How efficient are propane heat pumps compared to traditional heat pumps?
Language selection 📢
Published on: December 17, 2024 / Update from: December 17, 2024 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
🌱🔥 Propane heat pumps: efficiency, environmental benefits and technological comparison to conventional heat pumps
🌍✨ In times of rising energy prices and increasing environmental requirements, heat pumps are becoming increasingly important as an alternative to fossil heating systems. Propane heat pumps that use the natural refrigerant R290 represent an advanced, efficient and sustainable solution in many respects. The following text highlights the key advantages, efficiency metrics, technological advances and challenges of this technology. A detailed comparison with conventional heat pumps is also made.
1. ⚡📊 Efficiency of propane heat pumps
The efficiency of heat pumps is indicated by the Coefficient of Performance (COP), which describes the relationship between the electrical energy supplied and the heat emitted. Propane heat pumps achieve impressive values here. For example, a prototype from Fraunhofer ISE achieved a COP of 4.7, meaning that 4.7 kilowatts of heat are provided with just 1 kilowatt of electrical energy. In further series of tests, values of 4.8 were even measured.
Comparison to conventional heat pumps:
- Heat pumps that use synthetic refrigerants such as R32 or R410A achieve comparable COP values, but efficiency depends heavily on the design, environmental conditions and the refrigerant used.
- The optimized design of propane heat pumps enables the same or even higher efficiency while requiring less refrigerant.
- Thanks to their high efficiency, propane heat pumps help reduce electricity consumption and operating costs. This is particularly advantageous in regions with high energy prices.
2. 🌿🌎 Environmentally friendly: A future-proof refrigerant
A central advantage of propane heat pumps is the use of the natural refrigerant R290 (propane), which is characterized by a particularly low environmental impact. The most important aspects at a glance:
Low Global Warming Potential (GWP)
The Global Warming Potential (GWP) of propane is 3, which is almost negligible. In comparison, synthetic refrigerants such as R410A have a GWP of around 2088 and R32 have a GWP of 675. This means that synthetic refrigerants contribute significantly more to the greenhouse effect.
No ozone depletion effect
Propane does not have an ozone-depleting effect, while older refrigerants such as CFCs or HCFCs have contributed significantly to the depletion of the ozone layer through their release.
Reduced refrigerant requirement
Thanks to technological innovations, propane heat pumps require a significantly lower refrigerant charge.
- Current standard: Commercially available systems require around 60 grams of propane per kilowatt of heating output.
- Research projects: Optimized technologies reduced the requirement to 10-15 grams per kilowatt.
The combination of high efficiency and extremely low environmental impact makes propane heat pumps a future-proof heating technology. They already meet strict legal regulations and offer a long-term solution for the decarbonization of the heating sector.
3. 🔧🚀 Technological advances and innovations
Modern propane heat pumps feature numerous technological improvements that optimize both efficiency and safety:
Optimized heat exchangers
By using asymmetrical plate heat exchangers, the refrigerant requirement is minimized without affecting heat transfer. This technology improves efficiency and enables more compact designs.
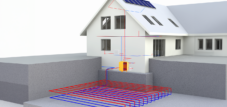
High flow temperatures
Another technological advance is the ability of propane heat pumps to reach flow temperatures of up to 75°C. This is particularly relevant for replacing gas or oil heating systems in old buildings that require higher heating temperatures.
Conventional heat pumps usually only reach 50-60 °C, which limits their use in existing buildings.
Safety precautions
Since propane is flammable, special safety measures have been developed to minimize the risks. This includes:
- Tightly sealed systems to prevent leaks.
- Limited indoor filling quantities to a maximum of 150 grams to avoid explosion risks.
Reduced additional components
By optimizing oil and additional components, not only is efficiency improved, but maintenance effort is also reduced.
Challenges and solutions
Despite their advantages, propane heat pumps face some challenges, which are increasingly being solved through technological development:
Flammability of propane
Since propane is highly flammable, safety measures are required. Particularly indoors, the filling quantities must be limited to 150 grams. However, with professional installation and modern safety precautions, this risk can be reduced to a minimum.
Cost
Propane heat pumps are currently often more expensive to purchase than conventional systems. However, the additional costs are offset by:
- Long-term energy savings through greater efficiency.
- Government funding programs that provide financial support for the use of environmentally friendly heating technologies.
Acceptance and awareness
The advantages of propane heat pumps are not yet widely known. Increased education and advice to end users can help to further disseminate the technology.
💡🚨 Propane heat pumps as the heating technology of the future
Propane heat pumps offer an optimal combination of high efficiency, low environmental impact and future-proof technology. With their ability to generate high flow temperatures, they are particularly suitable for old buildings and represent an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil heating systems.
While the flammability of propane initially appears to be a disadvantage, technological safety precautions effectively minimize this risk. The higher acquisition costs can be compensated for in the long term through energy savings and government subsidies.
Given the increasing demands for sustainability and efficiency, propane heat pumps will play a central role in the transition to environmentally friendly heating systems in the future. They meet the criteria of modern heating technology and make an important contribution to reducing CO₂ emissions - a crucial step on the way to climate neutrality.
📣 Similar topics
- 📣 Efficient and sustainable heating solutions: Propane heat pumps in focus
- 🌱 Why propane heat pumps are more environmentally friendly than traditional systems
- 🔧 Innovations in technology: How propane heat pumps add value to your home
- 💡 Propane as a refrigerant of the future: environmental and cost advantages in comparison
- 🌍 Reduce your carbon footprint with propane heat pumps
- 🏡 Heating old buildings sustainably: High flow temperatures with modern heat pumps
- 💰 Efficient and cost-saving: How propane heat pumps reduce your energy costs
- ⚡ Propane heat pumps vs. traditional systems: Which one is better for you?
- 🔥 Safety aspects of propane as a refrigerant: myths and facts
- 🚀 Future of heating technology: Why propane heat pumps are the new must-have
#️⃣ Hashtags: #propane heat pumps #efficiency #sustainability #refrigerantR290 #climateneutralheating
Our recommendation: 🌍 Limitless reach 🔗 Networked 🌐 Multilingual 💪 Strong sales: 💡 Authentic with strategy 🚀 Innovation meets 🧠 Intuition
At a time when a company's digital presence determines its success, the challenge is how to make this presence authentic, individual and far-reaching. Xpert.Digital offers an innovative solution that positions itself as an intersection between an industry hub, a blog and a brand ambassador. It combines the advantages of communication and sales channels in a single platform and enables publication in 18 different languages. The cooperation with partner portals and the possibility of publishing articles on Google News and a press distribution list with around 8,000 journalists and readers maximize the reach and visibility of the content. This represents an essential factor in external sales & marketing (SMarketing).
More about it here:
💶🏡 Heating with propane: How environmentally friendly heat pumps are also economically convincing
⚡🌍 Efficient, sustainable, innovative: Why propane heat pumps are the future of heating technology
Propane heat pumps are considered in many circles to be a promising alternative to conventional heat pumps using synthetic refrigerants. They are characterized by high efficiency, a particularly environmentally friendly balance and technological features that make them suitable for use in various types of buildings. In view of increasing requirements for the climate compatibility of heating systems and increasingly strict regulations for conventional refrigerants, the use of natural substances such as propane (also known as R290) is becoming increasingly important. The following explains in detail how efficient propane heat pumps are compared to conventional heat pumps, what advantages they offer, what technical advances characterize their development, but also what challenges they face. In addition, aspects such as long-term economic viability, integration into existing buildings, safety requirements and possible future trends in the market are examined in more detail.
🌬️💡 Features and efficiency of propane heat pumps
Propane is a naturally occurring gas that has a number of positive properties as a refrigerant. One of the most important key figures for assessing the performance of a heat pump is the so-called COP value (Coefficient of Performance), which indicates how much heat can be generated in relation to the electricity used. Propane heat pumps can achieve impressive values in this regard. In development projects and practical tests, for example, performance figures were observed that indicate that more than four times as much heat can be produced for every kilowatt hour of electricity used. This means that they are not only on a par with many conventional heat pumps, but in some cases even achieve higher efficiency values. This is particularly important because, in addition to environmental friendliness, the long-term operating cost balance also plays an important role for builders, homeowners and companies.
🔬⚙️ Technological advancements and environmental benefits
The high efficiency of propane heat pumps results from several factors. On the one hand, the chemical and thermodynamic properties of propane enable efficient heat transfer, which, in combination with optimized components, leads to very energy-efficient operation. On the other hand, device technology has developed further in recent years: Improved compressors, newly designed and flow-optimized heat exchangers as well as the reduction in the amount of oil and additional components make it possible to significantly reduce the refrigerant requirement without having to accept any loss in performance.
What is particularly attractive about propane is its extremely low GWP (Global Warming Potential) value. With a GWP of only about 3, propane is virtually negligible in terms of its impact on the greenhouse effect. This is in stark contrast to many synthetic refrigerants, whose GWP values are often well over 500. The ecological advantage is clear here: If a refrigerant leak occurs, the environmental impact of propane is extremely low compared to synthetic alternatives. In addition, propane is neither ozone-damaging nor harmful to the climate in the long term.
🏠🔧 Practical applications and challenges
Another big advantage of propane heat pumps is their ability to deliver high flow temperatures. While many conventional heat pumps with synthetic refrigerants are often limited in practice to flow temperatures of around 55 to 60 °C, modern propane systems can reach temperatures of up to 75 °C. This is particularly important for the renovation of old buildings, which often still have old radiators or radiators installed that require higher flow temperatures.
Despite all these advantages, the challenges cannot be overlooked. A central question is security. Propane is a flammable gas, meaning special precautions must be taken when using it indoors. Safety standards and technical standards therefore regulate the maximum permissible filling quantity of propane in internal heat pump systems in order to practically eliminate the risk of fire or explosions.
💰📉 Economic efficiency and prospects
From an economic perspective, propane heat pumps are currently often even more expensive than conventional systems. This is primarily because it is a comparatively new technology whose market penetration is still in its early stages. However, funding programs and government incentives can help reduce acquisition costs. It should also be taken into account that the long-term operating costs are positively influenced by the high efficiency and low maintenance effort.
Since propane is a natural refrigerant, its use requires a well thought-out device concept. Manufacturers continually work to improve designs to simplify service and maintenance. Less refrigerant in the system also means potential leaks are easier to identify and fix. With increasing experience on the part of craftsmen and specialist companies, this point will also become less important.
🌎💡 Future prospects for propane heat pumps
It is foreseeable that political and regulatory pressure on climate-damaging refrigerants will continue to increase in the coming years. Requirements already exist that restrict the use of certain synthetic substances or make them more expensive. This trend is expected to continue.
Looking ahead, it can be assumed that propane heat pumps will continue to expand their market share. Improved production processes, increasing quantities and growing awareness among end users and specialist companies are likely to increase their share of the heating market. Anyone planning a comprehensive renovation of a building can view propane heat pumps as part of a holistic energy concept.
Propane heat pumps are impressive in many ways compared to conventional heat pumps. They offer a balanced combination of efficiency, environmental friendliness, durability and adaptability that is superior to conventional heat pumps in many ways. This makes them an important building block in shaping a climate-friendly and resource-saving energy future. 🌱
📣 Similar topics
- 📣 Propane heat pumps: the future of climate-friendly heating systems
- 🔋 Efficiency comparison: propane heat pumps vs. conventional systems
- 🌿 Sustainability redefined: propane as a natural refrigerant
- 🔧 Technological advances in propane heat pumps explained
- 💡 High flow temperatures: Ideal for renovating old buildings
- 🔥 Propane Heat Pump Safety: Risks and Solutions
- 💰 Focus on the economics of propane heat pumps
- 🏡 Propane heat pumps: Suitable for new buildings and existing buildings
- 🌍 GWP comparison: Why propane is overtaking conventional refrigerants
- ♻️ Future trends: propane heat pumps and sustainable building technology
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Propane heat pumps #Climate friendly #Energy efficiency #Sustainability #Heating systems
🌡️🌿 Comparison of propane heat pumps and conventional heat pumps
🔥 When comparing propane heat pumps and conventional heat pumps, the following differences arise in various categories:
✨ Efficiency (COP)
Propane heat pumps achieve an efficiency of up to 4.8. This corresponds to comparable values for conventional heat pumps, which, depending on the model, can have similarly high efficiencies.
❄️ Refrigerant requirement
Propane heat pumps are characterized by a significantly lower refrigerant requirement. They only require around 10-15g per kW, while conventional heat pumps require around 60g per kW.
🌍 Environmental Balance (GWP)
The environmental impact of propane heat pumps is outstanding because the refrigerant propane used has a very low global warming potential (GWP) value of just 3. In comparison, many conventional heat pumps have a refrigerant with a GWP of over 500, which puts a significantly greater burden on the environment.
🌡️ Flow temperature
Propane heat pumps can reach flow temperatures of up to 75 °C, which makes them particularly flexible. Conventional heat pumps, on the other hand, usually deliver flow temperatures in the range of 50-60 °C.
🏠 Suitability for old buildings
Due to the high flow temperatures, propane heat pumps are very suitable for use in old buildings, where radiators with higher temperature requirements are often used. Conventional heat pumps can only be used to a limited extent in such cases.
⚠️ Security
Since propane is a flammable refrigerant, the use of propane heat pumps requires special safety precautions. In comparison, conventional heat pumps that use synthetic refrigerants are considered uncritical in terms of safety.
Propane heat pumps are ecologically and technically superior in many areas, especially when it comes to efficiency, environmental friendliness and possible uses in old buildings. There are only restrictions in relation to the security requirements.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus