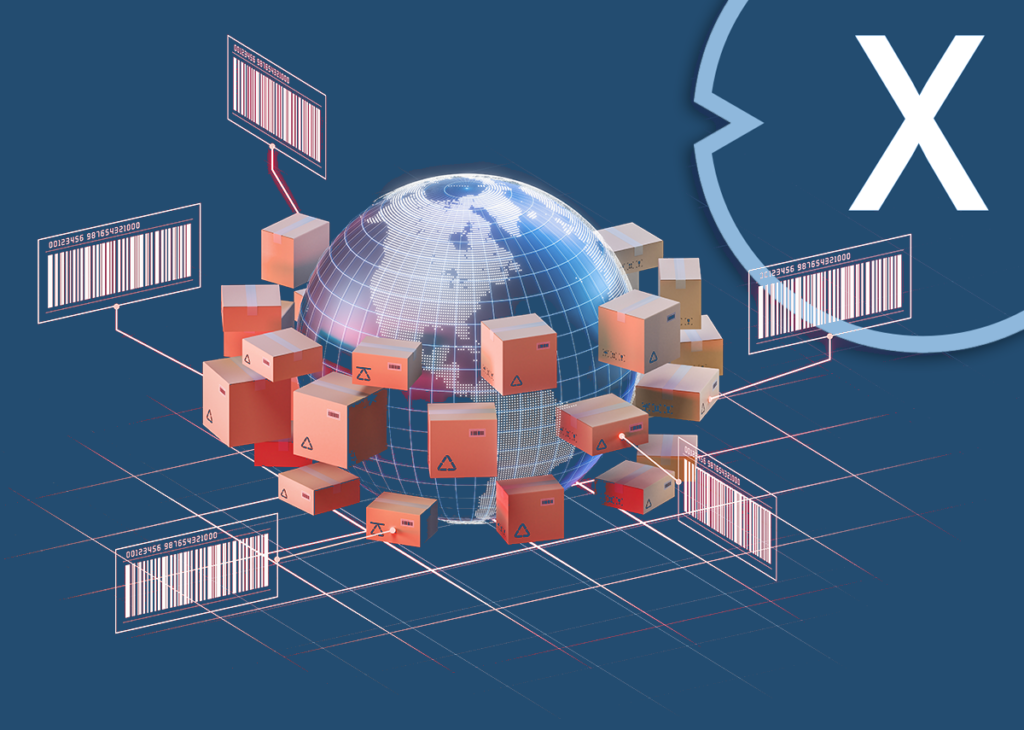
Sensor technology and industrial sensors convert to 2D matrix code: The conversion of sensors and scanners with parallel barcode/barcode support
Language selection 📢
Published on: June 22, 2023 / update from: June 22, 2023 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Converting to 2D matrix code: The conversion of sensors and scanners with parallel barcode/barcode support - Image: Xpert.Digital / Pavel Korsakov|Shutterstock.com
Conversion of sensors and scanners to 2D matrix code: A smooth transition with parallel barcode/barcode support
The ongoing development of technology will lead to the switch to 2D matrix codes in 2027, which offers significant advantages compared to traditional barcodes/barcodes. However, moving to 2D matrix code requires adapting sensors and scanners that are widely used in various industries and applications. Here we consider the challenges and opportunities of converting sensors and scanners to 2D matrix code, taking into account a transition period in which both options exist in parallel.
The need for 2D matrix code
The 2D matrix code offers higher data storage capacity and flexibility compared to the traditional barcode/barcode. It allows the encoding of alphanumeric characters, symbols, images and even small logos. In addition, the 2D matrix code can also contain error correction mechanisms to repair corrupted codes. These advantages make it ideal for complex applications such as logistics, inventory management, product tracking and document management.
Challenges in retrofitting
Converting sensors and scanners to the 2D matrix code presents some challenges as the existing infrastructure and applications are designed for the traditional barcode/barcode.
Some of the challenges are:
a) Hardware compatibility
Sensors and scanners designed to capture barcodes/barcodes may not be able to automatically read the 2D matrix code. Hardware may need to be updated or replaced to meet new requirements.
b) Software integration
Existing software designed to process barcode data may need to be customized to recognize and process the 2D matrix codes. Interfaces also need to be developed to exchange data between the sensors/scanners and the applications.
c) Training and acceptance
Users familiar with the traditional barcode/barcode may require training to correctly capture and interpret the 2D matrix code. Acceptance of new technologies can be challenging and may require gradual adoption and user training.
Transition period and bilateral options
To enable a smooth transition, a transition period is required during which both traditional barcode/barcode and 2D matrix code are supported. During this transition period, companies can use both options in parallel to ensure a smooth
to ensure a transitional solution. This can be achieved by:
a) Compatibility
New sensors and scanners should be able to read both the traditional barcode/barcode and the 2D matrix code. This allows companies to continue using their existing applications and infrastructure while gradually transitioning to 2D matrix code.
b) Training and awareness raising
Extensive user training is required to familiarize them with the new 2D matrix code. Companies should offer training programs to promote acceptance and understanding of the new technology.
c) Gradual implementation
Companies can plan a phased implementation of 2D matrix code, starting with selected applications or areas. This enables gradual adaptation of the infrastructure and minimizes possible disruptions to operations.
➡️ Converting sensors and scanners to 2D matrix code opens up new possibilities and increases in efficiency in various industries. However, a smooth transition requires careful planning, consideration of hardware and software requirements, and user training and awareness. Establishing a transition period to support both traditional barcode/barcode and 2D matrix code allows companies to migrate seamlessly and phase in the new technology.
The introduction of the barcode in 1973 revolutionized global logistics
The barcode has revolutionized global logistics in several ways:
Improved inventory management
By using barcodes, companies can manage their inventory more effectively. Each product is tagged with a unique barcode that can be scanned to automatically update inventory. This enables faster and more accurate inventory taking and reduces the risk of overstocking or understocking.
More efficient distribution of goods
Barcodes help to speed up the flow of goods and reduce the error rate. When each product is barcoded, shipping labels can be printed quickly and easily, speeding up the processing of orders and reducing the risk of shipping errors.
Improved traceability
Barcodes allow companies to track the whereabouts of products in the supply chain, from production to sale. This is particularly important when tracking products in the event of recalls or product quality issues.
Automation of business processes
The use of barcodes has helped automate business processes by reducing manual data entry and enabling the use of automated scanners and readers. This has led to greater efficiency and productivity in the logistics industry.
Overall, the barcode has revolutionized the logistics industry by enabling faster, more efficient and more precise processing of goods. Technology has helped increase productivity and reduce costs, which in turn has led to higher customer satisfaction and business competitiveness.
Our Industrial Metaverse configurator
Just try out our universally applicable (B2B/Business/Industrial) Metaverse configurator for all CAD / 3D demo options:
Xpert (B2B/Business/Industrial) Metaverse configurator for all CAD / 3D data can be used on all devices, one platform!
Suitable for:
Conversion of sensors and scanners to the 2D matrix code
Converting sensors and scanners to 2D matrix code requires careful planning to ensure a smooth transition. During the conversion process, it is important to offer parallel support for the traditional barcode/barcode to ensure seamless integration and continuous operation. Here are some steps to consider during the transition:
Analysis and evaluation of requirements
- Examine the current sensors and scanners in your system and evaluate their compatibility with the 2D matrix code.
- Analyze your applications and processes to determine where 2D matrix code can provide benefits.
- Identify critical areas or applications that require immediate conversion and plan appropriate actions.
Hardware upgrade or replacement
- Determine whether your existing sensors and scanners are suitable for capturing the 2D matrix code.
- If not, plan to upgrade or replace hardware to ensure required functionality.
- Also take into account the possibility that some sensors or scanners can read both the 2D matrix code and the traditional barcode/barcode.
Software adjustments
- Check your software solutions and make sure they support 2D matrix code.
- If necessary, perform necessary customizations or integrations to enable reading and processing of the 2D matrix code.
- Ensure that both types of code can be supported during the transition period to ensure continued functionality.
Training and user acceptance
- Schedule user training to familiarize them with the new 2D matrix code.
- Raise staff awareness of the benefits of 2D matrix code and the need for a smooth transition.
- Ensure that sufficient support and assistance is available to users during the transition period.
Transition period and parallel operation
- Determine a transition period during which both 2D matrix code and traditional barcode/barcode are supported.
- Communicate this transition period both internally and externally to include customers and partners.
- Establish clear guidelines on which applications or areas should use which code.
Monitoring and optimization
- Track the performance of upgraded sensors and scanners as well as user acceptance.
- Analyze feedback and resolve any issues or bottlenecks that arise.
- Continuously optimize systems and processes,
The error intensity of a 2D matrix code or QR code compared to a 1D barcode or barcode
How is the error intensity of a 2D matrix code or QR code compared to a 1D barcode or barcode?
The error intensity of a 2D matrix code or QR code can be considered higher compared to a 1D barcode or barcode. This is mainly because 2D matrix codes have greater data capacity and can encode complex information, while 1D barcodes are typically limited to numeric or alphanumeric characters.
Because 2D matrix codes can contain more information, there is also the possibility of errors occurring during their creation or printing. These errors can make the code more difficult or impossible for readers to read. For example, if a square in the QR code is damaged or dirty, it may affect decoding.
In contrast, 1D barcodes are typically less prone to errors because they have less complex structures. They consist of a series of parallel bars and spaces that are easier to print and read. However, if a 1D barcode is damaged or dirty, it can also cause problems with readability.
In order to minimize the error intensity of 2D matrix codes or QR codes, error correction mechanisms are usually used. These mechanisms allow the reader to recognize and reconstruct the code despite some corruption or errors. Error correction features vary depending on the QR code type and encoding level, providing varying levels of error detection and correction.
However, it is important to note that the error intensity for both 1D barcodes and 2D matrix codes depends on various factors, such as the quality of the print, the reader technology and the environmental conditions. Careful creation, verification and use of appropriate readers can help minimize error intensity for both types of code.
Is barcode and barcode the same thing?
Yes, “Strich code” and “barcode” are often used as synonyms and generally relate to the same concept. They refer to a graphical representation of data in the form of vertical lines and spaces that are attached to products, labels or packaging.
The term “line code” is often used in the German -speaking world, while “barcode” is rather internationally used. Both terms relate to the same principle: the lines and spaces represent a specific number or letter sequence that can be recorded and deciphered by scanners or reading devices.
There are different types of barcodes, such as the EAN code (European Article Number), the UPC code (Universal Product Code) or the QR code (Quick Response Code). Each of these codes has specific characteristics and areas of application, but all are based on the basic principle of the barcode system.
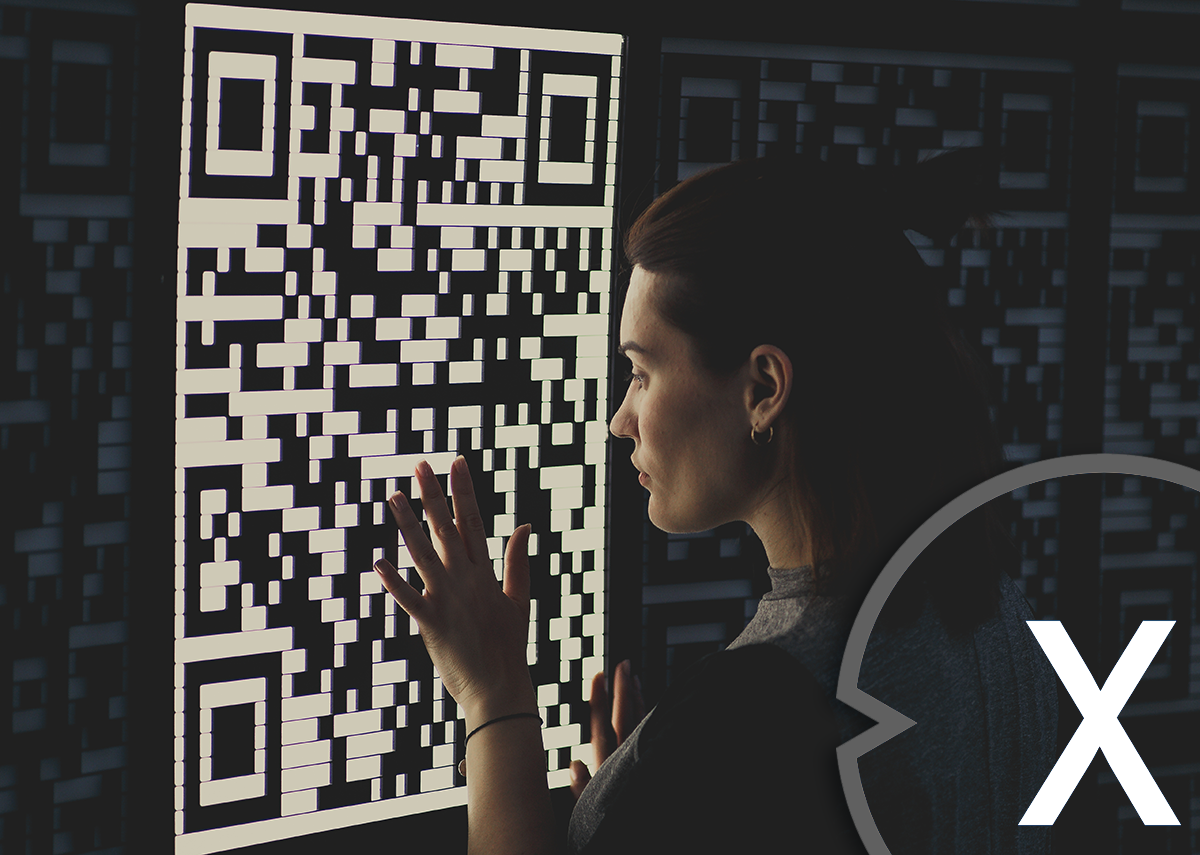
Is the well-known QR code a 2D version?
Because we are often asked: Yes, the QR code is a 2D variant of a barcode. The term “QR” stands for “Quick Response”, which indicates the quick recording and decoding of the code. In contrast to the conventional barcode, which only uses horizontal lines and spaces, a QR code consists of a matrix made of black squares on a white background. This matrix enables a larger data storage capacity compared to one -dimensional barcode.
The QR code can encode various types of data including text, URLs, contact details, WiFi credentials and more. By using a two-dimensional structure, QR codes can store a greater amount of information and are able to read data faster and more accurately, even if the code is partially damaged or dirty. QR codes are now used in a variety of applications including advertising, marketing, product tracking, mobile payments and digital tickets.
The data matrix code replaces the barcode
More about it here:
How the 2D matrix code will change global world logistics
The 2D matrix code has the potential to change global world logistics in many ways.
Increased efficiency
The 2D matrix code allows a greater amount of information to be encoded, including item numbers, batch numbers, expiration dates, production locations and much more. With more detailed coding, logistics companies can improve information flow, reduce errors and increase efficiency in the supply chain.
Real-time tracking and monitoring
With the 2D matrix code, individual products or shipments can be clearly identified and tracked. This enables improved monitoring of the supply chain, from production through transportation to delivery to the end customer. Companies can track the location, condition and progress of shipments in real time, resulting in greater transparency and effectiveness.
Inventory management and warehousing
The 2D matrix code facilitates more accurate and efficient inventory management. Companies can track inventory more accurately, identify products more quickly, and optimize inventory levels. This leads to better inventory management, fewer losses and more efficient use of storage space.
Traceability and product safety
The detailed coding in the 2D matrix code improves the traceability of products. In the event of recalls or quality problems, companies can quickly and precisely identify affected batches and take targeted action. This improves product safety and protects consumers from potentially dangerous or defective products.
Fraud detection and counterfeit protection
The 2D matrix code can serve as a security feature to verify the authenticity of products and detect counterfeits. Companies can implement authentication methods where the code is scanned and verified to ensure that the product is original and not counterfeit. This helps combat counterfeit products and protect trademark rights.
Integration of IoT and Big Data
The 2D matrix code can serve as a connector to connect physical products to the Internet of Things (IoT). By scanning the code, information about the condition of the product, environmental conditions or other relevant data can be collected. This data can be used for analysis and optimization of processes to make informed business decisions.
➡️ The 2D matrix code will significantly improve efficiency, transparency, traceability and security in global world logistics. It enables precise tracking of products along the entire supply chain, from manufacturing to delivery to the end user. By scanning the 2D matrix code, information such as production data, delivery data, inventory levels and transportation details can be captured and updated in real time.
Improved efficiency comes from automated data collection and processing, replacing time-consuming manual processes. This enables faster processing of orders, improved planning of transport routes and better coordination of logistics activities. Companies can identify bottlenecks and bottlenecks and take timely action to avoid delays and shorten delivery times.
Transparency along the supply chain is significantly improved by the 2D matrix code. All stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, logistics companies and consumers, can track the current location and status of products at any time. This enables better communication and collaboration between the different actors and reduces misunderstandings and information gaps.
Traceability of products is also facilitated by the 2D matrix code. In the event of quality issues, recalls or product safety concerns, companies can quickly and accurately identify the affected products and take appropriate action. This contributes to consumer safety and increases trust in the products and brands.
In addition, the 2D matrix code improves security in global world logistics. By integrating security features and encryption technologies into the code, companies can combat counterfeiting, piracy and other illegal activities more effectively. The code enables quick verification of the authenticity of products and thus protects consumers from counterfeit or inferior goods.
The benefits of 2D matrix code in global world logistics are available to both companies and consumers alike. Companies can optimize their supply chains, reduce costs and increase customer satisfaction. Consumers benefit from better product transparency, higher product safety and an improved shopping experience.
Overall, 2D matrix code is a powerful tool that can revolutionize the logistics industry. With its wide applicability and numerous advantages, it will contribute to more efficient, transparent and secure global world logistics.
How logistics and end users can use the 2D matrix code equally
The 2D matrix code offers a variety of usage options for both the logistics industry and end users. Here are some ways both logistics companies and end users can use the 2D matrix code:
For logistics companies
Product tracking and monitoring
Logistics companies can use 2D matrix code to track shipments and products throughout the supply chain. By scanning the code, they can monitor the location, condition and progress of shipments in real time.
Inventory management
The 2D matrix code allows for more precise inventory management. Logistics companies can scan the code to quickly and accurately record inventory, optimize inventory processes and avoid shortages or overstocks.
Efficient traceability
In the event of recalls or quality problems, logistics companies can use the 2D matrix code to quickly identify affected batches and take targeted action. This facilitates product traceability and improves product safety.
Anti-counterfeiting and authentication
The 2D matrix code allows logistics companies to check the authenticity of products and detect counterfeits. You can implement authentication methods where the code is scanned and verified to ensure that the product is original and not counterfeit.
For end users
Product Information: End users can scan the 2D matrix code to retrieve detailed product information, including origin, ingredients, instructions, expiration dates and more. This allows them to make informed purchasing decisions and obtain additional information about the product.
Product authentication
The 2D matrix code can help end users verify the authenticity of products and detect counterfeits. By scanning the code, they can confirm that the product is original and not counterfeit, increasing consumer confidence.
Interactive content and offers
Through the 2D matrix code, end users can access interactive content and special offers. Companies can use the code to link to websites, videos, promotions or other digital content that provide value to end consumers.
More about it here:
Fast payments and transactions
The 2D matrix code can also be used for mobile payments. End users can scan the code to capture payment information and complete transactions quickly and conveniently.
➡️ By using 2D matrix code, both logistics companies and end consumers can benefit from improved efficiency, transparency and security in the supply chain.
2D matrix code can be used for WebAR or WebXR (3D product presentation in augmented reality)!
The 1D barcode successor 2D matrix code is WebAR-compatible or WebXR-capable and therefore suitable for the e-commerce metaverse and also for the business metaverse with the XR technology from extended, augmented, mixed and virtual reality as well as virtual showrooms.
More about it here:

Consulting, planning and implementation of 2D matrix codes with integrated augmented reality and WebAR
Xpert.Plus is a project from Xpert.Digital. We have many years of experience in supporting and advising on (Extended) Augmented Reality and in warehouse optimization , which we bundle in a large network under Xpert.Plus .
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus