What to do in the economic and construction crisis? With a view to China – opportunities and challenges – Xpert support in the strategy
Language selection 📢
Published on: December 1, 2023 / update from: March 25, 2024 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

AI & XR 3D Rendering Machine: What to do in the economic and construction crisis? Xpert Support in Flexible Strategy Management – Image: Xpert.Digital
🇨🇳📈🔍 Background information on the current situation and developments related to China
🏢📉 In the current economic and construction crisis, it is crucial for companies to develop flexible and effective strategies in order to effectively meet the challenges. But above all, knowing where it comes from and what matters.
👨💼👩💼 High energy and personnel costs press particularly during this time, which is often described as a “unfavorable phase” in the modern economic language. It is of the utmost importance for companies to keep qualified employees, especially when there is a shortage of skilled workers. Discharges are not an option, especially in small and medium -sized companies, since the available talents are already scarce.
🤖🤝 Another innovative option is to use automation and robotics to address labor shortages , reduce costs in the long term and transform quality.
🤖 One of the biggest challenges in the current situation is the increasing planning uncertainty.
📝 In general, strategic thinking is required. Everyone in the solar industry has already noticed that it is not possible to continue as before. In addition to all the challenges, there is also planning uncertainty. Planning security is essential for companies as it forms the basis for investment decisions, resource management, budgeting and the development of long-term strategies. Without this security, it becomes increasingly difficult to operate efficiently and manage risks adequately.
🌐 A look at China reveals that this economic power is also faced with challenges.
🏢🏢🏢 An example of this is the city of Tianjin, one of the wealthiest and most modern cities in China, which nevertheless struggles with high vacancy rates. It is estimated that around 70% of the high-rise buildings there are empty, although exact figures are lacking. Even a vacancy rate of 20% would be alarming. In a healthy real estate market, a natural vacancy rate of 5-10% is considered normal and even necessary to allow flexibility for tenant changes and renovations. A higher vacancy rate can indicate various problems, such as excessive rental prices, outdated building infrastructure, an oversupply of space or, as is currently the case, the economic downturn.
Matching: ARD/Tagesschau | Tianjin's empty towers: symbols of an economic crisis in China
🏙️ The vacancy of high-rise buildings, especially in urban business centers, can be problematic. Because it leads to reduced income for the owners and negatively affects the economic vitality of the surrounding urban area.
📉 In short, the Chinese real estate crisis is putting a heavy burden on the country's economy. The real estate sector in China has been recording declining sales and rising vacancies for years. Several large construction companies such as Evergrande got into financial difficulties and were no longer able to repay debts. This led to a significant loss of confidence among buyers and investors.
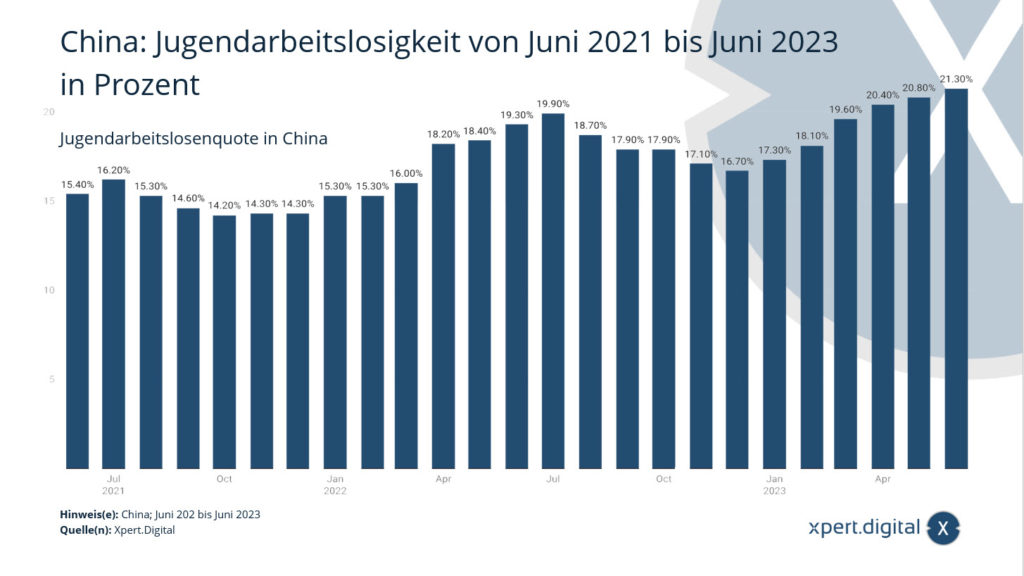
🧑🎓 One in five Chinese young people is looking for work
🔎👷♀️ Unemployment among urban youth aged 16 to 24 – 2023 (in percent)
👩🎓 The Chinese government is trying to cushion the crisis with government economic stimulus programs and investments in infrastructure projects. Nevertheless, the economic situation remains tense. To make matters worse, China continues to struggle with high youth unemployment of over 20%. Many young Chinese people cannot find an adequate career start after completing their studies or training.
Matching: Neue Zürcher Zeitung | China's hidden job crisis: Hidden youth unemployment is so explosive that China's government is withholding the numbers
📣 Similar topics
- 🏢 Challenges in the construction industry: Flexibility and efficiency as key
- 🏗️ Shortage of skilled workers in the construction industry: strategies for employee retention
- 🤔 Planning uncertainty: The dilemma of construction companies in times of crisis
- 🌏 China under the spell of the real estate crisis: lessons for the global construction industry
- 📊 Tianjin's empty high-rises: a symbol of economic challenges
- 🏙️ The consequences of urban vacancies: Economic and social impacts
- 🚧 China's construction sector: A fight against declining sales and financial crises
- 📈 Government measures against the real estate crisis: China's strategy under the microscope
- 👩🎓 Youth unemployment in China: An urgent problem in the shadow of the economic crisis
- 🔍 China's hidden jobs crisis: The reality behind the official statistics
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Construction industry #Economic crisis #Skills shortage #Real estate crisis #Planning uncertainty #Vacancy #China #Construction industry #Youth unemployment #Economic policy
🎯🎯🎯 Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, fivefold expertise in a comprehensive service package | R&D, XR, PR & SEM

AI & XR 3D Rendering Machine: Fivefold expertise from Xpert.Digital in a comprehensive service package, R&D XR, PR & SEM - Image: Xpert.Digital
Xpert.Digital has in-depth knowledge of various industries. This allows us to develop tailor-made strategies that are tailored precisely to the requirements and challenges of your specific market segment. By continually analyzing market trends and following industry developments, we can act with foresight and offer innovative solutions. Through the combination of experience and knowledge, we generate added value and give our customers a decisive competitive advantage.
More about it here:
🚨 High youth unemployment is a warning sign of structural problems in an economy 🚨
The impact of high youth unemployment on the economy is a complex issue that involves a variety of factors. Youth unemployment can significantly impact a country's economic development. This is because young people are seen as an investment in the future of a nation. Your skills, creativity and innovation are key drivers for growth and progress.
🎓 Lack of qualified workers
Young people who are unemployed cannot develop their skills and knowledge, leading to a loss of skills. This not only impacts individual career development, but also the competitiveness of the entire economy, as companies have less access to talented young workers.
🛑 Second: social costs
Unemployed youth may tend to engage in negative behaviors due to frustration and lack of prospects, which in turn leads to social tensions and weakens social cohesion. In severe cases, this can discourage investment and lead to an unstable business environment.
💸 Third: impairment of consumption
Young adults who work contribute to the economy by purchasing goods and services. However, when they are unemployed, they lack the income to act as consumers, which can lead to lower demand and thus a decline in economic growth.
🏛️ Furthermore: burden on public coffers
More unemployed people mean higher spending on social benefits and lower tax revenue. In the long term, this may lead to budget deficits and limit the government's financial scope to invest in education, infrastructure and other growth-enhancing measures.
🧠 Finally: Psychological effects
Long-term unemployment can lead to a loss of self-esteem and mental illness. This not only affects the quality of life of those affected, but can also have long-term effects on their ability to work.
📚 Approaches to combat youth unemployment
There are educational programs that ensure that young people's skills match the needs of the labor market, as well as promoting entrepreneurship and self-employment among young people. Adapting labor market regulations to enable flexible forms of work can also help make it easier to employ young people.
High youth unemployment is a warning sign of structural problems in an economy. It requires a coordinated response from governments, education institutions and the private sector to break the cycle of unemployment and promote sustainable economic development.
👩🏫 Similar topics
- 🔍 Youth as the future: The effects of unemployment
- 🛠️ Loss of qualifications due to high youth unemployment
- 🚔 Social costs of youth unemployment
- 📉 Impact of youth unemployment on economic growth
- 💼 Youth and the labor market: opportunities in the crisis
- 🏦 Youth unemployment and its consequences for state coffers
- 🧠 Psychological effects of long-term youth unemployment
- 🎓 Education against youth unemployment – time for change
- 💡 Stimulate innovation through young workers
- 🔄 The fight against youth unemployment: measures and strategies
#️⃣ Hashtags: #YouthUnemployment #Economic Development #SocialCosts #Educational Initiatives #Labour MarketFlexibility
🌞 Energy transition and solar energy: A global perspective 🌍
The global energy industry is undergoing change, driven by the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly energy production. Solar energy, as one of the main players in this change, has experienced a huge boom in recent years. A significant part of this development can be attributed to the massive investments and subsidies in the Chinese solar industry. China, as one of the world's largest solar panel producers, has boosted the solar industry with government subsidies to speed innovation and reduce manufacturing costs.
📉 Challenges of overproduction and the construction crisis in China 🏗️
This subsidy policy has led to a flood of low-cost, high-quality solar panels on the global market, with China as the main exporter. However, this development has not been without challenges. The construction crisis in China, characterized by overinvestment in the real estate sector, has led to overproduction in various industries, including solar. The resulting overproduction of solar modules is hardly sold domestically due to the faltering Chinese markets. This forces Chinese manufacturers to sell their products on international markets, especially in Europe, at extremely competitive prices.
🌐 Global impact and the balance between costs and local economy 🏭
The flooding of the European market with inexpensive solar modules from China has both positive and negative consequences. On the one hand, it has led to a reduction in the cost of solar energy, which has accelerated the adoption of this sustainable energy source. On the other hand, it represents a significant challenge for local manufacturers, who find it difficult to keep up with the low prices and high production efficiency of their Chinese competitors.
🔎 Data access and the implications of the Chinese real estate crisis 📊
The difficulty of obtaining accurate figures and data from China makes a comprehensive assessment of the situation difficult. Nevertheless, many indicators suggest that the Chinese housing crisis has the potential to spill over into the financial sector and have far-reaching effects on the global economy. The overproduction of solar modules may be just a symptom of a much larger problem that is deeply rooted in the structure of the Chinese economy.
🏦 Financial stability and the role of the Chinese government 💹
There is speculation that these challenges could be the last gasp before a major economic crisis in China. History has shown that such crises do not occur in isolation; they can trigger chain reactions that have global effects. The Asian financial crisis of 1997 is an example of the contagion effects that a regional crisis can have on the global economy.
The Chinese government now faces the challenge of controlling overproduction while ensuring the long-term stability of the economy. This could mean that subsidies for the solar industry need to be reassessed and possibly scaled back to find a balance between growth and stability. At the same time, it must find solutions to stabilize the real estate sector and strengthen trust in the financial market.
🌍 International reactions and strategic decisions 🤝
The international community is watching these developments with great attention. Europe, as the main buyer of Chinese solar modules, must consider how it should react to the flood of imports. Long-term strategic decisions are required to protect the domestic solar industry without completely giving up the advantages of cheap imports.
🔄 Collaboration and Trading Strategies: A Way Forward 🛤️
The situation shows how interconnected and interdependent the global economy is and how local events can have far-reaching consequences. In addition, the current situation requires greater international cooperation to balance the opportunities and risks of the solar energy industry. It is critical that governments worldwide, together with the private sector, develop robust mechanisms to maximize the economic and environmental benefits of solar energy, while minimizing the negative impacts on local markets and industries.
In this context, measures such as tariffs on imported solar panels could be considered to protect local companies. However, such trade barriers could also slow progress towards greener energy production and increase costs for end users. Therefore, careful consideration is required to avoid protectionism, which could ultimately cause more harm than good.
📣 Similar topics
- 🌞 Solar energy: engine of the global energy transition
- 🏗️ China's construction crisis and its consequences for the solar industry
- 🌍 Price drop: Chinese solar modules flood the European market
- ⚖️ Balancing act: China between overproduction and economic stability
- 💸 Import flood: Challenge for Europe's solar industry
- 📊 Lack of data: The problem with assessing China's economy
- 🔮 Signs of crisis: China on the verge of an economic crisis?
- 🌐 Chain reaction: Global effects of local economic crises
- 🤝 International cooperation against the solar module glut
- 🛡️ Tariffs on solar modules: protection or harm to the ecology?
#️⃣ Hashtags: #SolarEnergy #ChinaEconomy #EuropeanMarket #GlobalChain Reaction #EconomicCrisis
🌏🐉 China's economy on shaky ground: a superpower stumbling
🐉 China, the emerging superpower, is currently experiencing a period of uncertainty. Under the leadership of President Xi Jinping, an overhaul of the United States on the world stage was sought, but now citizens are faced with an unexpected turn of events: the country's economy is stumbling and hopes for a quick rise are giving way to worries about a possible one Recession.
💼 Economic growth, once the backbone of the Chinese dream, has noticeably subsided. The dream of an economic and political dominance seems to be at risk from the slow growth rate. The streets line closed shops and the mood in the country is depressed. Klaus Mühlhahn, a renowned sinologist, describes the atmosphere on T-Online as "shocking" and indicates a significant loss of trust in the leadership.
📉 While the world hoped for a rapid recovery in China after the COVID-19 pandemic subsided, the expected strong growth failed to materialize. Instead, the topic of a possible economic downturn is present in the discussions of economists around the world.
📊 While the Beijing Bureau of Statistics reported growth of 5.2 percent for the year through the end of September, which could be close to the Chinese government's target of 5 percent, there are signs that these numbers do not reflect the whole story. A series of measures, including interest rate cuts and subsidized loans, particularly for the struggling real estate sector, were taken to stabilize the economy. However, the presence of ruined buildings in cities is a silent testimony to deeper problems.
📦 Foreign trade, once a strength of the Chinese economy, is also showing cracks. Exports fell by almost 8 percent in October compared to the previous year and youth unemployment is showing an upward trend even after the end of the strict lockdowns.
🐉 The Chinese leadership is facing a breaking point. To boost foreign investment, it made a policy change that will allow citizens of six countries, including Germany, to enter visa-free from December. The move, which applies to both business travelers and tourists, represents a notable departure from previous policy and appears to be an attempt to revitalize the economy by opening it up to international influences.
Matching: t-online | China in crisis – The giant is reeling enormously
🔐 This measure is symptomatic of a larger shift in Chinese policy, manifesting itself in increasingly restrictive surveillance of its own citizens while granting greater freedoms to foreign visitors. A paradoxical approach that underlines the government's desperation to keep the economy on track while increasing control over its own population.
📊🗺 To understand the full dimension of China's economic challenges, we need to look at both the short-term measures and the long-term strategic plans. It is a time of rethinking and realignment, both for China and for the global economy, which is closely intertwined with the world's second largest economy.
📣 Similar topics
- 🎶 China's economy is weakening
- 🐉 China is experiencing turbulent economic times
- 👨💻 Beijing is trying to stabilize the economy with measures
- 📰 China's exports are declining
- 😕 Chinese leadership faces major challenges
- 📈 Economic growth in China is slowing
- 👀 Experts discuss possible recession in China
- 📉 Real estate sector and domestic consumption are weighing on China's economy
- ✈️ China relaxes entry rules for visitors
- 🤔 China between economic control and opening
#️⃣ Hashtags: #China #Economy #Conjuncture #Politics #Globalization
🐉 🇨🇳 China's national debt compared to gross domestic product by 2028
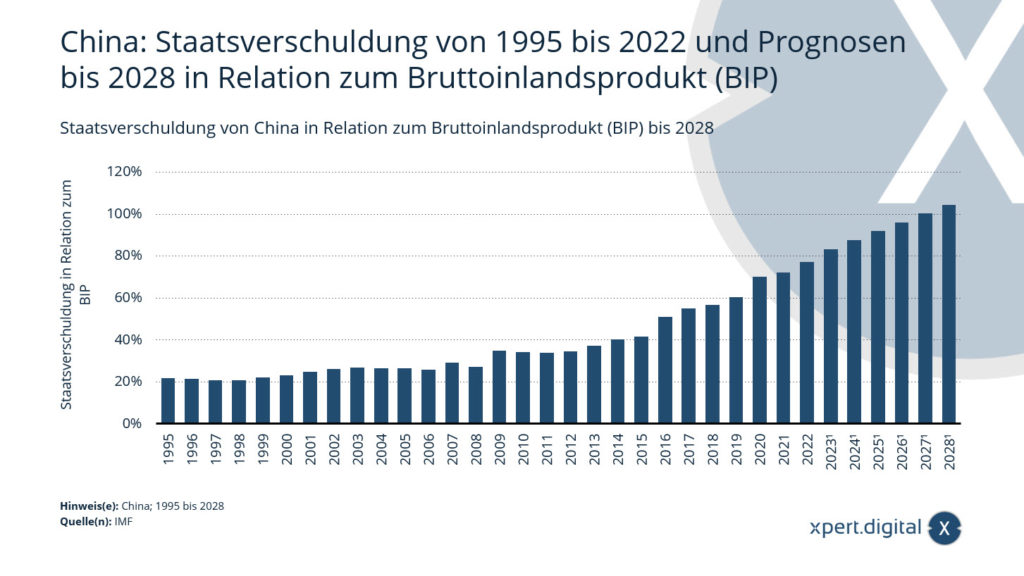
China: National debt from 1995 to 2022 and forecasts up to 2028 in relation to gross domestic product (GDP) - Image: Xpert.Digital
👉🏼 💵 China's national debt is continuously increasing and is estimated to have reached around 77 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2022. For 2023, the debt ratio is forecast to be around 83 percent of GDP. At first glance, this rate still appears moderate in international comparison. However, the significant increase in debt is surprising given that China's GDP has more than doubled in the last decade.
👉🏼 🏗 The reasons for the increase in national debt are diverse. In recent years, China has invested heavily in infrastructure projects such as roads, railways and ports. These debt-financed investments were intended to stimulate economic growth. At the same time, China's national deficit also worsened, reaching a peak in 2020. Although it was reduced slightly in 2021, it remains at a high level.
👉🏼 🏦 Another reason for the growing debt is the loose lending of Chinese banks. Loans are also being extended to high-risk companies and individuals, driving up the number of non-performing loans. Lack of regulation of the financial sector increases the risk of a financial crisis. If defaults occur, this could trigger a chain reaction and throw the entire banking system in China into disarray.
👉🏼 ⚖️ To maintain economic stability, the government is forced to continue taking on debt. According to forecasts, national debt will rise to over 90 percent of GDP by 2028. This would put China in the critical zone of high debt. Internationally, a ratio of 90 percent or more is considered to be an impending over-indebtedness.
👉🏼 📈 The national debt is expressed in absolute terms in the national currency, i.e. Renminbi (CNY). The debt ratio, also known as the debt ratio, indicates the ratio of national debt to GDP. It is an important indicator of a country's financial situation. If government spending exceeds revenue, it is called a budget deficit. The government can finance higher spending by borrowing from the capital market. To do this, it issues government bonds, i.e. interest-bearing securities.
👉🏼 📝 The amount of interest depends largely on the creditworthiness, i.e. the creditworthiness of the state. Rating agencies assess creditworthiness and assign debt ratings. The more reliable a country is assessed, the better its rating and the lower the interest rate tends to be. China's strong economic power and foreign exchange reserves currently speak in favor of China. However, the growing debt and the risk of a real estate or banking crisis are viewed critically. China's credit rating and thus refinancing costs could come under pressure.
🌍 Gross domestic product (GDP) growth in China by 2028
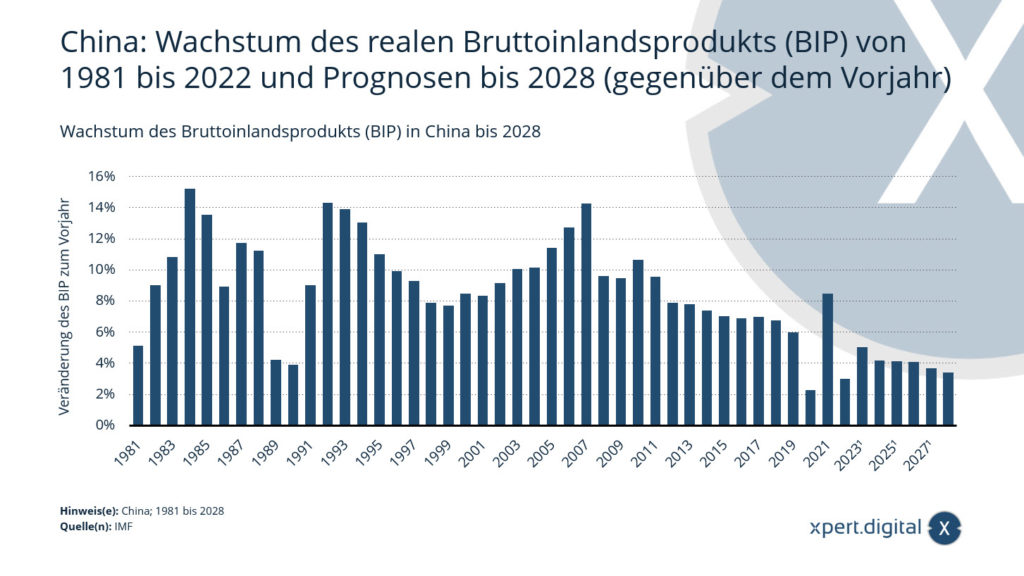
China: growth in real gross domestic product (GDP) from 1981 to 2022 and forecasts until 2028 - Image: Xpert.Digital
📈 China's economic development in the last few decades has been impressive. Since the beginning of the reform and opening-up policy in the late 1970s, China has experienced rapid economic growth. According to official statistics, the growth in real gross domestic product (GDP) was around 2.99 percent in 2022. Growth of around 5.01 percent is forecast for 2023.
📉 However, the trend of recent years shows that China's economic growth is slowing. While the growth rate was regularly above 10 percent in the 1980s and 1990s, it has declined steadily in recent years. This has various reasons. On the one hand, China's production capacities are increasingly approaching the limits of what is possible. Many traditional growth drivers such as exports or infrastructure expansion are losing momentum.
👵🌱 On the other hand, China faces major challenges such as demographic development and environmental problems. Due to the one-child policy of the past, Chinese society is aging rapidly. The proportion of the working population is decreasing, while more and more pensioners need to be cared for. At the same time, China suffers from serious environmental problems such as air and water pollution. The shift to a more sustainable economy will initially slow growth.
🔮 This downward trend in growth rate is forecast to continue. According to the forecast, GDP growth is expected to fall by a total of 1.6 percentage points to 3.38 percent by 2028. This shows that China is making the transition from an emerging economy to an industrialized country. As prosperity increases, the need for rapid growth rates automatically decreases.
💡🌱 At the same time, China is striving to increase the quality of growth. The aim is to strengthen innovation, sustainability and domestic consumption. This reorientation of the economy towards qualitative growth is also associated with lower growth rates. The focus is now more on issues such as the environment, social balance and technological progress.
💪🌍 Despite the declining growth momentum, China remains the second largest economy in the world. Even with more moderate growth of around 5 percent annually, China's economic power and geopolitical importance would continue to increase. In order to remain economically successful in the future, China must master the structural change in its economy and establish new growth engines. The coming years will show whether Beijing can manage this balancing act.

Industrial & B2B Business Metaverse: Reduce costs with XR technology for photorealistic product images (XR 3D rendering machine)
XR technology offers a superior solution for creating photorealistic images and allows companies to free themselves from the expensive fees of external media agencies. It is common knowledge that media agencies charge high costs to create such images as it requires expertise, special software and collaboration with various experts.
More about it here:
Plan your solar system for the most common applications conveniently online with our solar system planner!
With our user-friendly solar system planner you can plan your individual solar system online. Whether you need a solar system for your home, your business or for agricultural purposes, our planner offers you the opportunity to take your specific requirements into account and develop a tailor-made solution.
The planning process is simple and intuitive. You simply enter relevant information. Our planner takes this information into account and creates a tailor-made solar system that meets your needs. You can try out different options and configurations to find the optimal solar system for your application.
Additionally, you can save your plan to review later or share with others. Our customer service team is also available to answer your questions and provide support to ensure your solar system is optimally planned.
Use our solar system planner to plan your individual solar system for the most common applications and advance the transition to clean energy. Start now and take an important step towards sustainability and energy independence!
The solar system planner for the most common applications: Plan the solar system online here - Image: Xpert.Digital
More about it here:
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Smart City & Factory: Industry expert for energetic 5G buildings and halls as well as advice and installation of solar systems
☑️ Xpert.Plus - logistics consulting and logistics optimization
☑️ Industry expert, here with his own Xpert.Digital Industry Hub with over 1,500 specialist articles
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus