How is mechanical engineering in the various EU countries and outside in the USA, Bric, Mist, China and Japan?
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: February 10, 2025 / update from: February 10, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

How is mechanical engineering in the various EU countries and outside in the USA, Bric, Mist, China and Japan? - Image: Xpert.digital
Industrial added value: the mechanical engineering sector in global comparison
Mechanical engineering and globalization: new perspectives and markets
Mechanical engineering is a load -bearing pillar of industrial added value in many countries and is characterized by different structures, specializations and economic developments. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanical engineering sector in the European Union as well as in important international markets such as the USA, the BRIC countries, China and Japan.
Suitable for:
Mechanical engineering in the European Union
Leading countries and export quotas
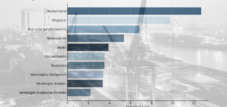
Germany is the undisputed leader in European mechanical engineering and has a significant contribution to the EU's industrial performance. The distribution of the production shares shows Germany's dominance:
- Germany: 27% of total mechanical engineering production in the EU
- Italy: 14%
- France: 12%
- Spain: 8%
- Poland: 6%
The export markets within the EU are particularly important for German mechanical engineers. The main buyers of German machines in the EU are:
- France: 16%
- Italy: 11%
- Poland: 10%
- Netherlands: 10%
- Austria: 9.5%
In total, 45% of all German machine exports are eliminated by the EU. This close economic integration shows that the EU's internal market is of central importance for the industry.
Suitable for:
- Successful mechanical engineering companies in Germany include Bosch, CLAAS, Dürr, Exyte, Festo, Krones, Voith, Zeiss and others
- Uncertainty when investing in mechanical engineering? What role does digital transformation play in investment security?
Corporate structure
The mechanical engineering industry in the EU is strongly medium -sized. This applies in particular to Germany:
- 95% of the approximately 6,600 mechanical engineering companies have fewer than 500 employees.
The distribution of company sizes in Germany:
- 62.6% small companies (up to € 2 million sales)
- 22.7% small businesses (up to € 10 million sales)
- 10.6% medium -sized companies (up to € 50 million sales)
- 4.1% large companies (over € 50 million sales)
This structure is typical of mechanical engineering in many EU countries, with a high proportion of specialized companies that are often the world market leader in niche markets.
Specialization and competitiveness
The specialization within the EU differs greatly between the member states:
- Luxembourg, Belgium, France and Ireland: Strong specialization in high-tech products and highly qualified workers.
- Germany, the Netherlands, Great Britain: wide and balanced portfolio with high technological competence.
- Denmark, Sweden, Finland: concentration on medium to low qualification requirements in production.
- Hungary, Italy, Portugal: Focus on areas with low to medium qualifications.
Growth and challenges
The European mechanical engineering industry is growing stable despite the challenges:
- 95% of the EU countries report stable or rising market shares.
- Investments in transport infrastructure, sustainable technologies and energy supply drive growth.
However, challenges remain:
- Profitability: The average operational profit in Europe is 10%, while it reaches 14% in North America.
- Cost increases: increasing work and material costs as well as bottlenecks in the supply chain put companies under pressure.
In order to remain competitive, European mechanical engineers are increasingly relying on digitization, automation and sustainable production methods.
Mechanical engineering outside the EU
China
China has developed into one of the leading actors in worldwide mechanical engineering in recent decades:
China is the main trade partner of the EU in mechanical engineering:
- 11.4% of machine imports come to the EU from China (2022).
Between 2010 and 2020, export grew rapidly in many segments:
- Packaging machines: +206.9%
- Paper machines: +266.8%
- Halfby production machines: +167.5%
China is investing massively in research & development and increasingly relies on his own innovations in order to be less dependent on Western technology.
USA
The United States is one of the most important export markets for German machines:
- The US market has high demand for German high-tech machines.
- Germany is one of the five largest machine suppliers for the United States.
In addition, US companies are increasingly investing in local production to minimize supply chain risks.
Bric countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China)
The BRIC countries are significant growth regions:
- 13.9% of German machine exports go to these countries.
- India and Russia show increasing industrial production while Brazil is weakening.
- China's influence continues to grow, while Russia loses importance due to geopolitical challenges.
Mist countries (Mexico, Indonesia, South Korea, Türkiye)
This group of countries is becoming increasingly important for mechanical engineering:
- 5.6% of German machine exports go to these countries.
- Indonesia and Turkey have high growth rates in industrial production.
- However, the export quota of German machines to these countries has stagnated at around 6%in recent years.
Japan
Japan remains an important market for European mechanical engineers:
- 13.8% of German machine exports go to Japan and the USA.
- Japan focuses on automation and robotics, which offers opportunities for European mechanical engineers.
Eastern Europe (non-EU countries)
Countries such as Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine are becoming more important for mechanical engineering:
- You benefit from free trade agreements with the EU that reduce tariffs and facilitate trading processes.
- The machine industry is growing particularly in Ukraine, which will increasingly rely on modern production technologies after reconstruction.
Innovations in mechanical engineering: The trends of tomorrow
The future of mechanical engineering depends largely on technological developments and economic framework conditions:
- Digitization and Industry 4.0 will increase efficiency and competitiveness.
- Sustainability plays an ever greater role, especially through the use of energy -efficient machines.
- New markets in Asia, Africa and South America offer potential for long -term growth.
European mechanical engineers have to adapt to stay competitive internationally. Important measures are:
- Investments in research & development, especially in the field of artificial intelligence and automation.
- Optimization of supply chains to reduce dependencies on individual markets.
- Stronger focus on sustainable technologies and environmentally friendly production processes.
With these strategic measures, mechanical engineering can continue to play a key role in the global economy in the future.
Our recommendation: 🌍 Limitless reach 🔗 Networked 🌐 Multilingual 💪 Strong sales: 💡 Authentic with strategy 🚀 Innovation meets 🧠 Intuition
At a time when a company's digital presence determines its success, the challenge is how to make this presence authentic, individual and far-reaching. Xpert.Digital offers an innovative solution that positions itself as an intersection between an industry hub, a blog and a brand ambassador. It combines the advantages of communication and sales channels in a single platform and enables publication in 18 different languages. The cooperation with partner portals and the possibility of publishing articles on Google News and a press distribution list with around 8,000 journalists and readers maximize the reach and visibility of the content. This represents an essential factor in external sales & marketing (SMarketing).
More about it here:
Mechanical engineering in focus: Europe's variety and global balance of power - background analysis
Insider view: Germany's key role in global mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering, as a backbone of the European and global economy, presents itself in the various regions of the world in a variety of structures and forms. A complex image is emerging within the European Union (EU) that ranges from Germany's dominance to specialized niches in smaller member states. Outside of the EU, the USA, BRIC countries and especially China and Japan shape the global balance of power in mechanical engineering.
Mechanical engineering in the European Union: a multi -layered structure
The EU represents one of the most important economic areas in the world, and mechanical engineering plays a key role here. He is not only an important employer, but also an innovation driver and an essential factor for the competitiveness of European industry as a whole. However, the structure of mechanical engineering within the EU is by no means homogeneous, but reflects the different economic and industrial traditions of the individual Member States.
Suitable for:
Germany: The undisputed primus
When you talk about European mechanical engineering, you can't avoid Germany. The country is the undisputed center of the industry in the EU and one of the global leaders. Germany generates more than a quarter of the entire mechanical engineering production within the EU, more precisely 27 percent. This dominance has grown historically and is based on a combination of factors: a long industrial tradition, a strong focus on engineering and innovation, excellent training infrastructure and a close network of suppliers and research institutions.
The export strength of German mechanical engineering is impressive. A significant part of the production is intended for export, which underlines the global competitiveness of German companies. Within the EU are the most important buyers for German machines France with 16 percent, Italy with 11 percent, Poland and the Netherlands with 10 percent each and Austria with 9.5 percent of exports. A total of 45 percent of all German machine exports go to the EU, with the top 5 countries mentioned alone and another five EU countries already accept 84 percent of these EU exports. These figures illustrate the close integration of German mechanical engineering with the other European economies and its central role in the European internal market.
Italy, France, Spain and Poland: The pursuers in the European field
It is followed by an some distance from Italy with 14 percent, France with 12 percent, Spain with 8 percent and Poland with 6 percent of EU-wide mechanical engineering production. These countries represent important pillars of European mechanical engineering, even if they have differences in their structure and specialization.
Italy
Italian mechanical engineering is characterized by a high level of specialization in certain niches, especially in the areas of automation technology, packaging machines, textile machines and agricultural machinery. Italian companies are often family businesses that are characterized by flexibility and customer proximity. The regions of Emilia-Romagna and Lombardy are considered centers of Italian mechanical engineering.
France
French mechanical engineering is more geared towards large companies and corporations and traditionally strong in the areas of aerospace, defense, energy and automotive industry. French mechanical engineers are often leading in high technology areas and value research and development. The regions Île-de-France and Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes are important locations.
Spain
Spanish mechanical engineering has experienced considerable growth in recent decades and has established itself in the areas of renewable energies, machine tools and automotive delivery. Spain benefits from its geographical location as a bridge to Latin America and from comparatively lower labor costs within the EU. The Basque Country and Catalonia are important regions.
Poland
Poland has developed into an important production location for European mechanical engineering after joining the EU. The country benefits from its proximity to Germany, lower wage costs and a growing number of qualified specialists. Poland is particularly strong in supply for the automotive industry and plant construction. Regions such as Silesia and Greater Poland play a central role.
The company structure: SMEs as a backbone
A formative feature of European mechanical engineering, especially in Germany and Italy, is the dominance of medium -sized companies. These companies, often family businesses in the second or third generation, form the backbone of the industry. In Germany, for example, 95 percent of the approximately 6,600 mechanical engineering companies are medium -sized companies with fewer than 500 employees.
The industry structure in Germany illustrates this medium -sized relation even more precisely: 62.6 percent are small companies with sales of up to 2 million euros, 22.7 percent are small companies with up to 10 million euros, 10.6 percent are medium -sized companies with up to 50 million euros in sales and only 4.1 percent are large companies with sales of over 50 million euros. These figures show that German mechanical engineering, and in a similar way, is characterized by a large number of specialized, flexible and innovative medium -sized companies. This structure enables high adaptability itself to changing market requirements and strong customer orientation.
Suitable for:
Specialization and competitiveness: diversity and niches
Within the EU there are significant differences in the sectoral specialization of the individual countries. Smaller EU countries such as Malta, Luxembourg and Finland often have a stronger concentration on certain niche areas. Larger countries such as Germany, Great Britain, Italy and France, on the other hand, have more diversified and more balanced production structures.
If you look at the specialization according to qualification level, interesting country groups can also be identified. Countries such as Luxembourg, Belgium, France and Ireland specialize more in activities with high qualification requirements, for example in the areas of research and development, high technology and specialized services. Germany, the Netherlands and Great Britain show a balanced profile across various qualifications. Denmark, Sweden and Finland have a stronger specialization in medium to low qualifications, which indicates their strengths in production and traditional mechanical engineering. Hungary, Italy and Portugal tend to be low to medium -sized qualifications, which reflects their role as production sites and suppliers.
These specializations are not accidental, but the result of historical developments, industrial policy decisions and the respective strengths and weaknesses of the individual countries. They lead to a complementary structure within the European mechanical engineering, in which the countries complement each other in different levels of value and niche areas.
Suitable for:
Growth and challenges: between optimism and headwind
European mechanical engineering shows overall positive growth tendencies. A large majority of companies, namely 95 percent, report stable or growing markets. Important growth drivers are investments in transport infrastructure, climate adjustment and energy infrastructure. In particular, the demand for modern and efficient technologies in these areas fueled the demand for machines and systems.
Despite these positive prospects, European mechanical engineering also faces considerable challenges. An important point is profitability. European mechanical engineers achieve an average operational profit margin of around 10 percent, which lies behind the North American competition, which reaches around 14 percent. This difference is worrying and indicates structural disadvantages or lower efficiency in Europe.
Other stress factors are increasing work and material costs as well as persistent supply chain problems. In particular, the strongly increased energy prices in Europe and the global scarcity of certain raw materials and components put companies under pressure. The geopolitical uncertainty and the increasing trade conflicts also contribute to a more difficult economic environment.
Future prospects: transformation and innovation as a key to success
Despite the challenges, European mechanical engineering also offers great opportunities. In particular, the transformation of important buyers, especially the automotive industry, opens up new growth potential. The transition to electromobility, the development of autonomous vehicles and the digitization of production require new technologies and machines. In the area of battery production alone, the market volume will be estimated at 300 billion euros by 2030. This offers enormous opportunities for European mechanical engineers to position themselves in this future market.
In order to remain competitive and take advantage of these opportunities, European mechanical engineers have to actively act. Important fields of action are:
Optimization and diversification of the supply chains
The dependence on individual suppliers and regions must be reduced in order to increase resilience compared to disorders. A stronger regional diversification and the structure of alternative supply chains are necessary.
Consistent orientation towards sustainability
The demand for environmentally friendly and resource -saving technologies is steadily increasing. European mechanical engineers have to make their products and production processes more sustainable and develop innovative solutions for a circular economy.
Investments in research and development
Innovation is the key to competitiveness. European companies must continue to invest in research and development in order to develop new technologies and products and to position themselves in future fields. Digitization and the use of artificial intelligence play a central role.
Safety of skilled workers
The lack of qualified specialists is a growing challenge. European mechanical engineers have to create attractive working conditions and invest in the training and further education of their employees in order to meet the need for specialists.
Overall, European mechanical engineering remains an important economic factor with promising future prospects. However, the prerequisite for this is that companies are actively tackling the current challenges, adapting to the changes and consistently using the opportunities offering. Innovation, sustainability and flexibility will be the decisive success factors.
Mechanical engineering outside the EU: global dynamics and new balance of power
Outside the European Union, mechanical engineering presents itself in an even more diverse and more dynamic form. In particular, the development in Asia, especially in China, has fundamentally changed the global balance of power in recent decades. But there are also interesting developments and specific structures in the USA, the BRIC countries and other regions.
China: Ascent to the global mechanical engineering power
China has experienced an unprecedented climb in mechanical engineering in recent decades and has developed from a pure production site into a global power in this sector. China is now the most important trading partner for Germany and the EU in the area of machine import. In 2022, 11.4 percent of machine imports came to the EU from China. This number illustrates the growing importance of China as a supplier and competitor for European mechanical engineers.
Chinese mechanical engineering has recorded enormous growth in many segments. Between 2010 and 2020, numerous areas experienced three -digit export growth. Examples of this are fluid pumps with growth of 124.6 percent, plastics machines with 146.3 percent, textile machines with 132.5 percent, HALKEDER production machines with 167.5 percent, woodworking machines with 184 percent, packaging machines with 206.9 percent and paper machines with even 266.8 percent. These impressive growth rates show the dynamics and enormous potential of Chinese mechanical engineering.
This ascent is due to various factors:
Government support
The Chinese government strategically promoted mechanical engineering and supported it through industrial policy, subsidies and investments in research and development. Initiatives such as “Made in China 2025” aim to develop China into a leading industrial nation and make mechanical engineering a key area.
Enormous internal demand
China's rapid economic growth has led to an enormous internal demand for machines and systems. The expansion of the infrastructure, the modernization of industry and growing consumption inspired Chinese mechanical engineering.
Low production costs
A comparatively low wage costs and high availability of workers have long made China an attractive production location. This cost advantage has helped Chinese companies to be competitive on the world market.
Technological catch-up
China has massively invested in technological development in recent years and has shortened the gap to western industrialized countries in many areas. Chinese companies are increasingly able to produce high -quality and technologically demanding machines.
The challenges and opportunities of Chinese mechanical engineering
However, Chinese mechanical engineering also faces challenges. This includes increasing labor costs, increasing competition in Germany and on the world market, environmental protection requirements and the need to develop from pure mass production into higher quality products and services. Despite these challenges, China will further expand its role as a global player in mechanical engineering and change the competitive landscape.
USA: an established market with innovative strength
The United States has long been an important market for German and European mechanical engineering and traditionally belong to the top 5 export countries. The US market is characterized by a stable demand for high-quality and technologically advanced machines. American companies invest strongly in automation, digitization and Industry 4.0, which increases the need for corresponding machines and systems.
The US mechanical engineering itself is also an important industry that is characterized by innovative strength and specialization in high technology areas. Strengths are particularly in the areas of aerospace, medical technology, robotics and software for mechanical engineering. The United States has an excellent innovation ecosystem with worldwide leading universities, research institutions and venture capital.
However, US mechanical engineering also faces challenges. This includes increasing competition from Asia, a shortage of skilled workers, rising health costs and the question of how the industrial basis can be strengthened in Germany. Initiatives to strengthen domestic production and withdraw production capacities (“Reshoring”) could play a greater role in the future.
BRIC countries: Different dynamics and potential
The BRIC countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China) were long considered to be growth engines in the global economy and important sales markets for mechanical engineering. In 2022, the Bric countries took up 13.9 percent of all machine exports from Germany. However, the dynamics within the BRIC group have developed differently in recent years.
Brazil
Brazilian mechanical engineering is strongly shaped by the raw material economy and agriculture. The country has a large internal market and potential for growth in various areas, but also structural problems such as political instability, bureaucracy and infrastructure deficits.
Russia
For a long time, Russian mechanical engineering was strongly geared towards the energy and armaments industry. The geopolitical situation and international sanctions have strongly influenced the development in recent years and have led to an economic weakening. The future prospects are unsure.
India
India is an emerging market with great potential for mechanical engineering. The country benefits from a young population growth, a growing middle class and investments in the infrastructure. However, there are also challenges such as poverty, bureaucracy and an inadequate infrastructure. The “Make in India” initiative of the Indian government aims to strengthen domestic production and promote mechanical engineering.
China
As already shown in detail, China is the most dynamic and most important Bric state in mechanical engineering.
Self-sufficiency of the BRIC countries: challenge for German mechanical engineers
Overall, the export quota of German machines has decreased to the BRIC countries since 2012, although industrial production in India and Russia has increased. This indicates that the Bric countries are increasingly able to cover their machine needs themselves or to switch to other suppliers.
Mist countries: focus on the focus
The so-called manure countries (Mexico, Indonesia, South Korea, Türkiye) are becoming increasingly important for mechanical engineering. In 2022 they made up 5.6 percent of German machine exports. Indonesia and Turkey in particular have strong growth in industrial production.
Mexico
Mexico benefits from its geographical proximity to the USA and its role as a production location for the North American industry. The country is strong in automotive delivery and in other areas of the processing trade. The USMCA free trade agreement (successor to NAFTA) ensures access to the North American market.
Indonesia
Indonesia is a populous island state in Southeast Asia with a growing internal market and potential for further growth. The country is investing in infrastructure and industrialization. Mechanical engineering plays an important role in this development.
South Korea
South Korea is a highly developed industrial country with a strong focus on technology and innovation. South Korean mechanical engineering is competitive in various areas, especially in the automotive industry, the electronics industry and shipbuilding.
Türkiye
Turkey is an important location in the region and benefits from its geographical location as a bridge between Europe and Asia. The Turkish industry is diversified and includes various areas of mechanical engineering. However, there are also economic and political challenges.
Mist countries: New opportunities for German mechanical engineering?
The export quota of German machines to the manure countries rose to 6.5 percent by 2013, but has stagnated at around 6 percent since then. Nevertheless, the manure countries remain important growth markets with potential for mechanical engineering.
Japan: Traditional strength and technological excellence
Together with the USA, Japan is a traditionally important buyer of German machines. Together, the two countries took up 13.8 percent of German machine exports in 2022. Japanese mechanical engineering is characterized by the highest precision, quality and technological excellence. Japanese companies are leaders in areas such as robotics, automation technology, machine tools and precision instruments.
However, Japanese mechanical engineering also faces challenges. This includes the aging population, the shrinking internal market and the increasing competition from Asia, especially from China and South Korea. Japanese companies have to adapt and open up new growth fields, for example in the areas of renewable energies, medical technology and services.
Eastern Europe (non-EU countries): Emerging markets with potential
Some Eastern European countries outside the EU, such as Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine, are becoming increasingly important for mechanical engineering. These countries have concluded free trade agreements with the EU, which have led to the abolition of most tariffs and more efficient customs procedures. Machines and devices are particularly important export goods for Georgia and Moldova.
These countries offer potential as production locations and sales markets for European mechanical engineers. However, there are also risks and challenges, especially with regard to political stability, corruption and infrastructure. Ukraine is also severely affected by the consequences of the war, which significantly affects economic development and perspectives for mechanical engineering.
Global relocation and growing competition intensity
In summary, it can be stated that mechanical engineering outside the EU is characterized by increasing dynamics and global shift in the balance of power. Asia in particular and especially China have become more important in recent decades and have become important competitors for European and Western machine builders. While traditional markets such as the USA and Japan remain important, the weights are increasingly moving towards the emerging economies.
This development poses great challenges for global mechanical engineering. The competition becomes more intensive, technological requirements are increasing, and geopolitical uncertainty increases. Companies must be flexible, innovative and internationally set up in order to be successful in this dynamic environment. The ability to adapt to changed market conditions, develop new technologies and manage global value chains will be crucial for future competitiveness in mechanical engineering.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus