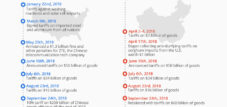
Customs dispute on the trade war.
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: April 9, 2025 / update from: April 9, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
The US-led economic and trade war: an analysis of politics, effects and geopolitical consequences (2018-2025)
A turning point in global trade
The years 2018 to 2025 mark a period of profound upheavals in the global economy. What started as a supposed “trade war” has developed into a complex argument that goes far beyond tariffs and trade balance sheets. Under the keyword “America First”, the United States under the Trump administration pursued an aggressive economic policy, which was characterized by departure by multilateral agreements and a turn to unilateral measures. This policy was partially continued under the subsequent bid administration and experienced massive tightening under a second Trump administration in 2025.
In its complexity and its effects, the current situation far exceeds the problems that were created in 2021 by the six-day blockade of the Suez Canal through the container ship Ever Given or Corona pandemic. Compared to the current situation, those crises in world logistics appear almost harmless and manageable.
Suitable for:
Global supply chains in transition: long -term consequences of protectionism
The consequences of this policy are far -reaching and not only affect the economies involved, but also the entire global order. Increasing tensions, disturbed supply chains, falling economic growth and the erosion of the multilateral trading system are just a few of the effects that we observe today. It is therefore of crucial importance to analyze the causes, mechanisms and consequences of this policy comprehensively in order to understand the challenges and to be able to make sound decisions for the future.
The Global Risk Report as well as other analyzes of the latest commercial and economic wars initiated by Donald Trump and his administration are a dark picture of the global economic situation. Here are the most important findings:
Effects on the global economy
- According to the Cepii Working Paper, the trade war, which was triggered by drastic customs increases, will cause considerable costs for the global economy by 2030. Global GDP could decrease by 0.5 %, while world trade could decrease by 3.4 %. The USA and China are particularly affected by 1.3 %with a forecast decline in GDP.
- For 2025, the FITCH Ratings forecast a slowdown of global economic growth to 2.3 %, which is significantly below the trend. The United States itself could achieve growth of only 1.7 % due to the increased tariffs.
Strategic changes in trade policy
- Trump's trade policy is based on a protectionist strategy that prioritizes national security and economic independence. This includes increased tariffs on strategic goods such as cars, steel and aluminum as well as export controls.
- The introduction of so -called "reciprocal tariffs" has led to retaliation measures by other countries, which further exacerbates the economic losses for the USA.
Long -term risks
- The Global Risk Report emphasizes that this phase of the trade war promotes fragmentation of global supply chains and financial systems. This could endanger globalization in the long term and make technological decisions more difficult.
- In addition, the increased tariffs in the USA could lead to an increase in consumer prices, reduce real wages and inhibit investments.
The trade and economic wars initiated by Trump have far-reaching negative effects on the global economy. While some countries such as Canada and Mexico could benefit at short notice, the measures overall lead to weakening international trade and increased uncertainty for companies worldwide. The Global Risk Report warns of the long -term consequences of this policy, in particular with regard to the fragmentation of global systems and geopolitical tensions.
Suitable for:
- Resilience through diversification: Strategic realignment of global supply chains in the geopolitical area of tension
Anatomy of US trade and economic policy (2018-2025)
US trade and economic policy has been described by a number of key features since 2018:
Unilateralism
A departure of multilateral agreements and a preference for bilateral agreements or one -sided measures.
protectionism
The use of tariffs and other trade barriers for the protection of domestic industries.
Techno nationalism
The linking of technological innovation with national security and economic competitiveness.
Economic state policy
The use of economic instruments for the persecution of foreign policy and geopolitical goals.
The USA of the USA: tariffs, export controls and investment tests
The US government used a variety of instruments to achieve their economic policy goals. Are among the most important:
Tariff
Aggressive use of tariffs on imports: overview
Using various laws and justifications, the United States imposed a large number of tariffs on imports from different countries, especially China. Both strategic economic sectors and national security and trade deficit concerns were addressed. The central measures are summarized below:
1. Section 301: tariffs on Chinese goods
- Introduction: Originally in 2018, with the aim of reacting by China's theft of intellectual property and unfair trade practices.
- Expansion (2024):
- Affected sectors: electric vehicles, semiconductors and medical goods (strategic industries).
- Scope: 382 tariff categories with an annual commercial value of around $ 18 billion.
- Measures: increased customs sets and wider coverage.
2. Section 232: National security tariffs
- Introduction: As early as 2018, tariffs on steel (25 %) and aluminum (originally 10 %, later 25 %) were collected.
- Changes (2025):
- Resumption and expansion: Earlier country and product exceptions were largely deleted.
- Additional tariffs: A special customs of 25 % was charged on imported automobiles and auto parts.
3. Ieepa: Use of the International Emergency Economic Powers Act
The law grants the President far -reaching powers in national emergencies and has been used several times to justify tariffs:
a) Fentanyl/border security (2025)
- Customs on Canada and Mexico:
- Introduction: February 2025.
- Height: 25 % on imports (later for USMCA conformity were partially exposed to).
- Customs in China:
- Introduction: initially 10 %, later increased to 20 %.
b) Reciprocal Zölle (trade deficit emergency, 2025)
- Introduction: April 2025, due to a declared national emergency in connection with the trade deficit.
- Measures:
- Basic customs set: 10 % on almost all global imports (from April 5), with exceptions:
- Canada and Mexico.
- Certain countries (Belarus, Cuba, North Korea, Russia).
- Already polluted by section 232 or other measures.
- Higher individualized tariffs: introduced from April 9, varied between 11 % and 50 %, depending on the country.
- Examples:
- EU: 20 %.
- China: 34 %.
- Examples:
- Basic customs set: 10 % on almost all global imports (from April 5), with exceptions:
- Chinese retribution and escalation:
- After China's retaliatory measures, the effective customs set for China was increased cumulatively, which gave it up to 104 %:
- 20 % fentanyl-customs.
- 34 % reciprocity.
- 50 % retaliation.
- After China's retaliatory measures, the effective customs set for China was increased cumulatively, which gave it up to 104 %:
The US customs policy increased the economic pressure on strategic trading partners and addressed specific problems such as unfair trading practices, national security interests and the commercial balance deficit. However, the measures also led to global trade conflicts and retaliation measures, especially China.
Suitable for:
- In truth, the Magnificent 7, according to estimates, ensure a US trade surplus of EUR 112 billion (2023) to the EU
Export controls
The tightening of export controls, especially towards China, to limit access to advanced technologies, especially in the semiconductor area. The aim is to hinder the military modernization of China and the development of skills in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). This includes controls for semiconductor manufacturing systems (SME), software tools, High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and the recording of Chinese companies on the Entity List.
Investment tests
Intensification of the investment test
The review of investments is tightened for both incoming (inbound) and for outgoing (outbound) investments.
Inbound (Cfius - Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States)
- Goal: Increased testing of Chinese investments in strategic sectors within the United States:
- technology
- Critical infrastructure
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- energy
- Trend:
- Preferred blocking of transactions compared to complex reduction agreements.
- Particularly strict measures in investments by Chinese investors.
Outbound (“Reverse Cfius”)
- New rules: Restriction of US investments to Chinese companies in the following sectors:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Halfcase/microelectronics
- Quantum computing
- Possible sanctions:
- Application of the ** International Emergency Economic Powers Act (Ieepa) ** to restore US investments.
- Goal: Prevention of the financing of the Chinese military-industrial complex by US capital.
The United States is strengthening its control mechanisms for Chinese foreign investments in the USA and for US investments in strategic Chinese sectors. The aim is to secure national interests and the restriction of resource flows into security areas.
Trade War vs. Economic War: A necessary distinction
The terms “trade war” and “economic war” are often used synonymously, but describe different aspects of the global tensions that were triggered by US politics.
A trade war typically refers to a conflict in which states raise tariffs and other trade barriers to influence trade streams, protect domestic industries or correct trade balance sheets.
Economic war
On the other hand, a more comprehensive concept in which economic instruments - such as sanctions, financial aids, investment restrictions and export controls - are used strategically to pursue foreign policy and geopolitical goals.
The current US policy shows characteristics of both concepts:
Elements of a trade war
The massive use of tariffs against a large number of countries, especially China and the EU, with the declared goal of reducing trade deficits and protecting domestic industries, as well as the subsequent retaliation tariffs from other countries.
Elements of an economic war
The strategic use of export controls to contain the technological progress of China in key areas such as semiconductors and AI as well as the tightening of the in and outbound investment controls to limit the flow of capital and technology are clearly overriding geopolitical and national security goals. The linking of trade policy with national emergency stands (fentanyl, economic security) under the IEEPA also underlines the character of economic state policy.
The US strategy, especially when dealing with China, is more than just a trade war; It represents a form of hybrid discussion. While traditional trade wars primarily rely on tariffs and trade barriers to influence trade rivers or protect domestic industries, the US government has also used significant non-tariffs in addition to the extensive customs measures. This includes in particular the strict export controls for high technology and the restrictions on investments that targeted to limit China's strategic skills.
Suitable for:
- Unequal trade balance USA-EU? Digital US services are missing-Revaluation of transatlantic trade is necessary!
Economic effects: global and national consequences
The commercial and economic conflicts initiated by the USA have profound effects on the global economy and the economies involved.
Global growth and world trade under pressure
The escalation of the trade conflicts and the associated uncertainty put a significant impact on global economic growth and international trade. International organizations and research institutes have tried to quantify these effects, whereby the forecasts consistently indicate negative consequences.
Forecasts
Global macroeconomic forecasts under the influence of trade conflicts:
1. CEPII (Center d'études Prospectives et d'Idukungen Internationales)
- Forecast:
- Global GDP could decrease by 0.5 % by 2030.
- World trade could decrease by 3.4 %.
- Scenario:
- US tariffs: 60 % in China, 10 % to other countries.
- Consideration of retaliation measures.
2. Fitch ratings
- Forecast:
- Global GDP growth 2025: 2.3 % (previously: 2.6 %).
- 2026: 2.2 % (still weak).
- Reason:
- Commercial war, initiated by the United States.
3. International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Forecasts (January 2025):
- Global economic growth 2025/2026: 3.3 %.
- Emphasized downward risks: inflation, political uncertainty.
- Update (February 2025):
- Correction of world trade growth down.
- Industrialized countries:
- 2025: 2,1 %.
- 2026: 2,5 %.
- Main factor: escalating trade voltages.
4. World Bank
- Forecast (January 2025):
- Global growth 2025/2026: 2.7 %.
- Evaluation:
- Inadequate for sustainable development.
- Main risks:
- Political uncertainty.
- Negative trade policy shifts.
- Special concern:
- Commercial voltages.
5. United Nations (UN):
- Forecast:
- World trade growth 2025: 3.2 % (originally).
- Uncertainties:
- Emphasized by commercial restrictions.
6. World trade organization (WTO)
- Forecast:
- Growth of goods trading 2025: 3.3 %.
- Warning:
- Effects of political uncertainty and new tariffs.
- Estimation:
- US tariffs could reduce global trading volume by 1 %.
7. Yale budget lab
- Assessment:
- US tariffs from 2025 burden global economic growth.
Challenges and risks
1. US trade policy
- Introduction of high tariffs (60 % in China, 10 % to other countries).
- Escalating trade voltages.
2. Important downward risks
- Political uncertainty.
- Inflation.
- Negative trade policy shifts.
3. Global implications
- Falling growth in global trade and GDP.
- Special effects on industrialized countries.
4. Long -term projections
- CEPII: decline in global GDP and world trade until 2030.
- WTO: Reduction of the global trade volume by 1 % by tariffs.
Mechanisms of action
The tariffs have a negative effect on the global economy over different channels. They increase the costs of imported goods, which leads to inflation and reduces the purchasing power of consumers. They disrupt established global supply chains and reduce the demand for traded goods. The uncertainty generated by the tariffs and the unpredictable political design also inhibits investment decisions from companies worldwide. Finally, unilateral tariffs provoke retaliation measures that further restrict trade and increase the economic costs for everyone involved.
Consequences for the US economy
Contrary to the declared goals of politics, the analyzes indicate that the US economy itself takes considerable damage.
GDP effects
The forecasts consistently show negative effects on US economic growth. CEPII expects a GDP loss of 1.3 % by 2030. Fitch lowered the growth forecast for 2025 to 1.7 % and estimates the GDP reduction by tariffs to about 1 percentage point until 2026. % smaller GDP in the long term.
Inflation and consumer costs
A central point of criticism is that the tariffs increase import prices and thus heat inflation and burden consumers. The Yale Budget Lab estimates the short-term price increase due to all 2025 tariffs to 2.3 %, which means average additional costs of $ 3,800 per year. Clothing prices (+17 %) are particularly affected.
occupation
While jobs may arise in protected sectors (such as steel), analyzes indicate that these profits could be overcompensated by losses in other sectors that are dependent on imports or who are affected by retaliation. The general slowdown of economic growth and specific production stops indicate negative employment effects.
Commercial balance sheet
Despite the goal of reducing the commercial deficit, this is unlikely, since deficits are primarily determined by macroeconomic factors (difference between national savings and investments). In fact, the US trade deficit rose significantly in 2024 and reached record heights in early 2025, partly through early imports in anticipation of tariffs. Remodeling measures also damage US exports.
Company investments
The considerable political uncertainty that arises from the unpredictable customs policy has a negative impact on the willingness to invest of the companies.
🎯🎯🎯 Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, fivefold expertise in a comprehensive service package | R&D, XR, PR & SEM

AI & XR 3D Rendering Machine: Fivefold expertise from Xpert.Digital in a comprehensive service package, R&D XR, PR & SEM - Image: Xpert.Digital
Xpert.Digital has in-depth knowledge of various industries. This allows us to develop tailor-made strategies that are tailored precisely to the requirements and challenges of your specific market segment. By continually analyzing market trends and following industry developments, we can act with foresight and offer innovative solutions. Through the combination of experience and knowledge, we generate added value and give our customers a decisive competitive advantage.
More about it here:
Commercial conflict US-China: Effects on the global economy and Europe
Resilience to China's economy
China as the main goal of US measures is also severely affected, even if the country has certain resilience.
GDP effects
The high export dependency from the US market leads to expected growth losses. CEPII predicts a GDP loss of 1.3 % by 2030. Fitch expects a reduction of approx. 1 percentage point until 2026, with fiscal support measures being dampening. Recent estimates, based on the tariffs from April 2025, assume a decline in Chinese GDP by up to 2.4 % in 2025 alone.
Trade effects
A burglary of bilateral trade with the United States is expected. China tries to redeem exports to other markets (EU, Canada, Mexico), but total exports are likely to decrease.
Economic challenges
The tariffs exacerbate existing problems such as the weakness of the real estate sector, subdued consumption, deflationary tendencies and demographic challenges.
Political reaction
China reacts with fiscal and monetary policy measures to support the economy and accelerates efforts to “de-Americanization” of its supply chains.
Suitable for:
- The economic situation in global mechanical engineering: a comprehensive analysis - UA Germany, EU, USA and China
Effects on the European Union and Germany
The EU and especially Germany also feel the negative consequences of US politics.
GDP effects
Negative spillover effects are expected. Fitch forecasts weaker growth and a GDP reduction by approx. 1 percentage point by 2026 for the 2025 euro zone, with German fiscal measures cushioning the blow. The effects could be alleviated by loosening the ECB policy and devaluation of the euro.
Trade effects
Direct export losses to the United States are to be expected because most EU goods are subject to an additional custom of 20 %. Indirect effects arise from trading in trade when, for example, Chinese goods are increasingly pushing the EU market (a “second China shock”).
Financial spillovers
Rising risk surcharges on US bonds Due to the US budget deficits, the financing costs in Europe could increase and affect debtability and investments.
Specific Germany
As a strong export -dependent nation with the USA as the most important trading partner, Germany is particularly vulnerable. Key industries such as automobile, mechanical engineering and chemistry are badly affected.
Sectoral analysis: the case of Germany
The effects of US trade policy affect German key industries, in particular automotive construction and mechanical engineering, which are of central importance for Baden-Württemberg's economy. The analysis of these sectors reveals specific challenges and adaptation strategies.
The automotive industry under pressure (including the Baden-Württemberg)
The German automotive industry is particularly at risk from the US tariffs.
High exposure
The United States is an indispensable sales market for German manufacturers such as Volkswagen, BMW, Mercedes-Benz and Porsche.
Customs effects
The US inches from 25 % to imported cars since April 3, 2025 represents a massive load.
Production adjustments
Although German manufacturers already produce in the United States, this only covers part of the paragraph. The tariffs create an incentive to shift more production to the USA.
Pricing
It is expected that the prices for imported vehicles in the USA will increase.
Effects on Baden-Württemberg
The state is heavily dependent on the automotive industry. State politicians and local companies are concerned. Suppliers such as Bosch and ZF are also directly or indirectly affected.
Suitable for:
- Central points of a sustainable market economy: resilience and social responsibility as central values
Challenges for machine and plant engineering (including the Baden-Württemberg focus)
German mechanical engineering, another pillar of the German and Baden-Württemberg economy, also faces significant challenges.
Meaning of the US market
The United States is an important export market.
Customs effects
The industry is subject to the general “reciprocal” US customs of 20 % to EU goods.
Existing weakness
The sector already suffered from the recent customs increases from the weak global demand and declining order inputs.
Effects on Baden-Württemberg
The negative development in the mechanical engineering of the federal state continues. Local IHKs report on a declining industrial issue. The US tariffs exacerbate the pressure on a already battered sector in the region.
Supplier interruptions and strategic reactions
US trade policy leads to considerable faults in global supply chains and forces companies to strategic adjustments.
Increased complexity and costs
The tariffs disturb established global value chains, increase the complexity and more expensive procurement for international manufacturers. The high political uncertainty complicates long -term planning.
Anticipative behavior
Companies reacted to the impending tariffs with early imports.
Reshoring/Near -horing/Friend-Shoring
A declared goal of US policy is the relocation (reshoring) of production to the USA. Some companies consider relocations from Mexico to the USA (e.g. Samsung, LG). However, duties against allies such as Canada, Mexico and the EU make the so-called “friends horing” (relocation to friendly countries).
Diversification
Companies are increasingly looking for alternative markets and suppliers to reduce the dependency on the USA and China.
Investment shifts
German companies increase their investments in North America, partly out of worry about trade barriers.
Evaluation of US policy: intentions vs. reality
The “America First” trade agenda pursues ambitious goals, but the previous results and analyzes indicate that the effectiveness of the instruments used is questionable and considerable unintentional negative consequences occur.
Declared goals of the “America First” trade agenda
The policy, formulated by the Trump administration and reiterated in the 2025 trade policy agenda, pursues several main goals:
- Strengthening domestic production
- Reduction of trade deficit
- Increase in real median income
- Strengthening national and economic security
- Ensuring fair trade / “Level Playing Field”
- Generation of state revenues
Evaluation of the effectiveness and achievement of goals
The previous findings indicate that politics only reaches its declared goals very limited or not at all, while it causes considerable costs.
Production/employment
There is hardly any evidence of a significant revival of US production through the tariffs.
Trade deficit
The US trade deficit has remained or even increased despite the tariffs.
Income/consumer costs
The overwhelming evidence shows that tariffs increase consumer prices and reduce real income or purchasing power.
National/economic security
The results are mixed. Targeted measures such as export controls against China may take specific security concerns into account. However, the broad tariffs against allies and the resulting supply chain disorders could weaken the general economic resilience rather than strengthen.
fair Trade
The concept of “reciprocity”, as used by administration, is very controversial.
State revenue
Customs generate income, but this is done at considerable overall economic costs in the form of reduced GDP growth and stress for consumers.
Critical perspectives and unintentional consequences
US trade policy has met with broad criticism and numerous negative unintentional consequences are observed.
- Economic damage
- Political uncertainty
- Regressive distribution effect
- Undermination of alliances
- Weakening of multilateralism
Global reactions: retaliation and countermeasures
The US measures did not remain unanswered. Important trading partners reacted with extensive countermeasures, which further increases the economic costs and exacerbates the conflicts.
- China: reacted quickly, comprehensively and escalating to every round of US tariffs.
- European Union: announced a two -stage retaliation.
- Canada/Mexico: It was initially faced with 25 % IEEPA tariffs. The tariffs were later exposed or modified for USMCA-compliant goods.
Geopolitical shifts and systemic implications
The aggressive trade policy of the United States not only has direct economic consequences, but also triggers profound geopolitical shifts and questions the existing international system.
Economic fragmentation and strategic realignment
The global economy is experiencing increasing fragmentation, which is accelerated by the trade conflicts.
- Decoupling/Derisking
- Shifting of supply chains
- Rise of techno nationalism
The link between economic and security policy
The boundaries between economic and security policy are increasingly blurred.
- Safety of the trade
- Focus on strategic sectors
- Alliances and pressure
The multilateral trading system under pressure
The rule-based multilateral trading system, embodied by the WTO, is massively under pressure due to the unilateral US measures.
- Erosion of WTO standards
- Paralysis of the dispute resolution
- Declining use of the WTO
- Shifting to bilateralism/unilateralism
Suitable for:
- Commercial war threatened? Possible effects of a 20 percent US custom on German goods and the global economy
The further path: current status and future scenarios
The trade and economic relationships between the USA, China and the EU are in a state of high tension and uncertainty. The further course depends on a variety of factors, including political decisions, economic adjustments and global developments.
USA-China-EU relationships: State of things (April 2025)
- USA-China: The relationship is highly confrontative.
- Usa-EU: The relationships are tense, but dialog channels remain open, albeit loaded.
- EU-China: This relationship is strongly influenced by the US measures.
Possible developments and outlook (2025-2026)
Based on the current dynamics, various scenarios for the near future can be outlined:
- Scenario 1: Continued escalation
- Scenario 2: Negotiated Deescalation / Patt
- Scenario 3: Wursting with structural shifts
Conclusions and strategic recommendations
The analysis of US trade and economic policy from 2018 to 2025 draws the image of a profound change with far-reaching consequences. The departure of multilateral principles in favor of unilateral measures has created a state of permanent tension and uncertainty in the global trading system.
Central conclusions
- Hybrid conflict
- Significant economic costs
- Dubious achievement of goals
- Escalation and retaliation
- Geopolitical fragmentation
- Persistent uncertainty
Strategic recommendations
For companies:
- Diversification of supply chains and markets
- Scenario
- Localization/regionalization
- Advocacy
- Compliance and monitoring
For political decision -makers (especially EU/Germany):
- Prioritization of negotiations
- Strengthening European unity and ability to act
- Credible but moderate retaliation
- Strengthening alliances and diversification of partnerships
- Reform of the multilateral system
- Strengthening your own resilience
The economic and trade war initiated by the United States has heralded a new era of global economic relationships, which is characterized by increased confrontation, uncertainty and fragmentation. A return to stable, rule -based conditions requires considerable diplomatic efforts and a strategic realignment of all actors involved.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus