Opportunities and risks for a Western-European metaverse - data & figures - power consumption & renewed (iterative) solutions
Language selection 📢
Published on: October 25, 2023 / update from: October 25, 2023 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
🌐 As things stand, the realization of large metaverses faces long-term challenges
The necessary conditions for this do not yet exist. One of the main reasons for this is the enormous energy requirement associated with the implementation of such metaverses.
🔋 Today, data centers already consume around 5 percent of global energy consumption, and experts estimate that this share could rise to as much as 30 percent in the coming years.
📊 There is no generally accepted, always up-to-date breakdown of global electricity consumption between different electronic devices and technologies.
💡 Energy consumption can change significantly over time and depends on various factors, including technological developments, population growth, energy efficiency and usage patterns.
🌎 Nevertheless, it is possible to give a rough estimate of how global electricity consumption might be distributed across different categories:
1. Data centers
Data centers could account for around 5% of global electricity consumption. These are crucial for data processing and storing information in the digital world.
2. Smartphones and mobile devices
The share of global electricity consumption from smartphones and mobile devices is around 3%. These devices have become an integral part of modern life and contribute to networking and communication.
3. Computers
Computers, including desktop PCs, laptops and servers, account for about 9% of global electricity consumption. They are the basis for most digital activities.
4. Other electronic devices
This category is extremely diverse, but in total it can account for around 20% of global electricity consumption. These include, for example, household appliances, consumer electronics and other everyday gadgets.
5. Industrial and commercial applications
Industrial applications and processes are the largest consumer, accounting for around 65% of global electricity consumption. This includes the energy requirements of factories, manufacturing plants and other commercial operations.
6. Private households
Energy consumption in private households is estimated at around 27%. This area covers the needs of millions of households worldwide.
⚡ It is important to note that power requirements in these different areas can vary greatly depending on the scenario. The development of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud systems and the introduction of 5G and 6G private networks, especially for the metaverse, will influence the energy requirements in the respective areas. For example, metaverses based on immersive technologies could result in a significant increase in energy demand in data centers and among private users.
🌿 Overall, it turns out that the implementation of metaverses represents a complex challenge in terms of energy consumption. Not only technological advances are required, but also a sustainable energy supply and a more conscious use of electronic devices to enable the long-term realization of such virtual worlds.
📣 Similar topics
- The Future of the Metaverses: Energy as a Key Factor ⚡
- The Energy Hunger of the Metaverses: Challenges and Solutions 💡
- Electricity consumption in the digital world: An analysis 🔌
- Metaverses and Global Energy Consumption: A Forecast 🌍
- Technological developments and their influence on energy requirements 💻
- Metaverses and Data Centers: The Energy Balance 🏢
- Sustainability in Metaverse Development 🌱
- Electronic devices and their contribution to energy consumption 📱
- The Role of 5G and 6G in Metaverse Evolution 📶
- Metaverses and Energy Efficiency: An Outlook 🔋
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Metaverse #Energy Consumption #Technology #Sustainability #5G6G
📊 Electricity consumption structures worldwide and in Germany
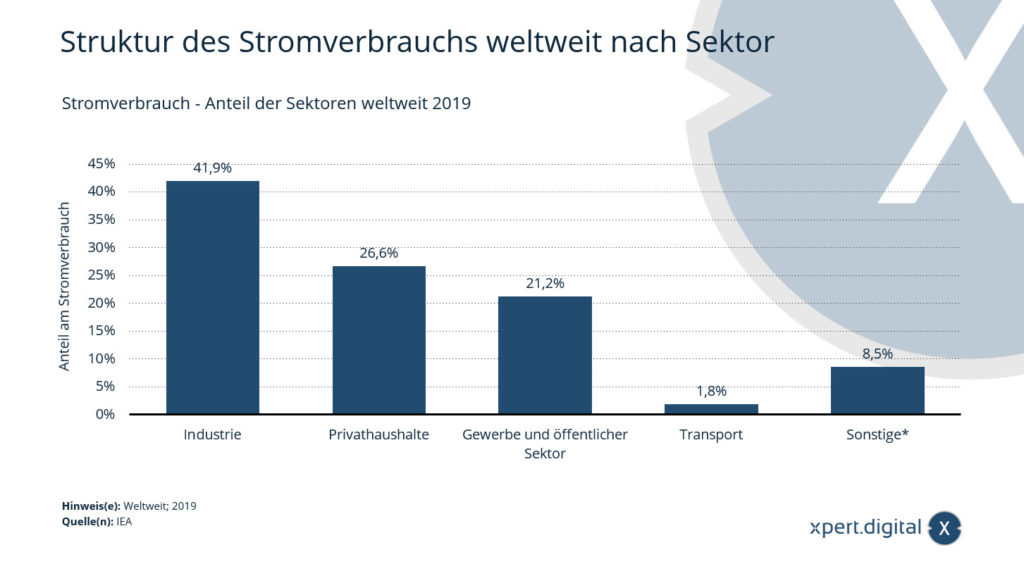
🌍 Structure of electricity consumption worldwide by sector in 2019
The structure of global electricity consumption in 2019 provides interesting insights into the distribution of electricity consumption by different sectors. This report shows that energy demand depends primarily on the type of use. Here is the key information:
1. Industrial sector (41.90%)
In 2019, the industrial sector was the largest consumer of electricity in the world. It claimed an impressive 41.90% of total global electricity consumption. This reflects the intensive use of energy in production and manufacturing. Industry is a key driver of economic development, but at the same time it is also a significant energy consumer.
2. Private households (26.60%)
Households were the second largest sector consuming electrical energy, accounting for 26.60%. This highlights the electricity requirements for lighting, heating, cooling and various electrical devices in households worldwide.
3. Commercial and public sector (21.20%)
The commercial and public sector, which includes offices, schools, hospitals and government buildings, consumed 21.20% of the world's electricity. This highlights the importance of energy efficiency in these areas to reduce consumption.
4. Transportation (1.80%)
The transport sector used comparatively little electricity, namely only 1.80%. This shows that electromobility and energy-efficient transport systems were still relatively unpopular in most countries.
5. Other sectors (8.50%)
Other sectors that do not fall into the above categories accounted for 8.50% of global electricity consumption. This includes areas such as agriculture, mining and leisure activities.
🇩🇪 Distribution of electricity consumption in Germany by consumer groups 2022
Germany, as one of Europe's leading economies, has a unique electricity consumption structure. In 2022, this distribution looked like this:
Distribution of electricity consumption in Germany by consumer groups in 2021 and 2022 - Image: Xpert.Digital
1. Industry (approx. 50%)
Industry was the largest consumer of electricity in Germany in 2022. This sector accounted for almost half of the total electricity consumption, which corresponds to around 216 terawatt hours. This underlines the importance of German industry for the national economy.
2. Industry, trade, services (approx. 25%)
The commercial sector, which includes shops, service companies and trading companies, consumed around a quarter of the electricity in Germany. This shows the diversity of commercial uses of electricity.
3. Households (approx. 25%)
Households also accounted for around a quarter of all electricity consumption in Germany. This includes the energy requirements for apartments and houses.
💡 Electricity prices for industry and households
Electricity prices in Germany are an important factor that influences energy consumption. In recent years, electricity prices have risen continuously both in industry and for households. This could be due to various factors, including the cost of generating electricity, network charges and taxes. Although some alternative providers offer lower prices than basic providers, both industry and household providers increase their rates year on year.
🌐 Largest electricity consumers in comparison
In a global comparison, China was the largest electricity consumer in 2019, followed by the USA. These two countries dominate the global energy market due to their huge populations and economic activities. In Europe, Scandinavian countries, particularly Norway, showed high per capita electricity consumption. Norway consumed more than three times as much electricity per capita as Germany. This could be due to the high demand for electrical energy to power households, industries and operate electric vehicles.
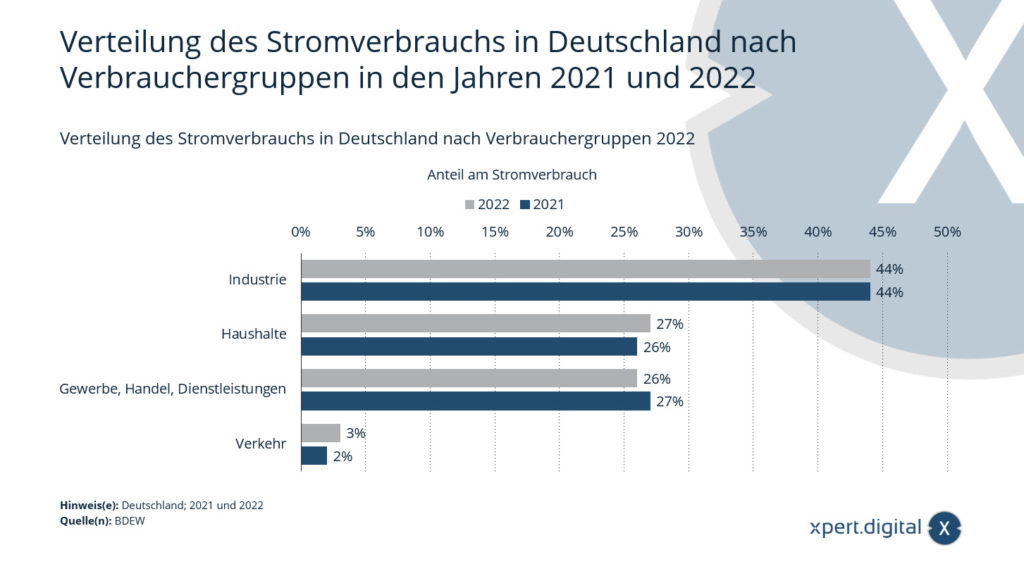
📊 Distribution of electricity consumption in Germany by consumer groups in 2021 and 2022
It is interesting to see how the distribution of electricity consumption in Germany changes from year to year. In 2021 and 2022, the differences in consumer groups were subtle but still notable:
Distribution of electricity consumption in Germany by consumer groups 2021
- Industry: 44%
- Households: 26%
- Industry, trade, services: 27%
- Traffic: 2%
Distribution of electricity consumption in Germany by consumer groups 2022
- Industry: 44%
- Households: 27%
- Industry, trade, services: 26%
- Traffic: 3%
💡 The slight shift from one year to the next reflects changes in the economy, transport sector and consumer habits. This highlights the importance of energy distribution data for energy policy and energy infrastructure planning.
🌿The structure of electricity consumption worldwide and in Germany shows how important it is to promote energy efficiency and renewable energies in order to cope with increasing electricity demand while minimizing environmental impact. It is crucial to optimize energy consumption across various sectors to promote sustainable energy solutions.
📣 Similar topics
- 💡 Energy distribution: global perspective
- 🏭 Industrial power consumption worldwide
- 🏠 Electricity requirements in private households
- 🏢 Commercial and public sector: energy consumption
- 🚗 Electromobility: The transport sector
- 🌍 Electricity consumption in different sectors
- 🇩🇪 Germany: Focus on electricity consumption
- 💰 Impact of rising electricity prices
- 🌐 International electricity consumption comparisons
- 📊 Changes in electricity consumption: Germany 2021-2022
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Electricity consumption #Energy efficiency #Electricity prices #Energy strategy #Global comparison
🌐 The Metaverse in Europe: Needs and Challenges
📜 The Metaverse, a term that has received a lot of attention recently, raises many questions, especially regarding its need and added value on a European scale.
🔍 1. Demand on a European scale
The need for a European-scale metaverse is not yet clear. Compared to Asia, where the development of the consumer metaverse has already progressed, Europe is still in its early stages. However, there is a need to set the course to become a global leader in the technological development of the Metaverse.
🤔 2. Unclear added value
Despite the enthusiasm for the Metaverse, there is still a lack of a clear vision of the undeniable value it can provide. This is a challenge that proponents of the Metaverse strategy face. There is a need to define the added value and the concrete benefits for society and the economy.
🚀 3. Group dynamics and early entry
The Metaverse is strongly influenced by group dynamics. Companies and organizations that invest in this technology early and participate in its development may have a competitive advantage. Similar to the introduction of smartphones, which were initially viewed by some as unnecessary, getting started early is often crucial to avoiding later failures.
🌐 4. Development of “smaller” meta-verse solutions
In addition to the large Metaverse platforms, smaller solutions are also developing. The success of such solutions depends on interest, education and information provision. When the added value and need are recognized, needs arise that these solutions want to meet. This can lead to an economic cycle that generates funding and profit.
🌍 5. Interest and need in different regions
The interest and need for the Metaverse develops differently in different regions. In Asia, especially among the young population, the metaverse is being driven forward by gamification and entertainment. This region is home to approximately 60% of the world's youth population, representing enormous potential. In the Western world, however, the metaverse is being driven forward by the concept of Industry 4.0, which means it is being applied in industrial production and professional life.
🌟 The Metaverse is promising, but many questions still remain unanswered. The need and added value at a European scale are not yet clearly defined and the challenge is to clarify these aspects in order to fully exploit the potential of this technology. It is important to track the development of the Metaverse on a global scale and identify opportunities for innovation and economic growth.
🌐 Key differences in metaverse development in Asia and the West
More about it here:
🌐 Metaverse and Europe: Opportunities and Risks
The EU Commission has recognized the transition to the Metaverse as a significant development that offers both new social and economic opportunities for Europe. This transition involves the efficient interaction between people and machines in different EU industrial ecosystems through the use of so-called digital twins. But in addition to the opportunities, certain legal, ecological and economic risks must also be taken into account.
🔒 Data protection and cybersecurity in the metaverse
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring fundamental rights, privacy and cybersecurity in the metaverse. Because the Metaverse is a virtual environment in which people actively interact, privacy and security issues may arise. The EU Commission recognizes these concerns and is working to develop appropriate measures and regulations to minimize these risks.
💼 Responsibility and liability in the metaverse
Another aspect that needs to be taken into account is the uncertainty surrounding responsibility, liability and contractual arrangements in the metaverse. When conflicts or damage arise in this virtual world, it is important to have clear rules for liability and contract enforcement. The EU Commission plans to create guidelines and recommendations in this area.
📶 Infrastructure and skilled workers
In order to successfully establish the Metaverse in the EU, significant investments are required. This particularly includes the expansion of 5G and 6G networks with low latency and high bandwidth. These networks are critical to ensuring a smooth and immersive experience in the Metaverse. Edge computing also plays an important role as it enables data to be processed in real time, thereby improving interactivity in the metaverse.
In addition to the infrastructure, qualified workers are also very important. The Metaverse opens up new career fields and requires professionals with knowledge of virtual reality, artificial intelligence and other relevant technologies. The EU Commission is working on initiatives to promote training and qualifications in these areas to ensure that sufficient skilled workers are available.
📜 Regulation in the Metaverse: Flexibility and Ethics
It is important to emphasize that the EU Commission supports the development of the meta verse, but does not try to provide comprehensive obligations through a “Meta-Verse law”. This makes sense for several reasons. First, the meta verse is a relatively new technology, and many of its applications and effects have not yet been fully understood. It is therefore difficult to issue comprehensive regulations that may be inappropriate or excessively restrictive.
Second, the metaverse is in constant flux. New technologies and applications are being developed, and user interactions are constantly changing. It is therefore advisable to remain flexible and respond to developments rather than adopting rigid laws that may become outdated before they even come into force.
Third, there are many ethical and societal issues surrounding the Metaverse that still need to be discussed and explored. These questions include, for example, real-world impacts, social interaction, content creation and protection, and economic impacts. It is important to clarify these questions in a broad social dialogue before comprehensive laws are passed.
🤝 Participatory approach and potential of the metaverse
In this context, the EU Commission has announced that it will adopt a participatory approach, involving various stakeholders, including the public, in the design of Metaverse policies and regulations. This is to ensure that different perspectives and concerns are adequately taken into account.
🌟 Metaverse opportunities in Europe
The opportunities that the metaverse offers for Europe are diverse. It can usher in a new era of digital collaboration and communication that increases efficiency across various sectors of the economy. Companies can use digital twins to create realistic simulations of products and processes, improving product development and quality assurance. In education, immersive learning environments can be created that promote student understanding and motivation.
In addition, the metaverse opens up new opportunities for the cultural and creative industries. Virtual art galleries, concerts and theater performances are becoming increasingly popular, giving artists the chance to perform in a global virtual arena. This can help promote European culture worldwide.
There is also potential for the metaverse in healthcare. Telemedicine and virtual health consultations can be made more efficient, and patients can recover and rehabilitate in virtual environments. This can improve overall healthcare.
🌱 Ecological sustainability in the metaverse
However, it is important to consider the ecological impacts of the Metaverse. Running data centers and using high-end graphics processors in virtual worlds requires significant amounts of energy. The EU Commission will therefore also take measures to promote energy efficiency and sustainability in the metaverse.
🚀 Opportunities and challenges in the Metaverse for Europe
The transition to the Metaverse for Europe brings both opportunities and challenges. The EU Commission recognizes the importance of this change and is working to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks. A participatory approach and regulatory flexibility are crucial to ensure that the metaverse is developed successfully and responsibly in Europe.
📣 Similar topics
- 🌐 Metaverse in Europe: Opportunities and Risks
- 💻 Data protection in the metaverse: challenges and solutions
- 📡 5G and 6G: The Future of Metaverse Networks
- 👩💼 Skilled workers in the metaverse: education and qualifications
- 📜 Metaverse Regulation: Flexibility and Participation
- 🎨 Metaverse for the creative industries: innovations and possibilities
- 🏥 Healthcare in the Metaverse: Telemedicine and Rehabilitation
- 🌱 Sustainability in the Metaverse: Energy efficiency and environmental protection
- 🤖 Digital Twins in the Metaverse: Applications and Benefits
- 🌍 Europe and the Metaverse: A Digital Future
#️⃣ Hashtags: #MetaverseEU #Privacy #MetaverseNetworks #MetaverseSkills #MetaverseRegulation #CreativeIndustry #Healthcare #Sustainability #DigitalTwins #Europe'sDigitalFuture
📖 🌐 Iterative Metaverse solutions - 'Small' Metaverse solutions in Germany are on the rise
An iterative metaverse solution is an approach to developing and improving metaverse technologies through incremental iterations and adjustments. This approach involves deriving smaller, efficient solutions from large metaverse visions that build on the experiences and insights from earlier development phases. The focus is on making continuous improvements and adapting technologies to changing requirements.
🔍 Here are some important aspects of an iterative metaverse solution
1. Smaller steps
Instead of developing large and complex metaverse systems from the start, start with smaller, manageable solutions. These can be developed and tested more quickly.
2. Experience-based
Development is based on user experiences and feedback from previous iterations. This makes it possible to continuously improve usability and functionality.
3. Adaptability
The iterative approach makes it possible to react flexibly to changes and new requirements. This means the metaverse can be continuously adapted to the changing needs of users.
4. Interoperability
An important component is the ability to link different Metaverse solutions together and make them interoperable. This allows users to seamlessly switch between different Metaverse environments.
5. Industry-specific applications
Iterative metaverse solutions can be industry-specific, such as in the consumer or industrial metaverse. These solutions are tailored to the specific needs of a particular industry.
The iterative approach plays a key role in the development of a comprehensive and functional metaverse, as it allows challenges to be addressed incrementally and to fully exploit the potential of this emerging technology.
Iterative meta -verse solution means to develop from large metaverse visions, “smaller” and efficient meta -verse solutions, for example in the area of consumers and industrial meta verses, from which a larger European meta -several interoperable can develop at a later date.
🔄 Interoperability
refers to the ability of different systems, technologies or organizations to work with each other and exchange data. This enables smooth communication and coordination between these systems. Typically, interoperability requires adherence to standards and protocols to ensure compatibility.
The development of the meta-verse concept has attracted worldwide attention in recent years, and in Germany too, “small” meta-verse solutions are on the rise. These specific applications offer industry and topic-specific solutions that can influence a wide range of areas. In this article, we will deal more closely with these iterative meta -verse solutions and explain their importance for Germany.
🏭 B2B application example hybrid trade fair and 3D product presentations
One of the first and perhaps most obvious application areas is the use of metaverse technologies for hybrid trade fairs. Companies like Bürkle and Kautec are already using 3D visualizations at trade fairs that are accessible via various devices and touchscreens. This eliminates the need for expensive exhibition stands and the transport of machines, saving not only costs but also valuable resources. Given the current staff shortage and rising personnel costs, this represents an efficient solution.
Related here:
The transformation of analog image brochures into 3D product presentations is another way in which small Metaverse solutions are gaining a foothold in Germany. This allows companies to present their products in an immersive and engaging way, which increases customer loyalty and understanding of the products.
But small metaverse solutions are not limited to the commercial sector. They also have a significant impact on the cultural and creative industries as well as other areas:
🎨 1. Cultural and creative sectors
The Metaverse offers artists and creatives the opportunity to work in virtual worlds and present their works globally. Virtual art galleries are becoming increasingly popular, allowing artists to perform in a global virtual arena. This not only promotes cultural diversity in Germany, but also opens up new income opportunities for artists.
📚 2. Education and learning environments
The Metaverse opens up completely new possibilities in the education sector. Virtual classrooms and immersive learning environments can be created to make learning more exciting and effective for students. This contributes to improving the education system in Germany and ensures that educational content is more accessible.
🏥 3. Healthcare
Metaverse solutions can also make a decisive contribution to healthcare. Telemedicine and virtual health consultations are made more efficient through the use of Metaverse technologies. Patients can recover and rehabilitate in virtual environments, which is particularly important in times of pandemics and the need for remote treatment.
🌱 Consider ecological impacts
However, it is important to consider the ecological impacts of the Metaverse. The operation of data centers and the intensive use of high-end graphics processors in virtual worlds require significant amounts of energy. The European Union (EU) has recognized that measures to promote energy efficiency and sustainability in the Metaverse are necessary to minimize environmental impacts. This is particularly important in Germany, a country that places great value on environmental protection.
🚀 Guidelines and standards
Regulation of the metaverse is another important aspect. The EU Commission is working to develop guidelines and standards to ensure that the development of the Metaverse in Germany and across Europe takes place responsibly. A balanced approach that promotes innovation while protecting society's interests is crucial.
🔗Iterative Metaverse solutions have significant opportunities and are efficient
“Small” meta -verse solutions offer considerable opportunities in Germany and Europe. You can boost the economy, improve the education system, promote cultural diversity and make health care more efficient. The challenge is to take advantage of these opportunities and at the same time ensure that ecological sustainability and responsible regulation are guaranteed.
German society and European institutions are called upon to accept these challenges and make the transition into the metaverse successful. Germany has the opportunity to take a pioneering role in this emerging digital world and set the course for an innovative and sustainable future.
🌐 Metaverse development in Germany, EU, USA, China, Japan and worldwide - exciting XR technology as an economic factor?
XR technology and the concept of the Metaverse are still in their early stages of development, but their potential as an economic driver is enormous. Companies that are able to adapt and leverage these technologies are likely to have a competitive advantage. At the same time, they offer consumers the opportunity to immerse themselves in a new, immersive world that can transform everything from social interactions to professional tasks. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is important to consider ethical and regulatory issues to ensure that the benefits of the Metaverse and XR technology can be enjoyed as broadly as possible. Ultimately, the success of this digital ecosystem will depend on how well different actors – governments, businesses and civil society – can work together. This is an exciting time for the Metaverse and XR technology, and we can't wait to see what innovations and applications lie ahead in the next few years.
More about it here:
🗒️ Xpert.Digital: A pioneer in the field of extended and augmented reality

We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
Xpert.Digital - Pioneer Business Development
Smart Glasses & KI - XR/AR/VR/MR industry expert
Consumer metaverse or meta -verse in general
If you have any questions, further information and advice, please feel free to contact me at any time.
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus