Photovoltaics (PV): Build a solar carport and solar system on a flat roof - looking for a system from Munich, Rosenheim, Salzburg or Vienna?
Language selection 📢
Published on: July 23, 2021 / update from: August 4, 2021 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
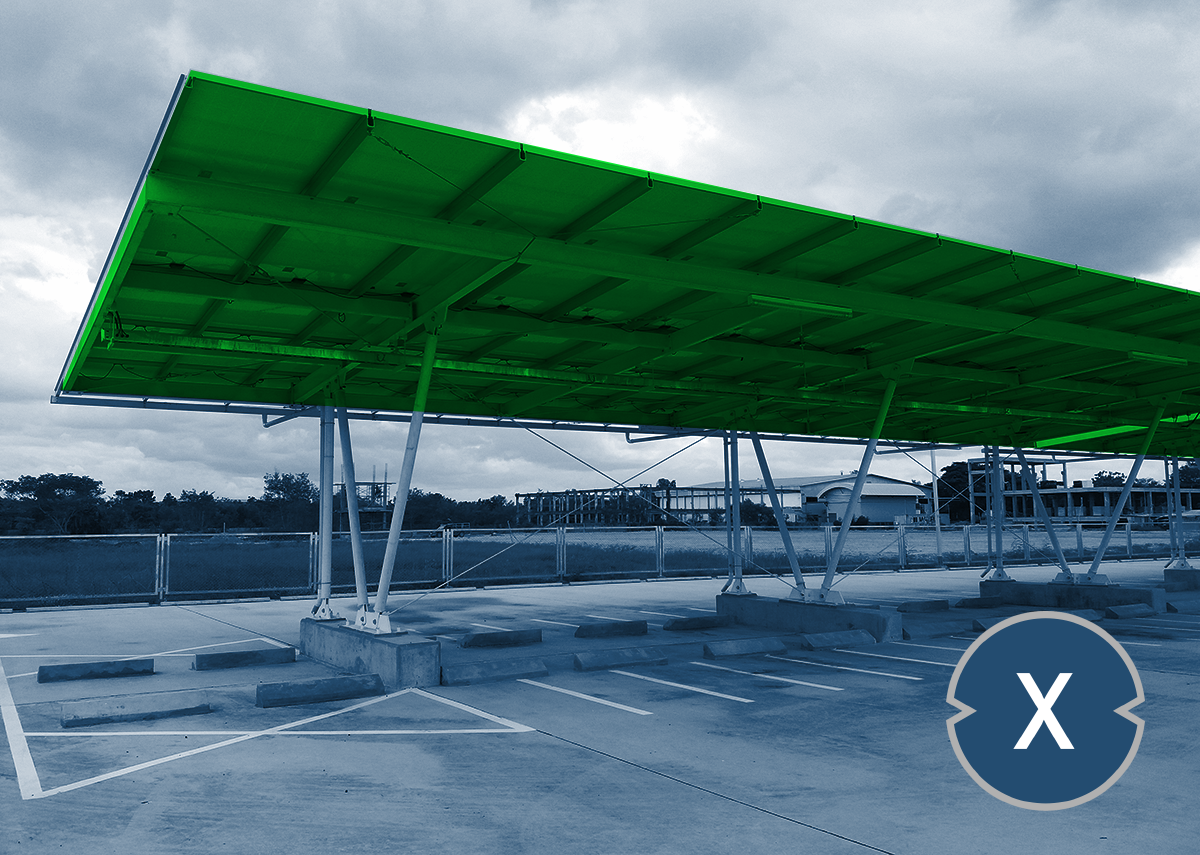

Solar carport parking space for companies or shopping centers – Image: Xpert.Digital / PATSUDA PARAMEE|Shutterstock.com
Solar Vanguard – The solar pioneer in a new energy world
For many it is nothing special and of course, and many still know it from their childhood: the fascinating celestial bodies “satellites” and their extensive solar cell antennas. In an online survey, many photovoltaics linked with solar systems on roofs, solar parks or PV outdoor facilities , but none mentioned the space-based solar energy. In 1958 the first satellite Vanguard I flew with solar cells for energy supply. It was the first professional use of a photovoltaic system and at the same time the starting signal for impressive technological development. At that time, oil, coal and nuclear energy were the main beams of energy generation.
📣 Parking areas solar solutions for industry, retail and municipalities
Everything from a single source, specially designed for solar solutions for large parking areas. You refinance or counterfinance into the future with your own electricity generation.
🎯 For solar engineers, plumbers, electricians and roofers
Advice and planning including a non-binding cost estimate. We bring you together with strong photovoltaic partners.
👨🏻 👩🏻 👴🏻 👵🏻 For private households
We are positioned across regions in German-speaking countries. We have reliable partners who advise you and implement your wishes.
At that time, no one could have even imagined that this solar cell technology would one day revolutionize energy supply. But now the time has come. The technology and possible uses have developed further with solar carports
Suitable for:
In addition to the solar obligation and the EU directives, many are now moving forward with the switch from fossil energy production to solar energy generation. The focus is currently on electromobility, as mobility in general is one of the main drivers of CO2 emissions, which now need to be reduced for the environment, humanity and the earth and reduced to a minimum in the next 20-30 years, at least in Europe to reduce. CO2 is bad for the climate. As a greenhouse gas, it prevents heat from escaping from Earth into space. As a result, the earth is heating up more and more.
Suitable for:
- Balcony solar: 600W balcony power plant with storage as a balcony solar system
- Plug-in solar device: the solar system for balconies and gardens, particularly interesting for long-term campers
Photovoltaics is also a step towards decentralized, autonomous power supply. Everyone has the chance to produce their own electricity at a comparable lower price, without depending on third parties. This was not possible in the case of coal-fired power plants and nuclear energy.
It is also about the higher future costs for environmental protection regulations, power peaks (infrastructure and network stability) and CO2 balance.
The CO2 balance, also known as the greenhouse gas balance or CO2 footprint, will become more important in the future if there are tax and cost surcharges in the CO2 labeling of goods and services.
Suitable for:
This means that anyone who does not contribute to their own autonomous power supply, but continues to use external fossil and nuclear energy technology, must expect to pay a CO2 surcharge (CO2 footprint) in the future, which puts them at a noticeable competitive disadvantage compared to third parties represents. Products that are more expensive than the competition are not marketable in the long term. It is therefore no coincidence that companies like Amazon started expanding autonomous power supply early on.
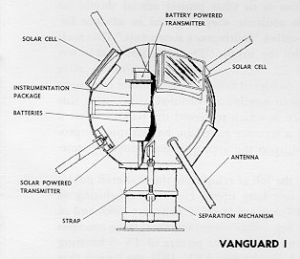
Vanguard I - The first professional use of photovoltaics
- Vanguard 1 satellite
- Vanguard 1 satellite
- Vanguard 1 satellite
On March 17, 1958, the United States' second satellite, Vanguard I, flew into space with a chemical battery and photovoltaic cells to power a transmitter on board. After much hesitation on the part of the US Army, Hans Ziegler (1911–1999) was able to prevail with his idea that an energy supply with solar cells would ensure the operation of the transmitter for longer than the use of batteries. Contrary to the expectations of the military, the station's signals could be received until May 1964 before it ceased its signaling activities.
The success of this small satellite and the scientists involved laid the foundation for the first sensible use of the previously almost unknown and, above all, very expensive solar cells. For many years, solar cells were developed primarily for space travel purposes, as they proved to be the ideal power supply for satellites and space probes up to Mars' distance from the sun. The long service life of the spacecraft compared to battery operation far outweighed the still high price of solar cells per kilowatt hour. In addition, solar cells were and are cheaper and less risky than radioisotope generators, which allow for similarly long operating times. Most spacecraft were and are therefore equipped with solar cells to supply energy.
In 2008, solar cells with increased efficiency delivered several kilowatts of power for communications satellites with over 30 transponders, each with around 150 watts of transmission power, or even provided the drive energy for ion engines in space probes. The Juno space probe, which launched in August 2011, draws its energy from particularly efficient and radiation-resistant solar cells for the first time in orbit around the planet Jupiter. Almost all of the approximately 1,000 satellites in use worldwide obtain their power from photovoltaics. In space, an output of 220 watts per square meter is achieved.
Photovoltaics - installed capacity in Germany
The cumulative electrical output of all grid-connected photovoltaic systems in Germany was around 54 gigawatt peak in 2020. Bavaria is by far the federal state with the most installed capacity, followed by Baden-Württemberg and North Rhine-Westphalia. The city states of Bremen, Hamburg and Berlin have the lowest nominal output of photovoltaic systems.
Photovoltaics
The conversion of light energy into electrical energy using solar cells describes electricity generation through photovoltaic systems. In Germany, the installed capacity of photovoltaic systems is increasing more and more. This development can also be seen globally: around a quarter of the total installed capacity worldwide is in China. This is followed by the USA, Japan and Germany, which in comparison have significantly less installed photovoltaic capacity.
Renewable energy
In addition to photovoltaic systems, hydropower, for example, is also a renewable energy source. In contrast to fossil fuels, they are renewable. Wind energy is particularly important in Germany. Even in a European comparison, electricity generation from wind energy is the highest in this country. The United Kingdom and Spain follow at a distance.
Installed capacity (cumulative) of photovoltaic systems in Germany from 2000 to 2020
- 2000: 114 megawatts
- 2001: 176 megawatts
- 2002: 296 megawatts
- 2003: 435 megawatts
- 2004: 1,105 megawatts
- 2005: 2,056 megawatts
- 2006: 2,899 megawatts
- 2007: 4,170 megawatts
- 2008: 6,120 megawatts
- 2009: 10,566 megawatts
- 2010: 18,006 megawatts
- 2011: 25,916 megawatts
- 2012: 34,077 megawatts
- 2013: 36,710 megawatts
- 2014: 37,900 megawatts
- 2015: 39,224 megawatts
- 2016: 40,679 megawatts
- 2017: 42,293 megawatts
- 2018: 45,158 megawatts
- 2019: 49,047 megawatts
- 2020: 53,848 megawatts
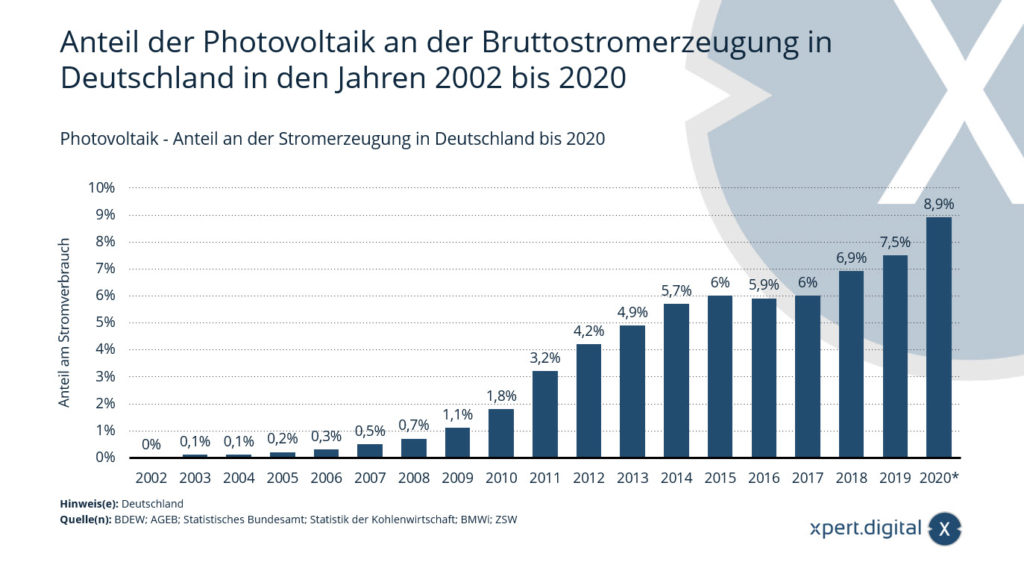
Photovoltaics - share of electricity generation in Germany
In 2020, nine percent of the electricity generated was produced by photovoltaics. The use of photovoltaic systems has become more and more important over the years. The share of the sun as a renewable energy source has increased continuously since 2003.
Sunlight as a source of energy
The advantage of the sun as an energy source is that it is available free of charge, without restrictions and indefinitely. People also take advantage of this and use solar cells to convert light energy into electrical energy. The increasing share of photovoltaics in total electricity generation can be explained, among other things, by the falling costs of the systems and a greater awareness of the use of renewable energies.
Renewable energy sources
While the share of nuclear energy and hard coal in electricity generation in Germany is decreasing, the share of all renewable energy sources is increasing at the same time. In addition to the use of photovoltaic systems, electricity is also generated from the renewable energy sources water, wind, biomass and geothermal energy. Onshore wind turbines produce by far the largest amount of renewable energy in Germany.
Share of photovoltaics in gross electricity generation in Germany from 2002 to 2020
- 2002: 0 in %
- 2003: 0.1 in %
- 2004: 0.1 in %
- 2005: 0.2%
- 2006: 0.3 in %
- 2007: 0.5 in %
- 2008: 0.7 in %
- 2009: 1.1 in %
- 2010: 1.8 in %
- 2011: 3.2 in %
- 2012: 4.2 in %
- 2013: 4.9 in %
- 2014: 5.7 in %
- 2015: 6 in %
- 2016: 5.9 in %
- 2017: 6 in %
- 2018: 6.9%
- 2019: 7.5%
- 2020: 8.9%
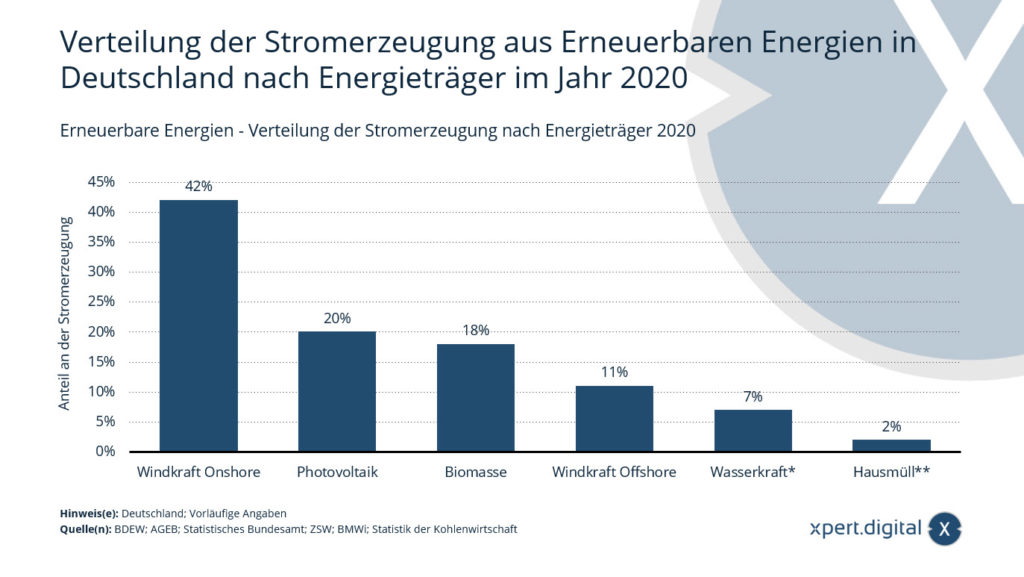
Renewable energies - distribution of electricity generation by energy source
In 2020, the share of electricity generation from onshore wind power was 42 percent of gross electricity generation from renewable energy sources in Germany. Based on all energy sources, including conventional ones, the contribution of onshore wind energy to gross electricity generation in 2020 was around 19 percent.
Renewable energy electricity generation
In contrast to fossil fuels such as coal and nuclear energy, renewable energy sources are renewable. They currently generate almost half of all electricity in Germany. Electricity generation from renewable energies has increased continuously over the past almost 30 years. In a nationwide comparison, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Schleswig-Holstein and Thuringia are among the federal states with the highest share of renewable energies in gross electricity generation.
Wind energy in Germany
When it comes to wind energy, Germany was one of the most important countries in the world in terms of installed wind turbine output in 2019, alongside China and the USA. The amount of electricity generated from wind energy has increased significantly in recent years, both on land and at sea. At the same time, both the number of offshore and onshore wind turbines increased noticeably.
Distribution of electricity generation from renewable energies in Germany by energy source in 2020
- Onshore wind power: 42 in %
- Photovoltaics: 20 in %
- Biomass: 18 in %
- Offshore wind power: 11 in %
- Hydropower*: 7 in %
- Household waste**: 2 in %
* Generation in run-of-river and storage power plants as well as generation from natural inflow in pumped storage power plants.
** Only produced from the biogenic portion of household waste (approx. 50%). Values were converted into percentages and rounded compared to the original source for a better understanding of the statistics.
That's why the Xpert.Solar advice on solar carports , solar systems and solar systems on flat roofs for Munich, Rosenheim, Salzburg and Vienna!
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus