive government investment in robotics and automation.
- An aging population and declining birth rate, encouraging the use of robots to compensate for labor shortages.
challenges
Despite the leadership position, there are some challenges:
- Job losses: There are concerns about possible job losses due to increased automation.
- Tax aspects: There are considerations of introducing a robot tax or reducing tax incentives for robots.
- Social acceptance: The government must inform the public about the benefits of robotics and make the transition socially acceptable.
- Skilled labor shortage: Despite high levels of automation, there is a shortage of qualified workers to operate and maintain complex robotic systems.
- Economic uncertainties: Trade conflicts, such as the one between China and the US, may impact the South Korean robotics industry.
- High initial costs: Implementing robotic systems requires high initial investments, which can be a hurdle, especially for smaller companies.
Despite these challenges, South Korea remains a leader in global robotics and automation. The government continues to rely on massive investments and long-term strategies to maintain and expand this position.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus