Contract logistics – service providers for logistics – 80% of all larger companies use them!
Language selection 📢
Published on: February 25, 2021 / update from: March 3, 2021 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
Efficient outsourcing of logistics services – with dynamic logistics
In the wake of ever-increasing competition and the resulting pressure to permanently increase productivity, outsourcing areas that are not part of the company's core has become an urgent management goal. This often also includes logistics, whose processes are increasingly being outsourced, at least in part, to external service providers. For this reason, the sector of specialized logistics service providers has experienced rapid growth in the last few decades. Sales of outsourced logistics services in Germany now amount to over 100 billion euros.
Contract logistics providers combine a bundle of logistical tasks for their customers into a service package that is specifically tailored to the needs of their client. Their range of services often goes beyond the mere transport and storage of goods. Due to their specialization, the providers develop considerable industry and customer-specific know-how. This knowledge enables them to carry out the services offered more efficiently and cost-effectively than the contracting company would be able to.
In the Anglo-American region, these contract logistics providers or providers of external logistics solutions are referred to as third-party logistics providers (3PL) or full-service providers. A term that has now also become established in Germany. Based on the original 3PL providers, further service approaches have developed, which we present in their different forms below.
According to a study by Capgemini in the USA, around 80% of all larger companies now use the services of a third-party logistics provider.
In line with this topic:
- Better networking of business development with logistics managers and planners (3PL & 4PL)
- Kuehne + Nagel – statistics and facts
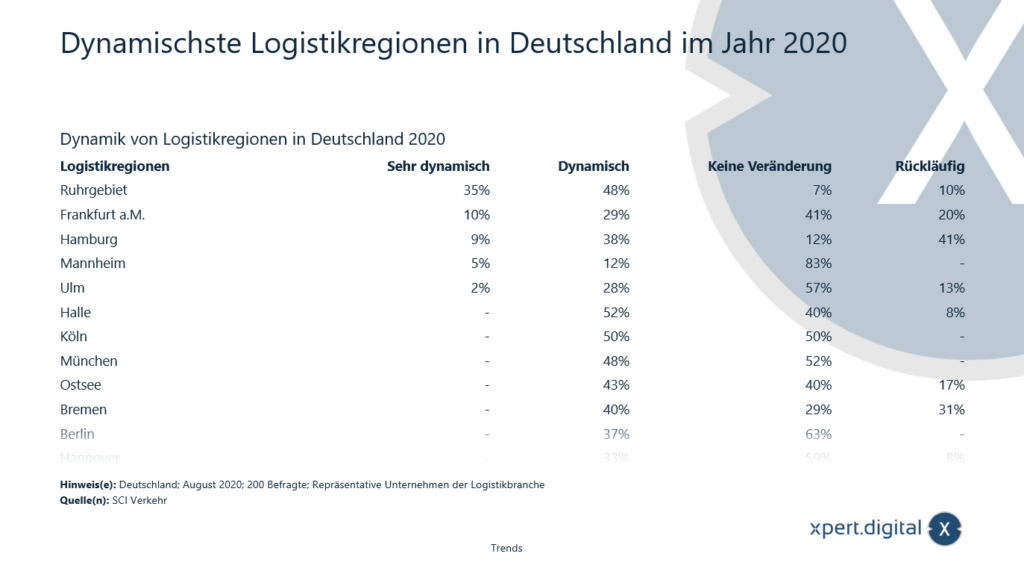
Where are the largest logistics regions in Germany?
In addition to the Ruhr area, the classics of Hamburg, Bremen and Frankfurt aM, it also includes regions such as Ulm, Mannheim and Halle. Of course not forgetting Cologne, Munich, Berlin and the Baltic Sea. According to a study, 35 percent of those surveyed said that the Ruhr area logistics region is the most dynamic. Another study says that the most dynamic logistics region is in the Leipzig-Halle area.
What is dynamic logistics?
What will be crucial for the future will be how we secure the infrastructure of our key industries! Key industries in Germany today include the automotive industry, construction industry, food, chemical industry, electrical industry, energy production, mechanical engineering and shipyards.
If we want to maintain the standards of our key industries and expand them further in the future, we need dynamic logistics that can react quickly and flexibly to the respective market changes. First of all, we are thinking about modern IT. Even without modern software, complex transport processes are no longer conceivable today.
The following factors also play a decisive and important role in dynamic logistics:
- Digital Intelligence (Digital Transformation, Internet Access, Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things)
- Intralogistics/logistics (full automation, mobility of goods and people)
- Autonomous power supply (CO2 neutrality, planning security, safety for the environment)
Suitable for:
They will be crucial to how we secure the infrastructure of our key industries in the future!
Market share of the leading companies in contract logistics in terms of total global sales
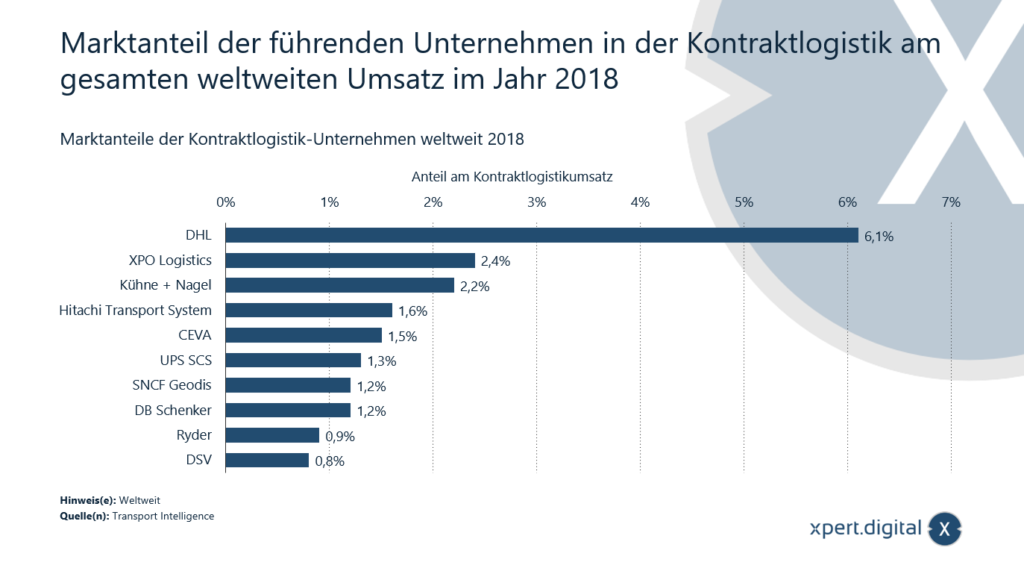
Market share of the leading companies in contract logistics in total global sales - Image: Xpert.Digital
Contract logistics – service provider for logistics – PDFs for download
- Logistics company – PDF download
- Transport and logistics industry Germany – PDF download
- Road freight transport Germany – PDF download
- Transport industry in Europe – PDF Download
- Deutsche Post DHL – PDF Download
- XPO Logistics – PDF Download
- Kuehne + Nagel EN – PDF Download
- Kuehne + Nagel DE – PDF Download
What types of logistics service providers are there?
The classification of logistics service providers into different areas can be traced back to a historical development. The range of services and solutions goes beyond the traditional freight forwarding industry: for example, customer-related storage, picking, assembly or invoicing are offered.
The different logistics service providers can be differentiated from one another and from other service companies in numerous, sometimes non-uniform, ways. One possibility is to classify logistics service providers according to their range of services. For example, a distinction can be made between transport, process chain development, supply, order processing including production and distribution, and disposal.
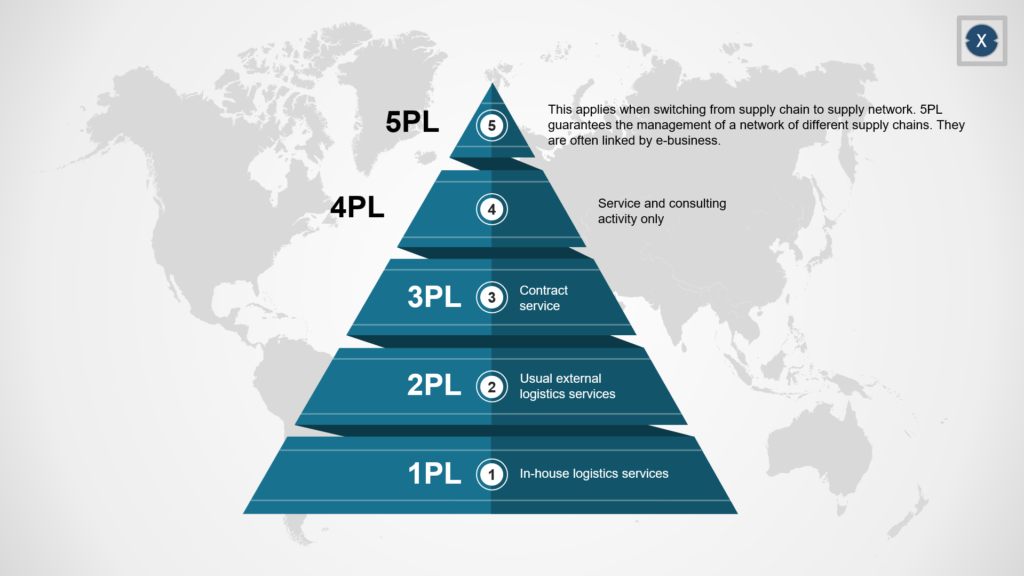
A second, very common way of demarcation is to classify logistics service providers into operational, coordination and strategic services and the use of fixed assets, so-called logistics assets. Providers are referred to as “Service Providers” and are hierarchically divided into areas (“Party Logistics”), starting with First Party Logistics up to Fifth Party Logistics Service Providers.
First Party Logistics Service Provider (1PL)
For decades, logistical processes were mostly handled internally by companies. These companies are part of the First Party Logistics Provider (1PL) segment. Here, a large part of the core logistics activities, the so-called transport, handling or storage services (TUL services), are carried out by the companies themselves. The prerequisite for this is the availability of suitable storage facilities and our own fleet of vehicles, as well as the employees required to carry out the work. However, in times of increasing specialization and the outsourcing of entire areas, this rigid solution has been weakened. The main reason for this is the costs that companies incurred in providing logistics services. With the emergence of large logistics service providers, cooperation partners quickly emerged who were able to offer the required tasks more cheaply and quickly - a main reason why the proportion of companies that handle all logistics internally has continuously fallen since the late 1970s.
1PL concept: This refers to a solution in which companies handle most of their logistics themselves. These only book additional services from external companies in special cases, such as handling international transport.
Second Party Logistics Service Provider (2PL)
With the trend towards outsourcing logistics services to external service providers that began in the 1980s, the industry continued to grow. The main cause was the lean management , in which companies concentrate on their core competencies and look for service providers for downstream processes, including logistics. These companies that offer the above-mentioned TUL services are called Second Party Logistics Service Providers (2PL).
This includes, for example, forwarding companies, storage and handling companies, shipping companies and providers from the CEP industry (operators of courier, express and parcel services), all of which have the necessary resources (warehouses, means of transport, employees).
2PL concept: Clients who do not want to process parts or all of their logistics using their own systems and resources choose the 2PL concept. Here, the required individual and combined services are purchased from various 2PL service providers or provided by them. The aim is to reduce your own logistics costs while at the same time accelerating processes through the companies that specialize in their respective services.
Third Party Logistics Service Provider (3PL)
Third-party logistics providers are external logistics service providers with an overall economic approach. Like 2PL service providers, they have their own infrastructure. However, in contrast to them, 3PL providers handle the entire logistics chain for their customers, and not just individual parts. In addition, 3PL providers take on activities such as returns management or financial and IT services for their customers.
3 PL service providers developed from 2PL service providers to so-called system service providers in the 1990s when they began to take on other activities in addition to organizing the flow of goods and information for their customers. In addition to the pure handling of the goods, customers receive far more intensive support from their service provider. These solution approaches, some of which are highly complex, ensure close cooperation between providers and customers and are usually designed for the long term due to the close integration.
Benefits of using external 3PL providers for businesses:
- Due to the specialization, the providers work much more efficiently and thus ensure that, according to surveys, clients can reduce their logistics costs by an average of 10 percent due to the high cost and time savings, while the delivery time can be shortened by 30 percent.
- In addition, due to the reduced fixed costs in the logistics sector, companies can significantly reduce the capital originally tied up there.
- The increased flexibility with regard to fluctuations in production or demand gives companies greater scope for action.
- Customers benefit from the industry know-how of the logistics service providers. These have usually set up global networks that the customer can use to their advantage.
3PL concept (contract logistics): Clients who want to outsource a large part of their cross-company logistics on a longer-term basis choose the 3PL concept. The aim is to streamline your own processes and hand over the outsourced tasks to an external service provider for a defined period of time. The client and 3PL service provider take care of controlling and management tasks together.
Fourth Party Logistics Service Provider (4PL)
In contrast to 3PL providers, 4PL service providers do not have their own resources in areas such as transport, storage or handling. Instead, 4PL providers make their know-how available to the companies that commission them. For example, a service frequently used by 4PL customers is vehicle fleet management. The core competence of the 4PL service provider lies in the planning and control of logistics processes on the customer side. He is seen as a system integrator who stands between his customers and other logistics service providers to ensure coordination and organization of all business processes within the value chain. In this respect, a 4PL provider acts in the role of a neutral coordinator between the client and the various service providers, striving to optimize the interaction of all those involved as a whole. Due to the complex structure of the processes, which can now only be managed with powerful software and hardware, 4PL providers must have a very well-developed IT structure.
The demand for this concept arose in the course of a further outsourcing effort, the aim of which is to outsource planning and control functions in companies to a fourth, neutral party. This takes over the optimization of the operational logistics chain on behalf of the customer and thus also the selection of 3PL service providers. As a kind of general contractor, the 4PL provider puts together all service components of the logistics chain in a process-optimal manner.
The approach of placing a neutral intermediary between the customer and the 3PL provider has the advantage for the former that the optimal package can be put together across the range of various service providers depending on their requirements.
Fifth Party Logistics Service Provider (5PL)
Providers in this category deal with supply chain management and specialize in offering system-oriented consulting services to their customers. This includes supporting the coordination and expansion of internal supply chains and delivery networks, where the 5PL providers ensure that the complex processes in these networks are managed efficiently. As with 4PL providers, the focus of the service is on advisory work.