America's last trump card? AI exemption for the United States, which lags behind in robotics and automation of the world?
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: January 26, 2025 / Update from: January 26, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

America's last trump card? AI exemption for the United States, which lags behind in robotics and automation of the world? - Image: Xpert.digital
AI exemption for the USA? A comparison of the degree of automation in the USA and other countries
Global automation: Why lag behind the United States
The United States are considered pioneers in many technological areas, but they have lost a lead in international comparison in robotics and automation. While South Korea leads with the highest robot density worldwide, China, Japan and Germany have also overtaken the United States in this regard. A study by the McKinsey Global Institute shows that around 30 % of the tasks in 60 % of professions in the United States could be automated. Nevertheless, for example, 80 % of warehouse logistics are still carried out manually in the United States. The question is: Could artificial intelligence (AI) help the United States to catch up with this gap and to play a leading role in robotics and automation again?
Suitable for:
- Warehouse optimization in the USA through warehouse automation and warehouse retrofit – 80% are not yet automated!
- “Stargate AI” – US President unveils $500 billion project for US AI dominance
Robotics and automation in country comparison
USA: challenges and potential
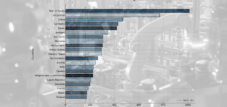
Although the United States once took a top position in robotics, you are now only tenth with a robot density of 285 units per 10,000 workers worldwide. The robot density in the automotive industry is particularly strong, followed by the electronics industry. In 2023, over 39,000 industrial robots were installed - growth of 10 % compared to the previous year. However, automation is unevenly distributed: 77 % of the robots are used in only five states - including Michigan, Iowa and Wisconsin. This concentration raises questions about regional inequality and the economic development of other areas.
The low automation rate in the USA is influenced by various factors. High costs for system integration, shortage of skilled workers and a conservative approach of many companies make it difficult to progress. At the same time, however, AI could help the United States to regain influence through innovative technologies such as autonomous robots and optimized logistics systems.
Suitable for:
South Korea: A pioneer in automation
South Korea is one of the global leaders in the automation of warehouse logistics. More than 40 % of the camps are already automated, which is due to the high technological progress and the strong innovation culture of the country. The increasing e-commerce boom and the focus on increasing efficiency are driving the use of AI-based systems. Industry analysts expect annual growth of over 10 % in the market for logistics automation until 2032. Leading companies such as Coupang and LG CNS invest intensively in AI-based solutions to optimize their supply chains and assert themselves in international competition.
China: aggressive pioneer in robotics
China has developed into the largest market for industrial robots in recent years. With a robot density of 392 units per 10,000 employees, the country is now far ahead. In 2022, 52 % of all robots installed worldwide were installed in China. This development is the result of a targeted government strategy: the robotic industry was identified as a key sector and encouraged by massive subsidies and investments.
Although China is the leadership of robots, the country still has to catch up on technological. China is still dependent on imports in the development of robot software and key components. However, the strategic objective of becoming technologically independent underlines China's long -term commitment in this area.
Japan: A pioneer of automation
Japan has been established as one of the leading nations in robotics for decades. With a robot density of 399 units per 10,000 employees, the country is one of the leaders. Companies such as Fanuc and Yaskawa Electric are worldwide in the production of industrial robots.
In addition, Japan is a pioneer in the development of humanoid robots, animal robots and other specialized applications. Japanese society shows a high level of acceptance for robotics, which is reflected in programs such as the "New Robot Strategy" of the government. This strategy aims to drive automation in sectors with low productivity, such as agriculture and healthcare.
Germany: efficiency and innovation
Germany is one of the world's leading industrialized nations in automation. With a robot density of 415 units per 10,000 employees, Germany takes fourth place. The country's strong automotive and electronics industry is driving this development. Automation is increasingly seen here as a solution for the shortage of skilled workers, since repetitive tasks can be taken over by robots.
German companies attach great importance to system integration and high -quality technology. However, the challenges exist in the high costs and the complexity of modern systems. Nevertheless, Germany is investing heavily in AI in order to optimize existing processes and open up new opportunities.
The rise of AI using the example of warehouse logistics
USA: moderate progress
The automation rate in US bearing logistics is still low in international comparison. Only about 20 % of the camps are automated. However, high labor costs and an increasing shortage of skilled workers drive investments in automation. Studies forecast an annual growth of the market for intralogistics automation solutions by over 8 % to 2032. Companies such as Amazon and Walmart are already relying on AI-based systems to optimize warehouse processes.
China: Progress through e-commerce
The e-commerce boom has triggered enormous demand for automated logistics solutions in China. Autonomous mobile robots (AMR) and other AI-based technologies are increasingly being used to increase efficiency and speed in warehouses. These developments are promoted by government investments and subsidies.
Japan: Tradition meets innovation
Although Japan has a high robot density in the manufacturing industry, automation in warehouse logistics is still relatively low. Traditional values and the high appreciation of human work have served as an obstacle in the past. In view of the increasing shortage of skilled workers, more and more Japanese companies are turning to modern automation solutions.
Germany: Efficiency in logistics
In Germany, the automation rate in warehouse logistics is also around 20 %. Challenges such as system complexity and the shortage of skilled workers inhibit the progress. At the same time, companies are increasingly relying on innovative AI solutions to increase efficiency and sustainability in logistics.
For decades, Germany has been considered a highly automated industrial nation with a high density of robots. Automated processes are deeply rooted, particularly in the automotive and mechanical engineering industries. Nevertheless, according to estimates in the area of warehousing, around 80% of the locations are still equipped without extensive automation (varies: production sometimes 43%, warehouse often <20%).
The role of AI in warehouse logistics
AI-based technologies have the potential to fundamentally change warehouse logistics:
- Autonomous vehicles: With the help of AI, autonomous vehicles calculate optimal routes and improve efficiency.
- Quality assurance: Systems for image detection analyze products to damage and ensure automated quality control.
- Investment management: AI monitors inventory in real time and optimizes reorder.
- Predictive maintenance: AI-based maintenance systems predict machine failures and reduce unplanned downtime.
KI: A liberation for the USA?
AI offers the United States the opportunity to regain its competitiveness in robotics and automation. The development and implementation of innovative technologies could increase companies efficiency, flexibility and productivity. At the same time, investments in research and training would be necessary to remain competitive in the long term.
Suitable for:
The United States has lost ground in international comparison, but through targeted measures you can play a leading role in automation. Are necessary:
- Investment in research and development: More government and private resources should flow into the development of AI and robotics.
- Promoting skilled workers: Training AI and robotics experts should be a priority.
- Regulatory support: An innovation-friendly regulatory environment is crucial to encourage companies to invest in new technologies.
By implementing these steps, the U.S. can benefit from an AI-powered automation strategy and increase its economic performance while finding sustainable solutions to global challenges.
🎯🎯🎯 Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, fivefold expertise in a comprehensive service package | R&D, XR, PR & SEM

AI & XR 3D Rendering Machine: Fivefold expertise from Xpert.Digital in a comprehensive service package, R&D XR, PR & SEM - Image: Xpert.Digital
Xpert.Digital has in-depth knowledge of various industries. This allows us to develop tailor-made strategies that are tailored precisely to the requirements and challenges of your specific market segment. By continually analyzing market trends and following industry developments, we can act with foresight and offer innovative solutions. Through the combination of experience and knowledge, we generate added value and give our customers a decisive competitive advantage.
More about it here:
With artificial intelligence: An opportunity for the USA to catch up globally - background analysis
AI as the key to regaining US leadership in robotics and automation?
The United States, once the undisputed leader in technological innovation, is facing increasing competitive pressure in the areas of robotics and automation. While other nations such as South Korea, China, Japan and Germany are significantly optimizing their production processes through the use of robots and intelligent systems, the USA appears to have fallen behind in this discipline. The question now is: Can artificial intelligence (AI) help the US catch up and regain leadership in robotics and automation?
A study by the McKinsey Global Institute reveals remarkable potential for automation within the US economy. According to this, 30 percent of the tasks in 60 percent of all professions could be taken over by automated systems. This contrasts with the reality where approximately 80 percent of warehouse logistics in the US are still handled manually. This discrepancy highlights a great opportunity, but also the need to act urgently in order to survive in global competition.
Robots and automation in an international comparison
The United States: A Loss of Former Leadership
The United States was once a leader in the development of robotics and automation. Today, however, their robot density in manufacturing has slipped to 10th in the world, at about 285 units per 10,000 workers. While the automotive industry is still the largest buyer of industrial robots, followed by the electronics industry, the installation of over 39,000 industrial robots in 2023, a 10% increase from the previous year, indicates increased interest in automation.
A notable phenomenon is the uneven distribution of robots in the United States. A study found that 77% of all industrial robots sold are used in just five states: Iowa, Michigan, Kansas, Wisconsin and Minnesota. These “robot centers” are mainly characterized by a strong automotive industry. This regional concentration raises questions about economic development and the availability of skilled workers in other parts of the country. The challenge is to distribute the benefits of automation more evenly across the country, strengthening the entire economy.
South Korea: World leader in automation and robotics
South Korea is the undisputed leader in robot density worldwide, with an impressive 1,000 industrial robots for every 10,000 manufacturing workers. This is more than three times the global average and reflects the country's consistent investment in automation technologies. The semiconductor and electronics industries are particularly driving forward the use of robotics, followed by the automotive industry, which also accounts for a significant share of the use of modern robotic solutions.
A key feature of the South Korean robotics landscape is the strong support from the government, which specifically drives innovation with funding programs and tax incentives. In addition, the high concentration of leading technology companies such as Samsung and LG ensures that South Korea sets global standards in both the development and application of robotics technologies. Nevertheless, the country faces the challenge of making the benefits of automation more accessible to small and medium-sized companies in order to ensure competitiveness across all economic sectors.
China: Aggressive Growth and Strategic Investments
In recent years, China has become the world's largest market for industrial robots. In 2022, 52% of all industrial robots installed worldwide were installed in China. The robot density is 392 units per 10,000 workers. The Chinese government has classified the robotics industry as strategically important and is massively supporting its development through government investments, funding programs and tax breaks. China's robot density is 12.5 times higher than would be expected based on manufacturing wage levels. This illustrates the Chinese government's aggressive strategy to promote automation in order to modernize its own industry and make it more competitive.
Although China leads the world in robot density, deficiencies remain in some areas. China is still dependent on imports, particularly for the development of robot software and the production of key components. This shows that although China uses a large number of robots, it has not yet reached the same technological maturity as, for example, Japan or Germany. The focus is now on closing this technological gap and reducing dependence on foreign providers.
Japan: pioneer and innovator in robotics
Japan has long been a leading nation in robotics and automation. The country has the highest robot density per employee in the processing business worldwide. In 2012, Japan delivered robots worth around 3.4 billion yen, which corresponds to almost 50 % of the global market share. Japanese companies such as Fanuc and Yaskawa Electric are among the world's leading manufacturers of industrial robots and have contributed significantly to the development of modern robot technology. The Japanese government supports automation by the “New Robot Strategy” (2016-2020) in order to speed up automation in economic sectors with low labor productivity, such as agriculture, infrastructure and healthcare.
Japan is characterized by a wide range of robotic applications that go far beyond industrial manufacturing. In addition to industrial robots, humanoid robots, animal robots, guard robots and even astronaut robots are also developed and used in Japan. This diversity shows the high acceptance of robots in Japanese society and the willingness to research and implement new technologies. Japanese culture often sees robots as partners and helpers in everyday life, which makes their integration into social life easier.
Germany: engineering skills and automation expertise
Germany is also one of the leading nations in robotics and automation. The robot density in the German manufacturing industry is 415 units per 10,000 employees, placing Germany third in the world. The German economy benefits from a strong automotive and electronics industry that relies heavily on automation. German companies see AI and automation as a solution to the shortage of skilled workers. By using robots, companies can fill vacancies while increasing productivity. The focus on precision, efficiency and quality in production has made Germany an important center for robotics and automation.
Germany is also relying heavily on the development of collaborative robots (cobots) that can work closely with human employees. These cobots are particularly suitable for flexible production environments and can support people in physically demanding or dangerous tasks. German engineering and the close collaboration between research and industry ensure that Germany will continue to play an important role in robotics.
The role of AI in warehouse logistics
The status quo in the USA
In the USA, the level of automation in warehouse logistics is still moderate compared to international standards. It is estimated that only about 20% of warehouses in the United States are automated. However, high labor costs and the increasing shortage of skilled workers are forcing US companies to invest more in automation. The intralogistics automation solutions market in North America is expected to experience annual growth of over 8% through 2032. Geopolitical events and uncertainties in global supply chains have increased the need for resilient and flexible logistics solutions, further driving automation. Many U.S. companies are realizing that if they do not modernize and automate their warehouse processes, they will not be able to remain competitive in the long term.
China: A new player in the field of warehouse automation
China has invested heavily in the automation of warehouse logistics in recent years. The e-commerce boom and the increasing demands for efficiency and delivery times are driving this development. Chinese companies are increasingly relying on autonomous mobile robots (AMR) and other AI-based solutions to optimize warehouse processes. The rapid expansion of e-commerce has led to the emergence of huge warehouses in China that can only be operated efficiently through a high level of automation. This dynamic is driving innovation in warehouse logistics.
Japan: tradition and new approaches
In Japan, the level of automation in warehouse logistics is still comparatively low despite the high density of robots in the manufacturing industry. Cultural factors and the high value placed on human labor have held back automation in the past. However, the increasing shortage of skilled workers is forcing Japanese companies to invest more in automation. Japanese companies are trying to combine traditional values with modern technologies and are looking for solutions that do not completely replace human work, but complement and facilitate it.
Germany: Innovative solutions for complex processes
For decades, Germany has been considered a highly automated industrial nation with a pronounced density of robots, especially in the automotive and mechanical engineering sectors, where automated processes are deeply rooted. Nevertheless, it turns out that the level of automation in warehouse logistics is comparatively low: according to estimates, only around 20% of warehouses are automated, while higher values of up to 43% are achieved in production. Around 80% of warehouse locations in Germany still do without extensive automation. The main challenges include the complexity of system integration and the shortage of skilled workers. Despite these hurdles, German companies are increasingly relying on innovative solutions to increase efficiency and flexibility in warehouse logistics. German engineering and high quality standards come into play, making it possible to efficiently automate even complex warehouse processes. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into existing systems is increasingly coming into focus in order to further optimize warehouse logistics and make them future-proof.
Concrete AI applications in warehouse logistics
AI has the potential to significantly increase efficiency in warehouse logistics. A McKinsey study shows that AI technologies have the potential to double companies' cash flow. A Bitkom study shows that the acceptance of AI in the logistics industry is constantly increasing. Examples of the use of AI include:
Autonomous vehicles (drive units)
AI-controlled vehicles calculate the most efficient routes through the warehouse, reduce empty trips and optimize transport times. They can adapt to changing conditions and ensure everything runs smoothly.
quality assurance
AI-based systems check items for damage or errors. By using image recognition, for example, the condition and size of packages can be recorded to ensure that only defect-free goods leave the warehouse.
Voice-controlled picking (pick-by-voice)
Voice assistants support the picking of goods and guide employees through the warehouse. This reduces errors and speeds up the process.
AI-based griffin arms
Robot greetets that learn to use and handle sensitive articles with the help of AI enable the automation of tasks that have previously had to be carried out by humans.
Inventory management
AI systems monitor inventory in real time and optimize re-orders, which reduces the risk of over or infringes. This leads to more efficient use of the storage space and improved capital loyalty.
Route planning
AI-based systems determine the optimal routes for delivery vehicles, which reduces transport costs and the delivery times are improved.
Predictive maintenance
AI systems say machine failures beforehand and optimize maintenance intervals to minimize downtimes and to extend the lifespan of the systems.
AI as a “game changer” for the USA?
AI can help the USA to catch up in robotics and automation by:
The efficiency in warehouse logistics Steiger
AI-based systems automate processes that have so far been carried out manually and thus increase productivity and throughput. This is particularly important to meet the growing requirements of e-commerce.
The development of new robot technologies accelerates
AI enables the development of more flexible, more intelligent and easier to use robot generations. These robots can better adapt to changed conditions and take on new tasks.
The integration of robots into existing systems facilitates
AI makes the integration of robots into existing warehouse and production systems easier and cheaper. This lowers the hurdles for companies to introduce automation solutions.
The competitiveness of the US industry strengthens
By using AI in robotics and automation, US companies can increase their productivity and flexibility and thus exist in international competition. This is essential to strengthen the US economy and secure jobs.
An McKinsey study predicts that companies that implement AI technologies at an early stage can double their cash flow. This underlines the enormous economic potential of AI in logistics and production.
Suitable for:
- From “Star Wars” (SDI) to “Stargate”: Can the USA finally break the curse of mega-projects? AI race like in the Cold War?
- Why companies find it so difficult to use AI
The use of AI in warehouse logistics also brings challenges
Data protection concerns
AI systems need access to large amounts of data, which can lead to data protection concerns. It is important that companies are transparently dealing with data use and protecting the privacy of employees and customers.
High implementation costs
The implementation of AI-based systems can be associated with high costs. However, these costs must be considered in the long term, since they can quickly amortize themselves through the efficiency increases and cost reductions.
Complexity of system integration
The integration of AI systems into existing warehouse and production systems can be complex. It is important that companies rely on experienced specialists when implementing.
Lack of qualified specialists
Qualified specialists are required to develop and implement AI systems. It is therefore important that companies invest in the training and further education of their employees.
At the same time, the use of AI uses the example of warehouse logistics considerable opportunities
Increased efficiency
AI-based systems can automate processes and thus significantly increase productivity and throughput.
Cost reduction
Optimized routes and warehousing reduce operating costs and enable better use of resources.
Improved customer experience
Faster and more precise deliveries improve customer satisfaction and strengthen customer loyalty.
Competitive advantage
Companies that use AI are better prepared for market changes and can adapt faster to new requirements.
sustainability
AI can optimize energy consumption and reduce CO2 emissions. A Samsara study shows that 87 % of managers in the German transport and logistics industry invest in AI technologies in order to increase efficiency and improve sustainability. This shows that AI not only offers economic advantages, but can also contribute to environmental protection.
Impact on the world of work
The use of AI in warehouse logistics will have an impact on jobs. Repetitive tasks, such as picking, are increasingly automated. This can lead to a loss of jobs, especially in the area of low -qualified activities. At the same time, however, new jobs are also created, for example in development, maintenance and monitoring of AI systems. It is important that companies and politics develop strategies in order to prepare employees for the changes in the world of work and offer further training opportunities.
Leading US companies in the field of AI-based logistics
Some US companies have already started to integrate AI into their warehouse processes:
- Amazon: Use AI-based robot to increase efficiency in the logistics centers.
- Walmart: Use AI systems to optimize the inventory and to shorten the delivery times.
- Honeywell: offers AI-based solutions for warehouse automation.
- Symboatic: Developed AI-controlled robot systems for warehouse logistics.
These examples show that change has already started and that companies that rely on AI early will have a competitive advantage.
Lessons from other countries
The comparison of the United States with China, Japan and Germany shows that the United States can learn from the experiences of other countries to strengthen its position in robotics and automation:
China
The United States can learn from China's proactive government policy that massively promotes the development and implementation of robotics and AI. State investments in research and development as well as targeted support programs for companies can accelerate automation.
Japan
Japan shows how important the development and use of collaborative robots (cobots) is. Cobots can improve cooperation between man and machine and thus increase productivity and flexibility in warehouse logistics.
Germany
Germany demonstrates how automation can help to address the shortage of skilled workers. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can occupy vacancies and at the same time improve working conditions for employees.
AI as the key to the future of the US economy
The United States has lost ground in robotics and automation to China, Japan and Germany. However, KI offers the potential to help the USA into a “liberation strike” and to catch up with the deficit. By using AI in warehouse logistics, US companies can increase their efficiency and flexibility and thus exist in international competition. The use of AI also has challenges, such as data protection concerns and high implementation costs. At the same time, AI also offers opportunities, such as efficiency increase, cost reduction and improved customer experience. The effects of AI on the jobs in warehouse logistics are ambivalent. Repetitive tasks are increasingly automated, but at the same time new jobs are also being created in the development and maintenance of AI systems.
In order to exploit the full potential of the AI, the USA should take the following steps:
- Investments in research and development: The United States should invest more in the research and development of AI-based robot technologies.
- Promotion of AI talents: The USA should promote the training of AI specialists and create incentives for employment in this area.
- Creation of a supportive regulatory environment: The United States should create a regulatory environment that supports the development and implementation of AI-based solutions in warehouse logistics.
- Promotion of cooperation between industry and research: closer cooperation between universities and companies can accelerate the technology transfer and promote innovations.
- Supporting small and medium-sized companies (SMEs): SMEs play an important role in the US economy, and it is important that they also have access to AI technologies.
- Development of strategies for the transfer of workers: It is important that the US government and industry develop strategies in order to prepare employees for the changes in the world of work and to offer further training opportunities.
If the United States takes these steps, you have the potential to play a leading role in robotics and automation and to use the advantages of these technologies for your economy and society. Artificial intelligence is not just a technological progress, but a tool that the United States can use to increase its competitiveness, create jobs and to shape a more sustainable future. The time to act is now.
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus