Germany's energy transition: More success than expected? Solar power and heat pumps drive renewable energies
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: March 10, 2025 / update from: March 10, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Germany's energy transition: More success than expected? Solar power and heat pumps drive renewable energies - picture: Xpert.digital
Germany's path to CO₂ reduction: progress in solar and heat pumps
Climate goals in view: The role of solar energy and heat pumps in Germany
In the course of the energy transition, a remarkable change in Germany has changed in recent years, which not only changes energy generation, but also the entire energy sector. The expansion of solar power and heat pumps in particular play a central role in this, because they make a significant contribution to replacing fossil fuels and significantly reducing CO₂ emissions. The following text illuminates the current developments, the success and challenges of the expansion of renewable energies in Germany and complements the original report with further, interesting aspects that provide a comprehensive overview of the topic.
Suitable for:
Renewable energies: a success story on the move
In 2024, the proportion of renewable energies in total energy consumption - i.e. in the areas of electricity, heat and traffic - rose to 22.4 percent. In the previous year, this value was 21.6 percent, which documents continuous progress. A dynamic development is particularly evident in the production of green electricity, which is reflected in ever higher production figures. However, this positive tendency is not only the result of state funding programs, but also a constant innovative strength in the energy industry. It is technologies such as wind power, photovoltaics and heat pumps that enable a balanced energy mix in cooperation and at the same time pave the way into a more sustainable future.
Renewable electricity as the engine of the energy transition
The electricity sector is the heart of the energy transition in Germany. In 2024, a record amount of 284 terawatt hours (TWH) was generated in renewable electricity, which corresponds to an increase of around three percent compared to 2023. If the moderately increasing power consumption (+1 percent), the proportion of renewable energies in gross current consumption also increased to 54.4 percent. This impressive development illustrates that the expansion of renewable energies not only progresses, but already contributes significantly to covering the national electricity requirements.
An essential success factor in this area is the wind energy that delivers the lion's share of the green electricity on land and at sea. With around 138.9 TWH, it represents the most important building block of the German electricity mix. Despite average weather conditions, which led to a slight decline in wind power generation by two percent, this technology was able to assert its leading position. Wind energy systems benefit from high availability and constant technological improvements, which makes it a reliable and cost -efficient energy source.
At the same time, photovoltaics also record a strong extension. Thanks to strong investments and a significant increase in the installed capacity-the PV system park has been expanded by around 20 percent within the past 12 months-the installed total output reached almost 100 gigawatts (GW) at the end of 2024. The resulting solar power generation rose by 16 percent to 74.1 TWh. The continuous expansion of the photovoltaic systems not only contributes to decentralized electricity generation, but also strengthens regional economic growth because many projects are realized on site.
In addition to wind and sun, other renewable sources such as hydropower could also make a contribution. An above -average rainy year led to an increase in hydropower production by twelve percent, which is reflected in a power generation of 22.2 TWH. However, there are regional differences here: While the potential is optimally exploited in areas with high rainfall and mountainous terrain, expansion potential remain unused in other regions. Biomass and geothermal energy play a rather subordinate role in comparison. The generation of electricity from biomass fell by about two percent to 48.6 TWh, and geothermal electricity production was still at a low level of 0.2 TWh.
These underline the fact that the expansion of photovoltaics and the increase in efficiency in wind energy are on the right track, but at the same time further measures are necessary to achieve the ambitious goals of the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG) and the European Renewable Energy Directive (Red). A balanced mix of all renewable energy sources is of central importance in order to operate the increasing need for electrification in the areas of heat and traffic.
Suitable for:
Renewable warmth: biomass, heat pumps and solar thermal energy
In the heat sector, the biomass continues to dominate as the primary renewable heat source. With a share of 81 percent, which corresponds to a produced heat of 159.1 TWH, it is undisputed the most important technology. Biomass systems that use wood, agricultural waste or other organic materials offer flexible and reliable way to create heat. At the same time, environmental friendliness is guaranteed by the sustainable management of the raw material sources.
Another significant progress in the heat sector is the increasing use of heat pumps. This technology uses the geothermal energy stored in the environment to efficiently heat buildings. In 2024, the usable amount of heat increased from geothermal energy and environmental heat by 14.2 percent. This is particularly due to the rapidly growing sales of heat pumps in the past two years. Heat pumps are not only energy -efficient, but also flexible - both in the new building and in retrofitting older buildings. Due to their high efficiency, they contribute significantly to the reduction of primary energy consumption and to reduce CO₂ emissions.
Solar thermal energy also contributes to renewable heat supply. At 8.8 TWh, it contributed around 4.5 percent to the total renewable warmth. However, the amount of heat generated by solar thermal systems decreases slightly, since older systems increasingly reach their end of life and have to be replaced by newer, more efficient technologies. The development shows that it is important to continuously invest in the modernization of the systems in order to secure stable and reliable heat sources in the long term.
Overall, the renewable amount of heat produced increased by almost two percent to 197.2 TWh compared to the previous year, while the total heat requirement also increases moderately. This positive development illustrates that the renewables are also becoming increasingly important in the heat sector - a crucial step to make the entire energy mix more sustainable.
Suitable for:
- Heating market & heat pump industry – figures, data, facts and background – renewable energies & solar systems combination
Challenges and developments in the transport sector
While the expansion of renewable energies in the electricity and heating sector lists impressive progress, the traffic sector continues to be a special challenge. In 2024, the biofuels used in traffic decreased by about eleven percent, which led to lower use of renewable energies in this area. The consumption of bioethanol rose slightly by one percent, while biodiesel decreased by 21 percent due to a change in the Federal Immission Control Ordinance (BImSchV). Among other things, this regulation led to mineral oil companies able to have their saved emission reductions credited only in certain years. For the coming years, however, a significant increase in the consumption of biofuels is expected, since the legal situation is adapted and companies can again fall back on renewable fuels.
Despite the decline in biofuels, the proportion of renewable energies in the traffic sector rose through the use of green electricity. The consumption of green electricity in traffic grew by 14 percent, which corresponds to a arithmetically determined amount of 9.2 TWH. Nevertheless, this increase was not sufficient to fully compensate for the decline in the biofuels. The proportion of renewable energy consumption in traffic fell from 7.6 to 7.2 percent. This development shows that the traffic sector continues to be more intensive to promote alternative drive technologies such as electrical or hydrogen vehicles and to further expand the infrastructure for loading and refueling systems.
Environmental effects and climate protection: avoiding greenhouse gases
A central aspect of the energy transition is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In 2024, the increased use of renewable energies avoided a total of 256 million tons of CO₂ equivalents. The majority of these emission savings - around 205 million tons - were in the electricity sector, followed by 41 million tons in the heat sector and about 10 million tons in the transport sector. These figures underline that the consistent expansion of renewable energies makes a decisive contribution to climate protection.
The reduction of greenhouse gases has far -reaching positive effects: it improves air quality, reduces the negative health effects through air pollution and makes an important contribution to achieving the climate goals that have been set in the Paris Agreement. The continuous reduction in emissions also shows that the change towards a climate -friendly energy supply is not only ecologically sensible, but also economically attractive.
Technological innovations and future perspectives
The development of renewable energies in Germany is inextricably linked to continuous technological innovations. Researchers, engineers and companies are working together to optimize existing technologies and to develop new approaches that increase both efficiency and the integration of renewable energies into the existing network. For example, research is being carried out on intelligent energy management systems, which enable flexible control of the energy flow and can better compensate for the fluctuating production from wind and sun.
Another focus of innovation lies in the further development of heat pump technology. Modern heat pumps are characterized by an even higher efficiency, which makes it particularly attractive for the new building and the energetic renovation of buildings. In addition, it is increasingly being worked on systems that combine heat pumps with other technologies - such as solar thermal energy - in order to enable even more efficient and sustainable heat supply. These hybrid systems offer the potential to provide reliable and environmentally friendly heating solution even in colder climates.
The storage of energy is also becoming increasingly important. Energy storage technologies, such as battery storage or power-to-gas systems, are indispensable to compensate for the discrepancy between energy generation and consumption. They enable excess electricity to be stored from photovoltaic or wind turbines and to feed back into the network in times of low generation. This flexibility is a crucial factor to ensure the stability of the power grid and further promote the expansion of renewable energies.
Political framework and economic opportunities
In Germany, the energy transition is supported by a closely interlinked network of legal requirements, funding programs and political goals. The Renewable Energy Energy Act (EEG) forms a central pillar by promoting the expansion of renewable energies and gradually liberalizing the market. At European level, the Renewable Energy Directive (Red) sets ambitious goals that the Member States have to implement. These framework conditions not only create planning security for investors, but also contribute to the fact that technological innovations are promoted.
The economic opportunities that result from the energy transition are enormous. The expansion of renewable energies creates numerous jobs - from planning to construction to the maintenance of the systems. Regional economic cycles are also strengthened because many projects are organized decentrally and thus integrate local suppliers and service providers. Companies that work in the areas of renewable energies, energy storage and energy efficiency benefit from a steadily growing market and an increased demand for sustainable technologies.
At the same time, politics and business are faced with the challenge of reconciling the expansion of renewable energies with social and ecological aspects. Above all, this concerns space consumption, environmental protection and acceptance among the population. Innovative concepts such as integrated agricultural photovoltaics or the use of fallow land for wind turbines offer solutions to deal with these challenges. The aim is to design a sustainable energy transition that is not only ecologically, but also socially acceptable and economically viable.
Plan your solar system for the most common applications conveniently online with our solar system planner!
With our user-friendly solar system planner you can plan your individual solar system online. Whether you need a solar system for your home, your business or for agricultural purposes, our planner offers you the opportunity to take your specific requirements into account and develop a tailor-made solution.
The planning process is simple and intuitive. You simply enter relevant information. Our planner takes this information into account and creates a tailor-made solar system that meets your needs. You can try out different options and configurations to find the optimal solar system for your application.
Additionally, you can save your plan to review later or share with others. Our customer service team is also available to answer your questions and provide support to ensure your solar system is optimally planned.
Use our solar system planner to plan your individual solar system for the most common applications and advance the transition to clean energy. Start now and take an important step towards sustainability and energy independence!
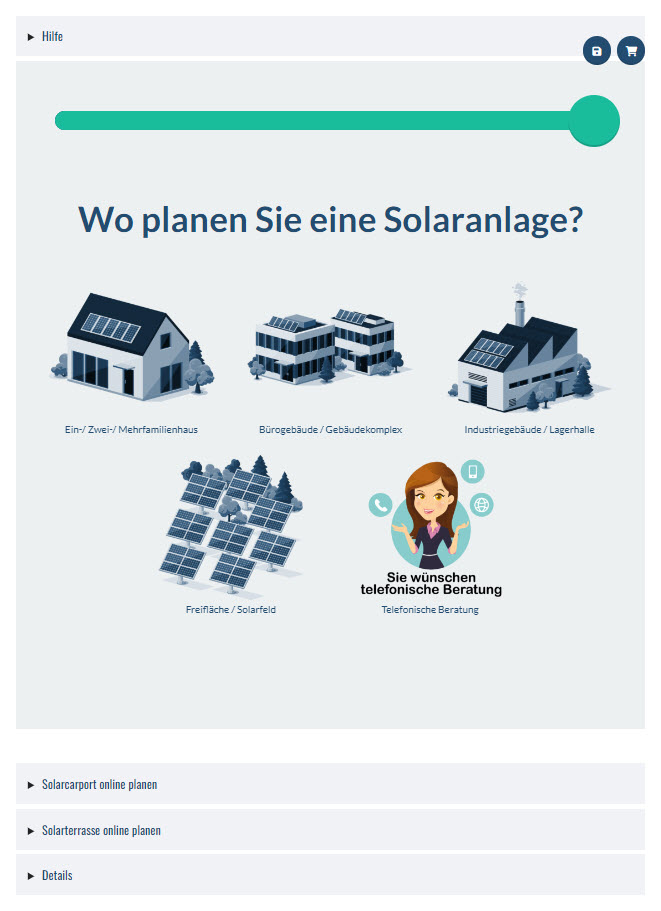
The solar system planner for the most common applications: Plan the solar system online here - Image: Xpert.Digital
More about it here:
Regional differences and international cooperation
Tailor -made solutions for renewable energies on site
The use of renewable energies also shows regional differences in Germany. Wind energy plays a dominant role in wind-rich regions such as Schleswig-Holstein and Lower Saxony, while photovoltaics are increasingly used in sunny areas such as southern Germany. The biomass and the use of heat pumps also result in regional peculiarities that are based on the local climatic and geological conditions. These regional differences offer challenges on the one hand, but on the other hand also opportunities for tailor -made solutions that optimally use the respective location advantages.
At the international level, the German energy transition is increasingly regarded as a model. Many countries are based on the successful concepts and political framework conditions that have been established in Germany. At the same time, cooperation across national borders is of great importance in order to tackle global challenges such as climate change together. International projects and research collaborations in the field of renewable energies promote the exchange of knowledge and contribute to the fact that technological advances can be implemented faster into practice.
Economic and social effects of the energy transition
The switch to renewable energies has far -reaching economic and social effects. In addition to the creation of jobs, regional economic cycles are also strengthened through the increased use of renewable technologies and innovative business models are developed. Companies are increasingly investing in research and development to realize more efficient technologies and new solutions. This not only leads to an increase in competitiveness, but also to a long -term reduction in energy costs, since the dependence on fossil fuels is reduced.
For society, the energy transition means an opportunity to reduce environmental pollution and improve the quality of life. Sustainable energy supply helps to reduce air pollution, which has a positive effect on the health of the population. In addition, the expansion of decentralized energy systems increases security of supply and strengthens regional self -determination. Citizens can become actors of the energy transition themselves-be it by installing photovoltaic systems on their own roof, participation in citizens' energy projects or using energy-efficient technologies in the household.
The influence of the heat pumps on the energy transition in the heat sector is particularly worth mentioning. These devices are able to work efficiently even in times of low outside temperatures and thus offer a reliable alternative to conventional heating systems. The combination with other renewable technologies, such as solar thermal energy, can create hybrid systems that can be met with even more effective blankets in buildings. The trend is clearly towards a holistic view of the energy supply, in which electricity, heat and mobility are networked with one another and interact synergetically.
Challenges on the way to the complete energy transition
Despite the impressive progress, Germany and other industrialized countries face considerable challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is the expansion of the necessary infrastructure. The increased use of renewable energies not only requires new systems, but also intelligent networks that are able to compensate for fluctuations in the production. Energy storage plays a central role in this because they enable excess energy to store and recall if necessary. Without the appropriate storage technology, the fluctuating generation values from wind and sun could lead to network instabilities.
Another problem area is space consumption. Wind and photovoltaic systems in particular need large areas, which can lead to conflicts in densely populated regions. Innovative concepts are required here that make it possible to efficiently integrate renewable energies without being impaired by nature and the environment. Approaches such as the combination of agricultural and photovoltaic use or the establishment of offshore wind farms are examples of how challenges can be solved creatively.
Last but not least, social acceptance also plays a crucial role. Despite the broad consensus on the need for the energy transition, there are always resistances, be it due to concerns about the change in landscape, noise or other negative effects. Transparent and participatory communication, which puts the advantages and opportunities of renewable energies in the foreground, is therefore essential. This is the only way to achieve broad social support and the success of the energy transition in the long term can be ensured.
Future prospects and innovative approaches
If you look into the future, numerous exciting perspectives open up. The progressive digitization of the energy sector, for example, offers new opportunities to optimize energy consumption and further improve the integration of renewable energies. Smart grids, i.e. intelligent power grids, enable real -time control of the energy flows and can thus help to increase security of supply and ensure network stability. The combination of renewable energies with innovative storage solutions and flexible load management systems will also play an increasingly important role in the coming years.
Another promising area is the sector coupling, in which various energy sectors - electricity, heat and traffic - are networked with each other. Surpluses from electricity generation can be used, for example, to produce green hydrogen, which in turn can be used in industry or in the traffic sector. This holistic view of the energy system opens up new opportunities to increase energy efficiency and further reduce the dependence on fossil fuels.
The further development of heat pump technologies and the combination with other renewable heat sources also offer potential to advance the decarbonization of the heat sector. Especially in older buildings, which are often heated energy -intensive, modern heat pumps can be a cost -effective and environmentally friendly alternative. In addition to the energetic renovation of existing buildings, innovative heating concepts that rely on intelligent networking and control are becoming increasingly important. These developments are part of a comprehensive modernization process that improves both living comfort and energy efficiency.
Suitable for:
The role of solar power and heat pumps in the energy transition
Solar power and heat pumps symbolize the change that the German energy transition is taking. While solar power as a decentralized and almost emission -free energy source revolutionizes the electricity sector, heat pumps enable efficient use of the heat stored in the environment. Both technologies complement each other optimally and contribute to the fact that fossil fuels are increasingly being replaced. It is this integrated approach that drives the transition to a sustainable energy system and brings Germany to a climate -friendly future.
The increasing spread of photovoltaic systems on private roofs, public buildings and in large-scale systems makes it clear that renewable energies are no longer only concentrated in large energy parks. Rather, energy generation is increasingly organized, which leads to a higher resilience of the entire system. This decentralization also has positive social and economic effects because it strengthens local added value and gives citizens the opportunity to actively participate in the energy transition.
In this context, heat pumps play a key role in this context, as they help to cover the heat requirement of buildings in a sustainable way. Especially in combination with modern insulation and energy -efficient building design, heat pumps can help reduce energy consumption significantly. This creates added value that is not only reflected in reduced operating costs, but also in improved living comfort and increased independence from fossil fuels.
Suitable for:
Economic opportunities and innovative strength
The energy transition not only offers ecological but also considerable economic opportunities. The expansion of renewable energies has already led to a dynamic growth market that creates numerous jobs and stimulates regional economic cycles. Companies that work in this sector are increasingly investing in research and development in order to further improve their technologies and expand to international markets. This innovative strength is an essential engine for economic success and helps Germany continue to play a leading role in the global energy sector in the future.
New business models are created based on the interaction of production, storage and intelligent control. For example, contracting models in which companies offer complete energy solutions also enable smaller actors access to the latest technology. Such models promote cooperation between municipal supply companies, private investors and research institutions and help to put innovations into practice faster.
Social changes and environmental awareness
The transformation of the energy sector also affects social awareness. More and more people recognize the need to question their own energy consumption and support more sustainable solutions. Citizens' energy cooperatives and local projects in which the population is directly involved in the planning and operation of renewable energy systems. These participatory models strengthen trust in the energy transition and help to grow acceptance and understanding among the population.
In addition, the energy transition also promotes cultural change in which environmental protection and sustainability are no longer considered a niche phenomena, but as central social values. By increasing the use of renewable energies and the associated reduction in air pollution, the quality of life in many regions is improved sustainably. This has positive effects on the health of the population and reduces the long -term social costs that are associated with environmental damage and climatic changes.
Challenges in network stability and energy storage
Despite all progress, the integration of renewable energies into the existing power grid remains a technical and organizational challenge. The fluctuating availability of wind and solar power requires innovative solutions in the area of energy storage and network control. Battery storage, pumped storage power plants and power-to-gas technologies offer promising approaches to ensure network stability. These storage solutions make it possible to store excess electricity and to recall them in times of low generation - a crucial factor to secure supply security in times of high feed -in from renewable sources.
An integrated energy management that flexibly adapts consumption to the current production is another key to master the challenges of network stability. Intelligent control systems and the networking of households, companies and energy suppliers create a dynamic balance that enables energy flows to optimize in real time. These approaches show that technological innovation and digitization are closely linked and together make an important contribution to the further development of the energy system.
Suitable for:
- There is talk of deception and dizziness: the new Solarspitzen Act 2025 - Come on the feed -in tariff
Germany's energy transition: progress, challenges and new opportunities
The progress in the generation of green electricity and heat supply through renewable energies in Germany are impressive and show that the course has been drawn in the right direction. The continuous increase in the generated renewable amount of electricity, the dynamic development in the photovoltaic sector and the increased use of heat pumps are decisive factors that pave the way to a sustainable future. At the same time, the challenges in the areas of network stability, space competition and social acceptance illustrate that an integrated approach is still necessary, which takes into account technical, economic and social aspects equally.
If you look into the future, it is essential to further promote the expansion of all renewable energy sources and at the same time to invest in intelligent storage and management systems. The increasing digitization of the energy sector and the integration of sectors such as electricity, heat and transport offer new opportunities to implement a holistic and sustainable energy supply. At the same time, international cooperation is becoming increasingly important in order to deal with global challenges such as climate change together and to spread technological progress worldwide.
In Germany, the energy transition is not only a technological and economic change, but also brings with it a profound social conversion. Citizens and citizens are working together to create a sustainable energy system that encounters the challenges of climate change and at the same time opens up economic opportunities. The switch to renewable energies leads to a more sustainable, environmentally friendly and socially just energy supply - a development that must also be significantly designed and promoted in the coming years.
Solar power and heat pumps as a symbolic technologies of the energy transition not only offer innovative solutions, but also pave the way to a decentralized, safe and environmentally friendly energy supply. Their increasing distribution and the resulting expansion of the entire energy sector are an expression of a profound change that goes far beyond technical improvements. It is a social transformation process that affects us all and leads to a more sustainable future - for the environment, the economy and society as a whole.
With a view to the coming years, it becomes clear that the success of the energy transition depends significantly on how to master the numerous challenges - from network stability to space consumption to acceptance among the population. Only through a holistic approach that combines technological innovation, political foresight and social cohesion can the transition to a fully sustainable energy supply. It remains exciting to observe how these developments will continue to develop in the next few years and which new technologies and concepts will pave the way into a climate -friendly future.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Construction and advice on photovoltaic open-space systems
☑️ Solar park planning ☑️ Agri-photovoltaic implementation
☑️ Solar outdoor systems with dual-use solutions
Xpert.Solar is your ideal partner for the planning, consulting and construction implementation of ground-mounted photovoltaic systems and agricultural photovoltaic projects due to our many years of experience and expertise in the solar energy industry. Xpert.Solar has an experienced team of professionals that offers tailored solutions to farmers and investors. From location analysis to financial and legal advice to technical implementation and monitoring, Xpert.Solar supports its customers professionally and reliably to ensure successful and sustainable implementation.
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus