Analysis | A profound cut in established trade patterns: 25% tariffs on auto imports in the USA
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: March 27, 2025 / update from: March 27, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

A profound cut in established trade patterns: 25% tariffs on auto imports in the USA - Image: Xpert.digital
Commercial war escalated: 25% tariffs on auto imports to the USA
Economy under pressure: New car tariffs meet manufacturers and consumers alike
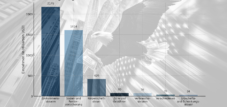
The introduction of 25% tariffs to auto imports to the USA becomes a reality and represents a profound cut into established trade patterns. In view of the considerable number of vehicles that are imported to the United States every year, this measure has extensive consequences. The global automotive industry is characterized by complex and cross -border supply chains, which means that the effects of these tariffs are not limited to foreign manufacturers, but also affect American companies, suppliers and ultimately the consumers.
Suitable for:
- 25% US criminal duties on all cars-the failure of politics, companies and consultants-misjudgments and dependencies
The motives behind the American auto import duties
Explained political and economic goals
President Trump argues that the introduction of 25% tariffs on auto imports aim to promote domestic production and to boost economic growth. The expectation is that these tariffs persuade both American and foreign automobile manufacturers to shift their production facilities to the United States. In addition, the government expects these tariffs to generate significant income that is estimated at around $ 100 billion a year with the potential goal of reducing public debt.
It can be seen that the primary goal of this policy is a protectorist nature, with the declared wish to shift production to the United States. The generation of tax revenue seems to be a secondary, albeit significant aspect. The support from unions and domestic production groups indicates a domestic dimension of this measure.
Historical context and earlier cases of trade inspectionism in the US automotive sector
It is not the first time that the United States use tariffs as a trading policy instrument, which indicates a recurring pattern of protectionism, especially in sectors that are considered strategically important or competitive. The customs duties introduced in 2018 on steel and aluminum imports serve as a precedent for this type of trade measure. The current proposal is based on an investigation by the Ministry of Commerce from 2019, which leads national security concerns. The appeal to national security offers a legal basis for tariffs that go beyond purely economic reasons.
Evaluation of arguments for and against tariffs based on economic principles and industry data
It is argued that tariffs could lead to increased domestic investments in the long term and increased production. However, there are also important counter-arguments, such as the potential for higher car prices for consumers, possibly up to $ 12,500 per imported vehicle, which could lead to general inflation. There is also concern that US automobile manufacturers are heavily dependent on global supply chains for components, so that tariffs would also increase their costs to imported parts. In addition, there could be a lower selection of new cars on the market. Analyzes indicate that tariffs could negatively influence the operational profit margins of the automobile manufacturers. The view is also believed that tariffs may not significantly reduce inflation and that the supply chains could even make it more susceptible.
The economic arguments for and against tariffs are therefore very controversial. While supporters emphasize domestic advantages, opponents emphasize the costs for consumers and the disorder of established supply chains. The global networking of the automotive industry makes unilateral tariffs a complex matter with potential unintentional consequences.
Settings and wrong decisions that lead to the current situation
Evaluation of the role and potential deficiencies of political decision -making in trade policy
Political motivations, such as the promise of elections and the desire to reduce the budget deficit and claim economic dominance, could have influenced the decision to consider tariffs. It is discussed whether the complexity of global supply chains and the potential for retaliation measures by trading partners are sufficiently taken into account. The back and forth in customs threats and reactions indicate instability in politics. It is also argued that broad tariffs do not effectively contribute to the remediation of commercial preservation weights.
Political considerations seem to be an essential driver of this policy, possibly at the expense of a thorough economic analysis and taking into account international relationships. The unpredictability of trade policy can create uncertainty for companies and hinder long -term planning.
Analysis of the strategic reactions and potential missteps of automotive companies
Although automobile manufacturers have global production networks, they have underestimated the probability or effects of such comprehensive tariffs. The initial rejection of the automobile manufacturers and the temporary suspension of some tariffs indicate their awareness of the negative consequences. The question arises whether the industry would not have diversified supply chains more proactive or previously invested more in domestic production in order to reduce this risk. The American Automotive Policy Council expresses concerns about avoiding price increases for consumers and the preservation of the integrated North American automotive sector.
Although automobile manufacturers are active worldwide, their dependence on established supply chains, especially in North America, makes susceptible to these tariffs. A proactive approach to diversify the supply chains and domestic investments might have reduced the potential effects.
Evaluation of the findings and possible blind spots of management consultants and industry analysts
Analysts play a role in predicting potential price increases and negative effects on profit margins. The question arises whether analysts have adequately emphasized the potential for such significant and broad -based tariffs in their previous reports and recommendations. The analysis of consulting companies such as the Anderson Economic Group on potential price increases and from Ducker Carlisle on the long -term versus short -term effects is known. It is to be considered whether the focus may be more on the optimization of global supply chains for cost efficiency than on resistance to protectionist measures.
Although analysts give an insight into the potential consequences of tariffs, a general underestimation of the likelihood and the extent of such a policy could have existed. The predominant focus on globalization and cost optimization could have overshadowed the risks of increasing protectionism.
Suitable for:
The reinforcing effect of global supply chain fuses
Analysis of how events such as the incident of the Ever Given illustrate the fragility of global logistics
The beaching of the container ship Ever Given in the Suez Canal and the resulting blockade of global trade dramatically illustrate the susceptibility of global logistics. The incident leads to considerable economic losses, which are estimated at several billion US dollars a day. It causes delays, traffic jams and increased shipping costs. This event shows the dependence of many industries on just-in-time supply chains and the susceptibility of important transport routes.
The incident of the Ever Given serves as a clear memory of the inherent risks of complex, geographically distributed global supply chains. A single fusiness point can have cascading and significant economic consequences. This susceptibility probably strengthens the argument for more localized or regionalized production.
Discussion of the interaction between supply chain risks and the reason for import tariffs
The susceptibility emphasized by events such as the incident of the Ever Given could strengthen the political justification for tariffs as a means of promoting domestic production and reducing the dependency on potentially unstable international supply chains. It is argued that political decision -makers see tariffs as an instrument to strengthen national economic security by reducing the dependence on foreign sources for critical goods such as automobiles. However, it should also be pointed out that tariffs interfere with existing supply chains and create new vulnerabilities.
While vulnerability in the supply chains in the eyes of some political decision -makers are a justification for tariffs, the introduction of tariffs itself can be a significant disruption of the supply chains. There is a potential compromise between reducing the dependency on international risks and creating new domestic and regional challenges in the supply chains.
Strategies for avoiding and bypassing American auto importing
Detailed analysis of "Customs bypass by wearing out the origin" (Circumvention), including "Avoiding tariffs through general cargo production" and "production splitting":
"Customs bypass by wearing out the origin" (Circumvention) refers to the veiling of the actual origin of goods in order to avoid tariffs. "Collective Avoid through general cargo production" (TARRIFT AVOAGHOGH Component Production) describes the strategy of producing components in a country with low tariffs and then assembling them in the target country (USA) in order to reduce the total load by customs duties. "Production splitting" (Production Splitting) includes the distribution of the manufacturing process to several countries in order to benefit from different customs sets or original rules.
Evaluation of the feasibility and effects of component production outside the USA and final assembly within:
Car manufacturers could consider to shift component production to countries with lower tariffs or free trade agreements with the United States (provided that they remain unaffected) and then mount the vehicles in the USA in order to reduce customs to the end product. However, it is crucial to observe the rules of the "substantial transformation" when determining the country of origin. The mere assembly of components may not be enough to change the origin and to avoid tariffs to the value of the components. It should be noted that the tariffs could apply to both finished cars and parts. The complexity of the determination of the content level for USMCA exceptions, in which tariffs may continue to apply to non-US-American content, is also relevant.
It should be borne in mind that the relocation of assembly alone may not change the place of origin and could lead to punishment as an illegal overload when classified. Although component production outside the USA and final assembly is within a potential strategy, it depends heavily on complex rules of origin and the specific details of the customs introduction. It may not offer complete avoidance of tariffs, especially if tariffs are also raised to imported parts. The risk of being classified as an illegal overload is also a significant problem.
Nearshoring as a strategic alternative
Investigation of the potential of nearshoring production to countries within the USMCA region (e.g. Mexico, Canada): Nearhoring refers to the shift of production facilities closer to the main sales market, typically within the same continent. Mexico proves to be a potentially attractive nearshoring destination due to lower labor costs, shorter supply chains and advantageous free trade agreements (USMCA). Canada represents another nearshoring option within the USMCA. The USMCA offers potentially simplified customs procedures and reduced trade barriers.
A trend can be observed that companies are considering nearshoring in order to react to rising tariffs and reduce the dependency on Chinese production. Nearshoring, especially according to Mexico, appears as a practical strategy for automotive companies in order to mitigate the effects of US tariffs, especially for production that is intended for the US market. The USMCA offers a framework for potentially customary trading within the region.
Analysis of the advantages and challenges of nearshoring for automobile manufacturers in the face of US tariffs:
Advantages: Potential reduction or elimination of tariffs to vehicles and parts that are produced within the USMCA region, depending on the rules of origin. Lower transport costs and shorter lead times compared to offshore production. Increased resistance of the supply chain and better control over quality and intellectual property. Proximity to the US market for a faster reaction to changes in demand.
Challenges: Potential costs in connection with the relocation or building up new production facilities. Possible differences in labor costs and the regulatory framework compared to other offshore locations. The need to build local suppliers and infrastructure in the nearshoring locations. Uncertainty regarding the long -term stability of customs policy, since tariffs may also be raised to imports from Mexico and Canada. Potential for increased costs of components related from the USMCA region if demand is increasing due to nearshoring.
Nearshoring offers significant advantages to reduce tariffs, but also harbors challenges in connection with implementation costs, development of the supply chain and the uncertainty of future trade policy within the USMCA region. Companies have to carefully weigh these factors.
Our recommendation: 🌍 Limitless reach 🔗 Networked 🌐 Multilingual 💪 Strong sales: 💡 Authentic with strategy 🚀 Innovation meets 🧠 Intuition
At a time when a company's digital presence determines its success, the challenge is how to make this presence authentic, individual and far-reaching. Xpert.Digital offers an innovative solution that positions itself as an intersection between an industry hub, a blog and a brand ambassador. It combines the advantages of communication and sales channels in a single platform and enables publication in 18 different languages. The cooperation with partner portals and the possibility of publishing articles on Google News and a press distribution list with around 8,000 journalists and readers maximize the reach and visibility of the content. This represents an essential factor in external sales & marketing (SMarketing).
More about it here:
Mastering trade uncertainties - effective warehouse strategies: buffer stocks in response to demand for demand
The role of buffer stocks in reducing customs and supply chain risks:
Explanation of how strategic buffer stocks can help to cushion the effects of tariffs and disorders
Buffer stocks, also known as security stocks or emergency stocks, are additional inventories that are kept in order to cope with unexpected increase in demand or delivery interruptions. The presence of buffer stocks can help companies continue to satisfy customer demand despite potential delays or increased costs in connection with tariffs. Companies could consider increasing stocks before tariffs come into force to avoid immediate price increases.
Buffer stocks play a role in protecting companies from fluctuations in demand and supply chain interruptions, including those caused by tariffs or retaliation. Buffer stocks can offer a temporary buffer against the immediate effects of tariffs, such as: B. price increases and potential disorders of the supply chain. They offer a certain degree of resistance in an uncertain trade environment.
Discussion of the optimal buffer inventory management in the context of potential trade barriers
Effective use of buffer stocks requires careful planning and administration, taking into account the accuracy of forecasts, lead times, storage costs and the potential for dynamic adjustments. The lead times for the replacement of inventory must be taken into account, especially if tariffs influence the import processes. The frequency of refilling and plans for the inventory filling are important. The costs associated with the warehousing of buffer stocks, such as B. Storage and potential outdoor age must also be taken into account.
Dynamic buffer management techniques that adapt the inventory on the basis of real -time data and market conditions could be considered. Technology and artificial intelligence can play a crucial role in optimizing buffer stock strategies in the face of trade uncertainty. Effective use of buffer stocks requires careful planning and administration, taking into account the forecast accuracy, lead times, storage costs and the potential for dynamic adjustments. Technology can play a crucial role in optimizing buffer stock strategies in the face of trade uncertainties.
Suitable for:
- Supply chain optimization: New logistics strategies due to the corona pandemic, including with digital twins
Further strategic reactions for automotive companies:
Investigation of options such as diversification of export markets: Automobile companies that depend heavily on the US market could consider diversifying their export objectives in order to reduce their susceptibility to changes in US trade policy. This could include concentration on markets in Europe, Asia or other regions with more stable trade relationships. The diversification of the export markets can reduce the dependency of a company on a single market and reduce the risks associated with protectionist measures in a specific country.
Adaptation of the price strategies
Car manufacturers can adapt their price strategies to absorb part of the customs costs or pass them on to consumers, depending on the market conditions and competitive pressure. The potential effects of price increases on sales volumes and market shares must be taken into account. The pricing is a crucial instrument for coping with the effects of tariffs. Companies must carefully analyze the price elasticity of demand and the competitive environment in order to determine the optimal price strategy.
Investments in domestic US production
Foreign automobile manufacturers could invest in the construction or expansion of production facilities within the United States to avoid import duties. Hyundai's project to build a steel mill in Louisiana is an example of this. However, this is a long -term strategy that requires significant investments and time for implementation. Investments in domestic US production are a direct way to bypass import tariffs, but require considerable capital funds and long-term commitment to the US market.
Custom design and HTS reclassification
The strategy of modification of products or their classification according to the harmonized system (HS) can be used to achieve lower customs sets. This could include the import of components, among other things, under other classifications or minor changes to the product in order to change its customs tariff number. Customs design can be a technical but potentially effective means of reducing customs pollution that requires specialist knowledge in customs law and in product classification.
Use of free trade zones and foreign trade zones (FTZS)
The use of FTZS in the United States offers the option of storing imported goods without paying tariffs until it uses or entered the domestic market. This can contribute to improving the cash flow and possibly reducing or eliminating tariffs to reproduced goods, or if sufficient US content has been added within the zone. FTZS offer a way to postpone customs payments or possibly reduce and thus create flexibility in the administration of imported goods.
Potential countermeasures of the EU and other non-I-US countries
Analysis of the types of retaliation measures that could be taken
The EU reacts to former US tariffs to steel and aluminum by introducing exposed countermeasures and considering new tariffs on US goods. The products that could be affected include agricultural products, industrial products and consumer goods. The threat of the EU with a 50%customs on US spirits and Trump's reaction with a potential 200%customs in customs on EU alcoholic indicates the risk of escalating trade disputes. Canada has also raised retaliation duties on US goods in the past. Other large car export countries such as Japan and South Korea could also take countermeasures. The concept of "reciprocal tariffs", in which countries reflect the customs sets raised by the USA, is also discussed.
The potential for retaliation measures of important trading partners such as the EU and Canada is considerable and can lead to a broader trade war that affects several sectors beyond the automotive industry.
Assessment of the potential effects of these countermeasures on the US and the global economy
Remandes of retaliation can make US exports in foreign markets more expensive, which may damage US industries and leads to job losses. The example of American agricultural exports, which suffered from retaliation in the past, is relevant. The OECD reports that Trump's customs policy is expected to slow down economic growth in the United States and worldwide. There is a risk of increased prices for consumers in both the United States and in the countries that took retribution measures. It is warned of the danger that escalating retaliation measures could bring global trade to a standstill and impair economic growth.
Countermeasures would probably have negative effects on both the US and the global economy and would lead to reduced trade, higher prices and potentially slower economic growth.
Suitable for:
- Work-path logistics and efficient reusable management-the optimization of logistics processes and supply chains
Global effects on the automotive industry and international trade
Evaluation of the potential shifts in global production and commercial flows
The US tariffs could lead to a restructuring of the global automotive supply chains, whereby companies may shift production to avoid tariffs or to operate markets that are less affected. There is the possibility of increasing regionalization of production, with more vehicles and components being produced within large trading blocks (e.g. North America, Europe, Asia). Some Asian and European automobile manufacturers with a limited presence in the United States could achieve competitive advantages due to price differences.
The tariffs could trigger a significant redesign of the production and trade patterns of the global automotive industry and may lead to more regionalized supply chains and shifts of the competitive advantages.
Analysis of the effects on consumer prices and market competition
It is likely that American consumers have to bear a significant part of the costs of these tariffs in the form of higher prices, especially for imported vehicles. The competition on the US market will decrease when tariffs imported vehicles significantly more expensive. The effects on the market share of domestic versus imported vehicles must be taken into account.
Consideration of the long -term effects on the structure of the global automotive industry:
It should be speculated whether these tariffs could lead to a more fragmented global automotive industry with less border -crossing integration. There is the possibility of increased investments in the production of electric vehicles within the USA in order to benefit from customs -related advantages for domestically produced electric vehicles. The uncertainty with regard to the long -term load -bearing capacity of such customs policies and the potential for future revisions or returns must be recognized.
The long -term effects on the global automotive industry are uncertain, but could include relocation to more regionalization, increased concentration on domestic production in important markets and potential investment shifts towards new technologies such as electric vehicles. The stability of this policy will be a key factor for the design of the future of the industry.
Global supply chains under pressure: strategies against new customs risks
The introduction of 25% tariffs to auto imports to the USA is driven by the declared goal of promoting domestic production and boosting economic growth. However, the analysis shows that this measure carries considerable risks, including higher prices for consumers, disorders of established supply chains and the risk of retaliation measures by international trading partners. The susceptibility of global supply chains, as the incident of the Ever Given illustrates, underlines the need for resistant production strategies.
Companies are available for various options to meet these potential tariffs, including Nearshoring, the adaptation of supply chains and price strategies as well as the use of free trade zones. However, it is crucial that political decision -makers carefully weigh up the extensive economic consequences and the potential effects on global trade relationships before taking such far -reaching measures.
recommendations
Policy makers
It is recommended to take into account the broader economic consequences and the potential for international retaliation measures before comprehensive tariffs are introduced. Targeted measures and negotiations should be checked as alternatives.
Automotive
It is advisable to develop flexible supply chain strategies, to examine nearshoring and domestic production options, to analyze the options for avoiding customs and diversify export markets.
Management consultants and analysts
It is important to submit comprehensive risk assessments that include the potential for significant protectorist trading policies, and to advise customers on the development of resistant supply chains.
The matter is complex and complex and requires a careful and strategic approach of everyone involved.