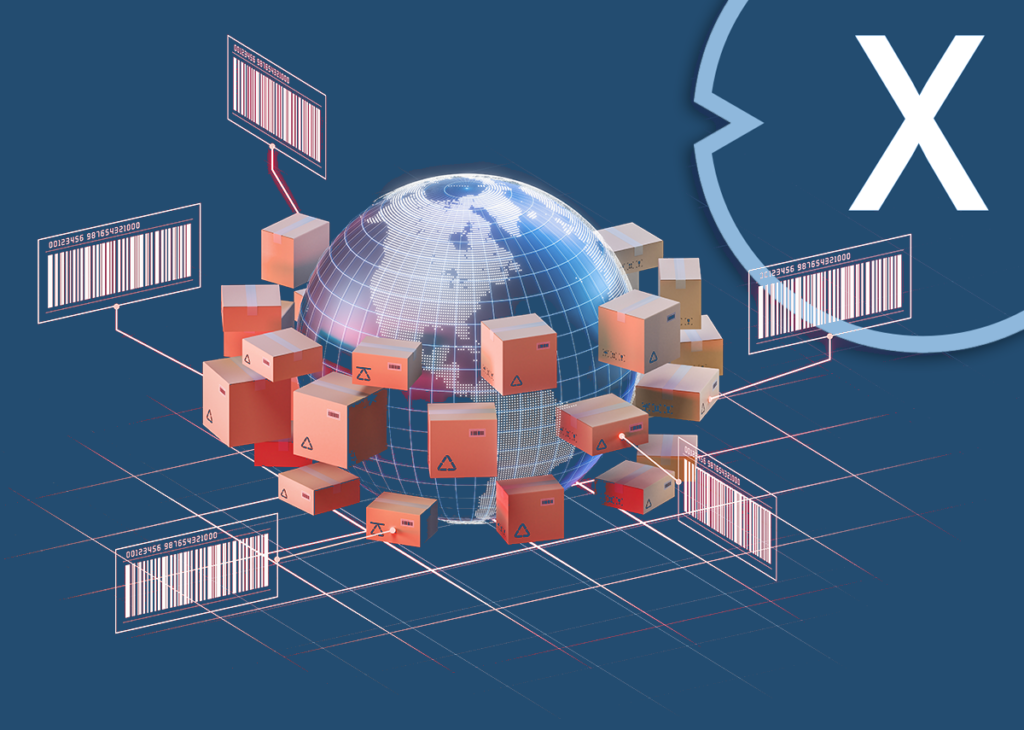
2D code, the logistical quantum leap: How the 2D stitch code (matrix code) transforms intralogistics and global logistics in real time
Language selection 📢
Published on: June 29, 2023 / update from: June 29, 2023 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

How the 2D matrix code transforms intralogistics and global logistics into real time - Image: Xpert.Digital
The future of 2D barcodes in retail
The retail industry is preparing for a pioneering change that has the potential to fundamentally revolutionize the way in which products are pursued and recorded worldwide. Under the name “Sunrise 2027”, the industry is planning to replace the conventional 12-digit barcode, which consists of vertical lines and is printed on packaging, with a two-dimensional, web-enabled 2D line code. This innovative step is coordinated by the non -profit organization GS1, which is responsible for the standardization of strich codes worldwide. In the United States in particular, the previous Universal Product Code (UPC) line codes are to be replaced by a new 2D type that encodes information both horizontally and vertically. The ultimate goal of this initiative is to accept only 2D cutting codes at the health insurers by 2027.
The advantages of the 2D barcode
The transition to 2D barcodes offers a variety of benefits for retailers and consumers. Compared to the traditional 1D barcode, which can only store limited information, the 2D barcode allows a larger amount of data to be encoded. By integrating horizontal and vertical information, it becomes possible to store detailed product information, including production date, shelf life, batch number and origin, in a single code. This significantly improves product traceability, allowing retailers to track deliveries more accurately, manage inventory more efficiently and ensure product safety.
Another advantage of the 2D barcode is its web-enabled nature. By integrating web-based functions, consumers, but also retailers and logistics service providers, can access advanced information and real-time data. Using smartphone apps or special scanners, consumers can access detailed product information, such as nutritional information, product reviews, manufacturer information and even sustainable proof of origin. This improved transparency builds trust and enables consumers to make informed purchasing decisions.
The role of GS1 and global implementation
GS1, the organization behind barcode standardization, plays a critical role in coordinating the global implementation of 2D barcodes in retail. As an international organization with members from various industries, GS1 ensures that the transition to 2D barcodes is smooth and consistent. GS1 works closely with retailers, manufacturers, logistics providers and regulators to establish consistent standards and guidelines.
The introduction of the 2D barcode will be gradual and will include training, information campaigns and technical support for the companies involved. Coordinating this global initiative is a complex task as there are a variety of stakeholders and technologies that need to be taken into account. Collaboration between GS1 and the companies involved is critical to ensure the transition goes smoothly and the desired goals are achieved.
The impact on unified commerce and omnichannel
The introduction of the 2D barcode will undoubtedly also have an impact on unified commerce and omnichannel. By integrating web-enabled features, 2D barcode opens up new opportunities for retailers to offer seamless shopping experiences across multiple channels. Consumers can research products online, scan them in-store and get more information, or order them from the comfort of their own home. This seamless integration of online and offline channels strengthens customer loyalty and creates consistent brand experiences.
In addition, the 2D barcode enables improved traceability of products along the entire supply chain. By integrating real-time data into the 2D code, retailers and logistics service providers can track the exact location and status of products at any time. This enables more efficient inventory management, more precise delivery scheduling and faster response to any supply chain issues.
➡️ The global initiative “Sunrise 2027” marks a significant step in the development of barcodes in retail. The transition from conventional 1D cutting codes to 2D cutting codes will improve the traceability of products, increase transparency and enable seamless shopping experience via different channels. GS1 plays a crucial role in coordinating this global initiative and works closely with companies from various industries. While the changeover to the 2D cutting code brings technical and logistical challenges, it also offers great opportunities for retail, supply chain and consumers. The 2D tapping code will undoubtedly play an important role in improving efficiency, transparency and customer loyalty in retail and falling into a new era of shopping.
The 2D barcode refers to the matrix code or 2D matrix code
Intelligent Smart Scan Area Cameras & 2D Matrix Code – Image: Xpert.Digital / Creativa Images|Shutterstock.com
The 2D barcode usually means the matrix code. The matrix code is a two-dimensional code consisting of square modules that encodes information both horizontally and vertically. Unlike the traditional 1D barcode, which consists only of vertical lines, the matrix code can store a larger amount of data and enables more precise and diverse encoding of information. The matrix code is a further development of the barcode and is often referred to as a 2D barcode or 2D barcode.
With the introduction of the barcode (1D barcode) in 1973, global logistics was revolutionized
The barcode has revolutionized global logistics in several ways:
Improved inventory management
By using barcodes, companies can manage their inventory more effectively. Each product is tagged with a unique barcode that can be scanned to automatically update inventory. This enables faster and more accurate inventory taking and reduces the risk of overstocking or understocking.
More efficient distribution of goods
Barcodes help to speed up the flow of goods and reduce the error rate. When each product is barcoded, shipping labels can be printed quickly and easily, speeding up the processing of orders and reducing the risk of shipping errors.
Improved traceability
Barcodes allow companies to track the whereabouts of products in the supply chain, from production to sale. This is particularly important when tracking products in the event of recalls or product quality issues.
Automation of business processes
The use of barcodes has helped automate business processes by reducing manual data entry and enabling the use of automated scanners and readers. This has led to greater efficiency and productivity in the logistics industry.
➡️ The barcode has revolutionized the logistics industry by enabling faster, more efficient and more precise processing of goods. Technology has helped increase productivity and reduce costs, which in turn has led to higher customer satisfaction and business competitiveness.
Here are some impacts of barcode on logistics:
Automation and efficiency
By using barcodes, manual data entry has been drastically reduced. Employees can easily scan products and inventory instead of manually entering information. This has led to significant automation and increased efficiency in logistics. The barcode enables faster and more accurate capture of data, resulting in faster order fulfillment, improved inventory control and an optimized supply chain.
Real-time data availability
Barcodes enable real-time tracking of products throughout the entire supply chain. When a product is scanned, the relevant information becomes immediately available. This allows companies to monitor the exact location, inventory and status of their products and respond to changes in real time. Real-time data improves transparency, planning and forecasting, enabling faster and more effective decision-making in logistics.
Inventory management and tracking
Barcodes enable precise inventory management and product tracking. By scanning the barcodes, companies can update inventory in real time, reduce inventory losses, and maintain accurate records of inventory. Accurate tracking of products also makes it possible to quickly identify bottlenecks or problems in the supply chain and take appropriate action.
Error reduction and quality control
Barcodes minimize human errors in data entry and processing. Automating data capture reduces errors caused by manual entry or reading errors. This leads to improved quality control and a reduction in errors in logistics. Accurately capturing product data and assigning it to specific orders or customers helps increase customer satisfaction and reduce error rates.
Efficient tracking of deliveries
Barcodes enable efficient tracking of deliveries. By scanning the barcodes, deliveries can be tracked in real time and companies can monitor the status and location of the shipments. This makes it possible to provide customers with accurate information about delivery status and to identify and resolve possible delays or problems at an early stage.
➡️ The success of the barcode lay in its ease of use, widespread adoption, and ability to improve efficiency, accuracy, and transparency in logistics. By implementing barcodes, companies have been able to streamline their operations, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and advance the entire logistics industry. The barcode has become a fundamental tool in logistics and has helped revolutionize global trade and supply chains.
What are the problems with the barcode that can be solved by switching to the matrix code?
The barcode undoubtedly has many advantages and is an effective tool to improve logistics. However, there are some challenges associated with the barcode and these could be resolved by switching to the matrix code.
Here are some problems with the barcode:
Limited data capacity
A barcode can only store a limited amount of information. It can be difficult to encode large or complex data in a traditional barcode. This may lead to limitations in traceability or accurate capture of product information.
Readability
Barcodes are prone to reading errors. Contamination, damage or distortion can affect the readability of a barcode and lead to errors in data capture. Difficulties can arise, particularly in poor lighting conditions or when using poorly printed barcodes.
Limited display options
Barcodes are limited in their appearance and offer little scope for displaying brand identity or additional information. They are limited to simple line and number combinations and cannot contain graphic or multi-dimensional elements.
Matrix code, such as 2D matrix code, offers potential solutions to these problems:
Expanded data capacity
Matrix codes can offer significantly greater data capacity than traditional barcodes. You can store richer information, including text, numbers, graphics, and even links to online content. This allows for more detailed traceability and more comprehensive capture of product information.
Better readability
Matrix codes are typically more robust and offer better readability than traditional barcodes. Their structure, which consists of a matrix of points, makes them less susceptible to damage or distortion. This increases the accuracy and reliability of data collection.
Advanced display options
Matrix codes offer more flexibility in terms of appearance and presentation. They can be created in different shapes and sizes and provide space for graphic elements or additional information. This allows companies to better represent their brand identity and provide additional information to consumers.
➡️ A switch to matrix code would therefore improve data capacity, readability and display options and meet the requirements for more precise, versatile and robust marking. This could further improve traceability, inventory management and overall efficiency in logistics.
To what extent will the 2D matrix code change unified commerce and omnichannel when it replaces the 1D barcode globally in 2027?
The transition from 1D barcode to 2D matrix code has already begun and will impact the unified commerce and omnichannel space.
Extended product data
2D matrix codes can store larger amounts of data than 1D barcodes. This allows for more detailed product information, such as batch numbers, serial numbers, expiration dates and other specific information. In unified commerce and omnichannel, this can help customers receive more product information across different channels and thus make informed purchasing decisions.
Better traceability
With the 2D matrix code, products can be traced better. By storing unique identification numbers and other information, companies can track the entire life cycle of a product, from manufacturing through the supply chain to sale to the customer. This enables more effective inventory management and traceability, which in turn can lead to an improved customer experience in unified commerce and omnichannel.
More efficient tracking of goods
The 2D matrix code enables faster and more accurate capture of product data. Employees in warehouses, fulfillment centers and stores can scan and track products more efficiently using 2D scanners or smartphones. This allows inventory to be updated in real time and the supply chain to function more smoothly. In unified commerce and omnichannel, companies can ensure better inventory control and more efficient fulfillment.
Improved personalization and interaction
The 2D matrix code can also be used for personalized offers and interactions. By scanning the code, customers can access specific offers, recommendations or information that meet their individual needs. In unified commerce and omnichannel, this can lead to a personalized and tailored customer experience by providing customers with relevant and targeted content across different channels.
Simplified payment processes
2D matrix codes can also be used for mobile payment services and digital wallets. Customers can scan the code to process payments quickly and securely without having to manually enter credit card information. This can simplify the checkout process and make payment in unified commerce and omnichannel more convenient.
➡️ The transition to 2D matrix code is therefore expected to help further improve unified commerce and omnichannel by enabling better product information, traceability, goods tracking, personalization and payment processes. Companies can take advantage of the extended code format to optimize customer experience and make operations more efficient.
Why is it so important that products can be traced better? What exactly is this needed for?
The improved traceability of products is very important in various areas of the economy
Quality assurance and product safety
Traceability allows companies to monitor and ensure the quality of their products. In the event of quality issues or recalls, companies can quickly and accurately determine which products are affected and take appropriate action to ensure consumer safety.
Compliance with regulations and standards
In many industries there are legal regulations and standards that require complete traceability of products. This particularly applies to areas such as food, pharmaceuticals and medical devices, where the safety and quality of the products are of crucial importance. Traceability allows companies to prove that their products meet the required standards and meet legal requirements.
Effective quality management and troubleshooting
Traceability allows companies to identify and efficiently correct errors or defects in their products. When a problem occurs, companies can trace the exact manufacturing process, materials used, and other relevant information to determine the cause of the problem and take appropriate action to avoid similar incidents in the future.
Supply chain optimization
Traceability plays an important role in supply chain optimization. By accurately tracking products throughout the supply chain, companies can monitor the location, status and condition of products in real time. This enables more efficient inventory management, improved planning and forecasting, faster response to changes in demand and an overall optimized supply chain.
Consumer trust and transparency
Traceability helps create trust among consumers. Customers want to know where their products come from, how they were made and what ingredients they contain. Through transparent traceability, companies can provide consumers with more accurate and comprehensive information about their products, thereby increasing customer trust and loyalty.
➡️ Improved product traceability enables better quality control, safety, regulatory compliance, supply chain efficiency and consumer trust. It is an important tool for ensuring product integrity, minimizing risks and increasing customer satisfaction.
No-line commerce, unified commerce and omnichannel - the differences
No-line commerce, unified commerce and omnichannel are closely related concepts that refer to the integration of different sales channels in retail. Although there are similarities between them, there are also differences in their emphasis and approach:
1. No-line commerce
The term no-line commerce refers to the transformation in retail that eliminates the traditional distinction between online and offline channels. It's about providing a seamless shopping experience, regardless of which channel customers use to interact with the company. The focus is on integrating various sales channels to provide customers with a seamless shopping experience.
2. Unified Commerce
Unified Commerce goes one step further than no-line commerce and refers to the complete integration of all of a company's sales channels and systems. It's about creating a unified platform that allows orders, inventory, customer data and other relevant information to be seamlessly synchronized and managed. Unified Commerce strives for central data storage to ensure a consistent customer experience across all channels.
3. Omnichannel
Omnichannel commerce refers to the concept of seamlessly integrating and collaborating across different sales channels to provide customers with a consistent and holistic shopping experience. It's about connecting the channels so that customers can, for example, research products online, view them in store and then order online, or they can shop online and pick up or return the products in store. The main goal is to provide flexibility and convenience to customers and ensure they have a seamless shopping experience across different channels.
➡️ The differences between these concepts lie in their emphasis and scope. No-line commerce focuses on integrating and removing boundaries between channels, while unified commerce focuses on comprehensive integration of systems and data. Omnichannel commerce emphasizes how channels work seamlessly together to provide customers with a consistent experience. Although there are differences, all three concepts are designed to provide customers with a seamless and frictionless shopping experience across different channels.
Therefore, it would not be correct to say that unified commerce is better than omnichannel or vice versa. Both concepts have their own benefits and are aimed at different aspects of the retail customer experience. The choice between unified commerce and omnichannel depends on a company's individual goals, resources and business model.
Unified Commerce strives for complete integration and synchronization of all of a company's sales channels and systems. It aims to create central data storage and ensure seamless collaboration between channels. This creates a unified and consistent customer experience. Unified Commerce can be particularly beneficial when a company has a variety of sales channels, complex business processes or an extensive product range. It enables efficient data management, inventory control and customer loyalty across all channels.
Omnichannel Commerce focuses on the seamless integration and collaboration of different sales channels to provide customers with a consistent shopping experience. It allows customers to flexibly switch between channels and offers them the opportunity to research products online, view them in store and then order online or vice versa. Omnichannel commerce emphasizes customer convenience and convenience. It is particularly beneficial when a company has a strong presence across channels and aims for seamless integration between online and offline experiences.
➡️ It is important to note that unified commerce and omnichannel are not mutually exclusive concepts. In fact, they can often go hand in hand, and many companies pursue a strategy that combines elements of both approaches to reap the benefits of both. Ultimately, the choice between unified commerce and omnichannel should be tailored to a company's specific needs and business goals. It is important to consider individual needs and resources to achieve the best possible solution for customer experience and business success.
➡️ The term “no-line commerce” was shaped to describe the change in retail, in which the traditional distinction between online and offline channels is lifted. Instead, various sales channels are seamlessly connected to offer customers a seamless shopping experience. “Omnichannel Commerce” describes the concept similarly, but refers more specifically to the seamless integration and cooperation of various sales channels, including physical shops, online shops, mobile apps, social media and other channels. The aim is to offer customers a consistent and holistic shopping experience, regardless of which channel they interact with the company. In the Omnichannel Commerce, the various channels are integrated so that customers, for example, research products online, view them in the shop and then order them online, or you can shop online and pick up or return the products in the shop. The main goal is to offer customers flexibility and convenience and ensure that they have a seamless shopping experience over different channels without discrepancies or inefficiencies. The term “Omnichannel Commerce” emphasizes the importance of an integrated and consistent customer experience across all channels, while “no-line-commerce” focuses on the fact that the boundaries between the channels disappear and customers have a smooth shopping experience regardless of the choice of channel. Ultimately, both terms describe the trend towards a holistic and cross -channel shopping experience in retail.
Omnichannel or multichannel?
Omnichannel and multichannel are two terms that are often used in the context of sales and marketing. They describe different approaches to interacting with customers through different channels. Here are the basic differences:
Multichannel refers to the provision of sales and communication channels through which customers can interact with a company. These can be, for example, physical stores, online shops, call centers, social media or mobile apps. In a multichannel approach, these channels are often separate and operate independently of one another. Customers can move between channels, but there may not be seamless integration or continuity between them. For example, a customer may search for a product online but then purchase it in the physical store.
Omnichannel, on the other hand, goes one step further. It refers to an integrated and seamless customer experience across all channels. In the omnichannel approach, the different channels are connected to each other and offer consistent communication and interaction. For example, customers can search for products online, add them to their shopping cart and pick them up later in the store, or vice versa. Information about the customer, such as shopping cart or purchase history, is synchronized across all channels to provide a personalized experience.
Although omnichannel is seen as an advanced form of multichannel, this does not necessarily mean that multichannel is a thing of the past. Multichannel can still make sense, especially for companies that are just starting out or have limited resources. It depends on the specific needs of the company and the target group. However, omnichannel is increasingly seen as more important as customers expect a seamless and consistent experience across all channels. Companies are increasingly investing in omnichannel strategies to increase customer satisfaction and gain competitive advantages.
No-line commerce - what you should know
The no-line commerce is a concept in retail that cancel the boundaries between online and offline shopping. The term “no-line” alludes to the lack of a clear dividing line between online and offline.
In traditional e-commerce, products are sold exclusively via online channels, while in stationary retail sales take place in physical stores. With no-line commerce, on the other hand, the advantages of both sales channels are combined and seamlessly integrated.
No-line commerce allows customers to research products online, compare prices, and place orders. However, they also have the opportunity to experience, touch and try out the products in brick-and-mortar stores before they decide to buy them. No-line commerce thus offers a seamless integration of online and offline experiences.
An example of no-line commerce is click-and-collect, where customers can order online and then pick up the products in a brick-and-mortar store. This allows customers to combine the convenience of online shopping with the immediate availability and personal contact of brick-and-mortar stores.
Another example is the ability to return or exchange online orders in physical stores. Customers can return products purchased online to physical stores, providing flexibility and convenience.
No-line commerce aims to take advantage of both channels and create a seamless and holistic shopping experience. Companies that implement no-line commerce offer their customers more flexibility, choice and convenience while strengthening loyalty to their brand.
It is important to note that no-line commerce requires a strategic approach to successfully implement the integration of online and offline channels. Companies must adapt their sales and logistics processes to ensure smooth communication and coordination between channels. This often requires the use of technologies such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, inventory management systems and integrated e-commerce platforms.
No-line commerce is a response to changing customer needs and expectations in a digitalized world. Customers want to shop flexibly and take advantage of both worlds. Companies that successfully implement no-line commerce have the opportunity to strengthen customer loyalty, reach new target groups and increase their competitiveness.
Unified Commerce - what you should know
Unified Commerce refers to a comprehensive and seamless integration of various sales channels and systems to create a unified and consistent shopping experience for customers. It's about overcoming the boundaries between different sales channels such as brick-and-mortar stores, online shops, mobile applications and social media.
In traditional retail, distribution channels were often disconnected, leading to inconsistencies in product range, pricing and customer experiences. Unified Commerce aims to eliminate this fragmentation and seamlessly connect all sales channels.
Unified Commerce allows customers to research products online, try them out in a store, and then purchase them online or offline. Transactions, inventory and customer data are synchronized in real-time across all channels to ensure a consistent experience. This allows customers to seamlessly switch their shopping experience between channels without losing information or experiencing inconsistencies.
To enable unified commerce, integration of the various backend systems such as e-commerce platforms, point-of-sale systems, warehouse management systems and customer databases is required. By integrating these systems, companies can provide unified information about products, orders and customers in real time.
Unified Commerce offers businesses a number of benefits. These include improved customer satisfaction as customers receive a consistent shopping experience across different channels. Businesses can also benefit from better use of customer information to provide personalized offers and recommendations. Additionally, unified commerce enables companies to manage inventory more efficiently and bring new products to market faster.
Unified Commerce is about overcoming the fragmentation and inconsistencies between different sales channels and creating a seamless, consistent and frictionless shopping experience for customers.
Another 'revolution' and complete market changes are coming!
How XR technologies (Extended, Augmented, Mixed and Virtual Reality) and Metaverse concepts will change no-line commerce, unified commerce and omnichannel in the next few years
XR technologies (Extended Reality, Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality and Virtual Reality) have the potential to significantly transform no-line commerce, unified commerce and omnichannel in the coming years:
Improved customer experience
XR technologies provide an immersive experience that allows customers to experience products and services in a whole new way. For example, augmented reality (AR) allows customers to view and test products in their real-world environment before purchasing them. Virtual Reality (VR) allows customers to visit virtual stores and explore products in a virtual environment. This improves customer loyalty and increases satisfaction.
Personalized shopping experiences
With XR technologies, retailers can create personalized shopping experiences. By collecting customer data and preferences, AR and VR applications can provide tailored product suggestions and recommendations. Customers can create and customize their own virtual spaces to showcase products based on their individual needs.
Virtual shops and marketplaces
XR technologies enable the creation of virtual stores and marketplaces in the metaverse. Merchants can showcase and sell their products in a virtual environment where customers can interact with other users. This opens up new opportunities for marketing and selling products, especially niche products or those that require immersive presentation.
Integrating XR into physical stores
XR technologies can also be used in physical stores to improve customer experience and promote no-line commerce. Merchants can implement AR applications to provide customers with information about products, special offers, and personalized recommendations. By using VR, retailers can create virtual fitting rooms or product presentations that offer customers unique experiences.
Social Interaction in the Metaverse
The concept of the Metaverse involves an immersive virtual world in which people can interact and communicate. XR technologies allow customers to interact with other users in virtual stores, marketplaces or social spaces. This social component can strengthen customer loyalty and create a sense of community.
The Industrial Metaverse, favored by Xpert as a visionary, is a digital parallel universe that promises its users an immersive experience through extended reality (XR). It is a potential business design of the future that enables seamless interaction between the digital and analog worlds. Many companies are exploring the potential of the Metaverse, with some using virtual reality technology to create virtual showrooms and increase their sales. The metaverse extends across all devices, including wearables, smartphones, laptops, tablets and smart home devices, and its connection to the real world is fluid.
More about it here:
➡️ XR technologies and the concept of metaverse no-line commerce, unified commerce and omnichannel will continue to evolve in the coming years, creating new opportunities for retailers to engage customers, deliver personalized experiences and increase sales. However, this is also expected to pose challenges around privacy, security and creating seamless integration between the different technologies.

Xpert.Plus warehouse optimization - high-bay warehouses such as pallet warehouses consulting and planning
Xpert.plus-industry expert, here with its own 'xpert.digital industrial hub' in the field of mechanical engineering of over 1,000 specialist contributions
Xpert.Plus is a project from Xpert.Digital. We have many years of experience in supporting and advising on storage solutions and in warehouse optimization, which we bundle in a large network under Xpert.Plus.
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus