Background knowledge: What about building permits for solar systems, solar carports and solar modules?
Language selection 📢
Published on: August 16, 2021 / update from: September 16, 2022 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Building permit for solar systems, solar carports and solar modules – Image: Xpert.Digital / Gearstd|Shutterstock.com
According to our Basic Law, every citizen is allowed to build whatever they want on their property according to Article 14 Paragraph 1 Sentence 1. With paragraph 1 sentence 2 of the 14th article in the Basic Law, the right to free use is again restricted: ownership obliges. Its use should also serve the public good.
Precisely because of the potentially great dangers that can arise from structures, a permit requirement generally applies: A structure may only be constructed, changed in its substance or its use or demolished if this has been approved by the building authority.
Freedom of construction, building law, building regulations and building permits
According to public building law in Germany, due to the constitutional protection of the freedom to build, the decision to grant approval is not at the discretion of the building authority: If a project is compatible with the regulations of public law, the citizen is entitled to the granting of a building permit.
The basis for the building permit is the building regulations or state building regulations of the respective federal state, because the authority for building regulations lies with the respective federal states.
The requirements of the building regulations mainly relate to the development, including parking spaces for motor vehicles. The aim of the building regulations is to avert dangers to life and limb, to avoid damage to other people's property and to ensure public safety and order.
Conference of Construction Ministers and the German Institute for Construction Technology (DIBt)
Conference of Construction Ministers
To ensure that the differences in building law in the respective countries are not too great, there is an annual conference of building ministers. A working group of ministers and senators from the 16 states of the Federal Republic of Germany responsible for urban development, construction and housing. The Federal Minister responsible for construction also regularly takes part in this conference of construction ministers.
Model regulations and model decrees adopted by the Conference of Construction Ministers serve as the basis for implementation into specific state law. So they have no direct legal effect. Each country decides to what extent the state regulation follows the model. The compilation is supplemented by instructions and work aids.
Suitable for:
German Institute for Structural Engineering (DIBt)
However, there is an agreement between the federal and state governments for the approval of non-regulated construction products and types. A technical authority in the construction sector, the German Institute for Construction Technology (DIBt), is responsible for this. It issues approvals, general building approvals, type approval and reports for construction products and types.
The background:
After the Second World War, building supervision and building regulations in the Federal Republic of Germany fell under the responsibility of the federal states. When it came to the approval of construction products, they were confronted with two problems: On the one hand, the technical complexity of the approval procedures increased significantly with the numerous new products and processes of the time of the economic miracle. On the other hand, the building materials industry demanded approvals with nationwide validity. In response to this, the Institute for Structural Engineering was founded in 1968 on the basis of a federal-state agreement. The institute took over the licensing system and other structural engineering tasks (nationally).
In the “ Model Management Technical Construction Determines (MVV TB) ”, DIBT combines the technical rules for the planning, design and execution of buildings and for construction products in a regulation.
These include mechanical strength, stability, safety and accessibility during use.
Construction products or types of construction for which there are no technical regulations are referred to as “non-regulated construction products” or “non-regulated types”. In Germany, general building approval can only be granted by the German Institute for Building Technology (DIBt) upon application. As a rule, the validity of a general building approval is limited to five years. After the validity expires, a corresponding application for an extension can be made.
If you want to use your construction product throughout Germany with a general building authority approval, your path automatically leads to the DIBt, the German approval body for non-regulated construction products. Our experts will accompany you step by step through the process – from application to approval.
➡️ Application for admission (abZ) to the DIBt
Suitable for:
General building authority approval (abZ)
In Germany, general building approval can only be granted by the German Institute for Building Technology (DIBt) upon application. As a rule, the validity of a general building approval is limited to five years. After the validity expires, a corresponding application for an extension can be made.
Before an abZ is issued for a construction product or type, all important aspects are checked, in particular safety-related properties and influences. These include stability, protection against harmful influences, health protection and protection of the natural resources as well as fire, heat, noise and vibration protection and traffic safety. The legal basis for general building approval is the model building regulations.
A typical product that is not uniformly standardized in Germany, but is applicable through general building authority approvals, is prestressing steel and corresponding accessories for prestressed concrete construction.
Thermal insulation composite systems and large-format facade panels for rear-ventilated facades are also among the building products that can be used with general building authority approval.
The approval process for issuing a nationally valid, general building authority approval begins with the submission of a corresponding application to the DIBt. The applicant is usually the manufacturer of a product. If necessary, following a recommendation from an expert committee, the DIBt determines the tests to be carried out and the evidence to be provided. After the applicant submits the evidence, the DIBt discusses the case and grants approval, again if necessary with the help of the expert committee.
The abZ is a temporary approval!
The costs for issuing a new abZ are set out in the DIBt statutes. Depending on the product or design and the effort involved, the fees for a five-year approval range between 500 and 30,000 euros . If a shorter period of approval is requested in the application, the costs are reduced by 10% per year of shortening. The fees for extending an existing license range between 10% and 50% of the cost of a new five-year license.
If an assessment document (EAD) exists at European level, a European Technical Assessment (ETA) can be applied for. The ETA regulates the placing on the market of the construction product/type in Europe. Further requirements (e.g. abZ) may exist at national level for usability in the respective member state.
No approval required - approval required
☑️ According to the model building regulations “MBO” of the construction ministerial conference, roof solar systems are free of building permit.
⚠️Carport or solar carport
A carport or solar carport is a structural system and is therefore subject to approval according to the public building law. In Baden-Württemberg, carports can be set up in the interior with up to 40 cubic meters and up to 20 cubic meters of gross space free of charge. In general, you should always ask the responsible building authority beforehand. Regulations and conditions of the respective federal state can change at any time. The best thing to do is search for it via the Internet with “Application for building permit in the simplified procedure” for the respective federal state.
⚠️ Solar parks or open space systems
Large photovoltaic systems such as outdoor systems always require approval.
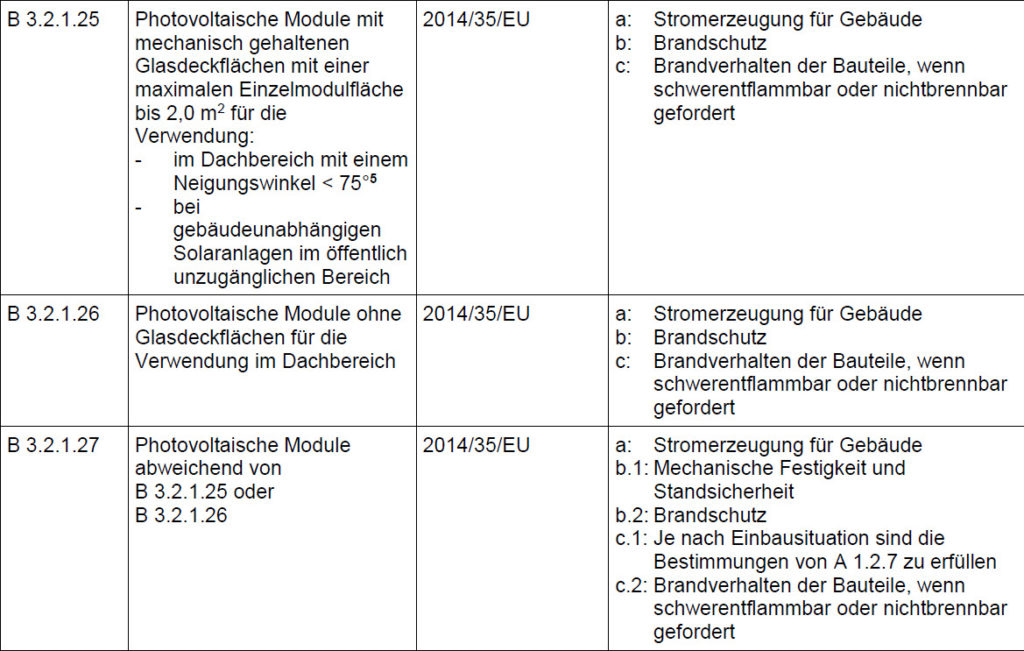
⚠️ Use of solar modules
According to the DIBt model administrative regulations for technical building regulations
Example of glass-glass solar modules (applies to B 3.2.1.25)
⚠️ Individual module area larger than 2.0 m²
⚠️ Tilt angle greater than 75° (e.g. as a solar facade)
⚠️ Solar carports without a roof (e.g. without trapezoidal sheet metal covering, modules are accessible from below)
➡️ Require general building authority approval (abZ), application for approval to DIBt
➡️ This particularly applies to overhead glazing on patio roofs or carports or solar carports
The sample management regulation Technical construction regulations (MVV TB) The DIBT stipulates that certain rules of the “DIN 18008 glass in construction- assessment and construction rules” are to be applied for glass constructions. For composite safety glass (VSG), the pendulum attempt is proof of “DIN EN 12600 glass in construction: pendulum attempt - procedure for the shock test and classification of flat glass”.
See also:
➡️ VSG float glass: laminated safety glass – float glass
➡️ VSG TVG glass : laminated safety glass – part toughened glass
Float glass is a flat glass of simple glass. It is manufactured using the “float glass process”. The disadvantage of float glass is that it breaks into many sharp-edged and pointed pieces. The risk of injury is high.
Xpert.Solar advice for solar systems, solar carports and solar modules
Xpert.Solar is a project from Xpert.Digital. We have many years of experience in supporting and advising on storage solutions and in logistics optimization, which we bundle in a large network Xpert.Plus With Xpert.Solar we combine the same know-how in the areas of photovoltaics and renewable energies.
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus