How augmented reality is revolutionizing the automotive industry
Language selection 📢
Published on: April 27, 2017 / update from: September 4, 2018 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
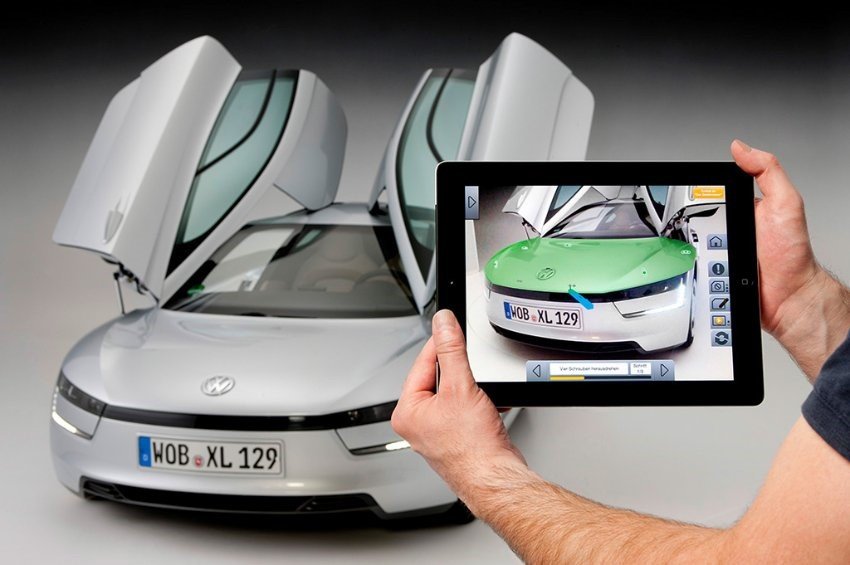
As part of a digitalized Industry 4.0, the automotive industry is also increasingly relying on augmented reality technologies. The reason for this is obvious, because the German automotive industry is one of the most progressive economic sectors in this country when it comes to digitalization. As in many industries, augmented reality is currently mainly used for marketing and sales purposes. AR has a large field of application, particularly in brand communication, as content can be presented extremely clearly with the help of interactive worlds of experience in order to create emotions among potential customers. The use begins with the virtual 3D representation of the desired vehicle using AR glasses and ends with a simulated test drive. In addition, the user is directly involved in the concept through the interaction. When presenting products, providers can therefore create completely new virtual car worlds and driving experiences. But beyond marketing, AR is also suitable for manufacturers for a variety of uses in the industrial sector.
Product development
In the case of design design, fashion position and choice of materials, AR offers multi -layered options: shapes, designs or colors can be clearly displayed and changed in any number without a new model to be manufactured by hand. At Mercedes Benz, engineers are thus supported in the visualization of their developments, for example by virtually “installing” different engine variants into an existing chassis. In this way you simulate how a planned aggregate fits into the engine compartment of the car. The designers save research and development costs and reduce the time required.
production
In production , the automotive industry also works with processes that are supported by augmented reality. Since last year, BMW, the technology for stud welding on test vehicles. Until then, this was done manually, which took several days per car. Now the employees equipped with data helmets and cameras are shown the respective welding points on the vehicles using AR visualization, which halves the time required. A challenge for broader use is markerless tracking, as the cars still have to be provided with markings in order to be able to be evaluated by the AR systems. What is possible with test cars still seems unrealistic for series production.
Kolbus, a manufacturer of tailor-made industrial products for the passenger car industry, among others, is also using augmented reality in manual production as part of a pilot project. There, the employee is shown his next work steps using displays positioned with millimeter precision. Incorrect production steps are identified and expensive waste is avoided.
In addition to production, augmented reality supports plant planning in the automotive industry because machines or buildings can be virtually displayed in real environments or material flows can be simulated using AR. All of this works regardless of location, at least in the planning phase, which is why expensive personnel and travel costs are saved when setting up a new plant in Brazil or China.
quality assurance
Another area of application in practice is quality assurance , because AR means can be used to analyze production processes and identify faulty production processes at an early stage. Problem solving can also be done with the help of AR by virtually illustrating the work steps required for improvement in the form of AR tutorials. The simplified solution works quickly and does not require the involvement of an expert, which is particularly useful for global car companies with their factories spread around the world.
Using AR, quality control can also be extended to incoming goods or supplier locations. Pre-products or externally produced parts can be clearly examined in real time without a team of experts having to be on site. This is particularly relevant since around two thirds of the costs resulting from quality defects can be traced back to supplier errors. The on-site check helps with the early detection of errors. Virtual checks reduce costs in the automotive industry, identify problems earlier and speed up repair work.
Vehicle service
Most of the regular maintenance of cars consists of routine steps. AR can create interactive instructions that represent and explain the upcoming work steps to the service technician. So he has all the relevant information at all times. the electroconzern Bosch developed a system exactly for the car maintenance: In the workshop, the mechanic focuses an AR camera on the engine of the vehicle in question, then the defective parts are marked on a monitor and displayed with the order number and installation references. All of this accelerates and specifies the vehicle maintenance and thus reduces costs for companies and customers.
outlook
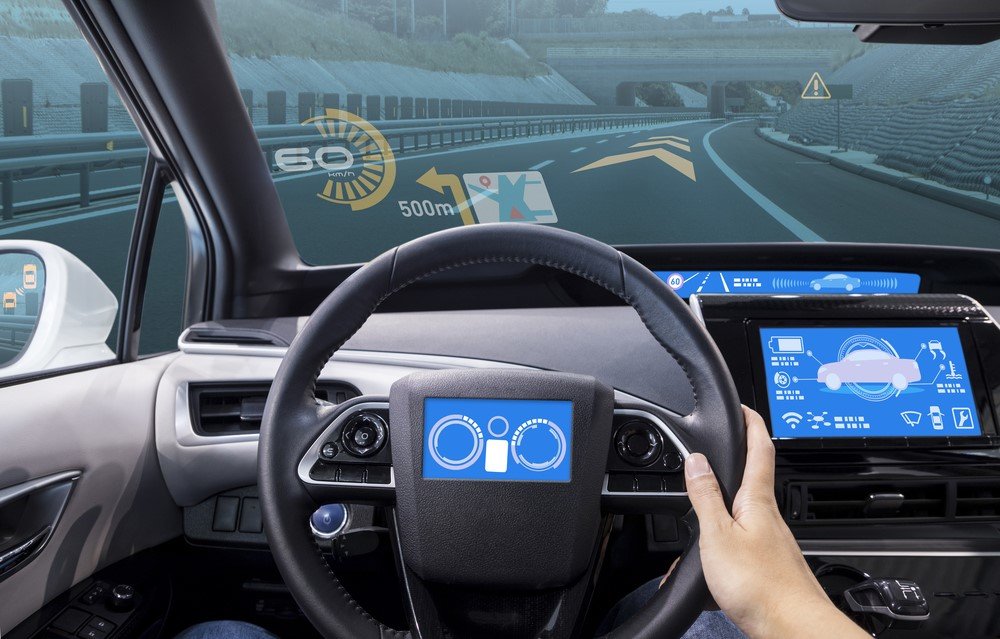
In addition to the application of augmented reality for the operating processes of automobile manufacturers, AR functions will also benefit customers in the near future, for example in the form of virtual cockpits. Many manufacturers drive the development of “smart” front discs through which the driver is supplied with information according to his individual preference. This includes data to the speed, as can already be found in vehicles more often. But navigation functions, warnings and settings for radio or telephone can also be displayed on the “virtual windscreen”. Great advantage: the information is integrated directly into the driver's field of vision, which means that he always keeps the road in view. The distraction from driving through not optimally placed ads is a thing of the past. In the future, a smart driving assistant could recognize the ideal line of the car and point out the driver by focal to it, or identify dangers through a camera system and warn before the driver sees them.