Commercial war threatened? Possible effects of a 20 percent US custom on German goods and the global economy
Xpert pre-release
Language selection 📢
Published on: April 3, 2025 / update from: April 3, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein

Commercial war threatened? Possible effects of a 20 percent US custom on German goods and the global economy-picture: xpert.digital
20% US customs on German goods: your wallet will feel it!
Customs shock for Germany: These industries meet the hardest
The threat of trade tariffs, especially through large business powers such as the United States, always throws long shadows on the global economy. If the US government under the leadership of Donald Trump-or a future administration with similar protectionist inclinations-imported a flat-rate customs of 20 percent to all goods from Germany, profound consequences for international trade, global economic growth and in particular for German industry would result. This report analyzes the potential effects of such a scenario, whereby special attention is paid to the affected sectors such as mechanical engineering and international IT and marketing companies.
Suitable for:
- Threatening trade conflict with the USA due to Trump tariffs: Flexibility as the key to success - Interview with Konrad Wolfenstein from Xpert.Digital
Customs and international trade: an introduction
Customs are essentially taxes or levies that are charged to imported goods. They are a classic instrument of protectionism that aims to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. The functionality is simple: by collecting a customs, imported products are more expensive. Ideally - from a customary manner's point of view - this means that consumers and companies increasingly fall back on domestic goods and services.
There are different types of tariffs. The 20 percent customs discussed here would be a so-called “ad-valorem custom”. This means that an additional 20 percent imported goods are charged. There are also “specific tariffs” that set a fixed fee per unit of imported goods.
However, the effects of tariffs are complex and extend far beyond the simple price increase. They act like a negative offer shock that increases the costs of imports and can thus dampen the economic activity as a whole. Customs distort global markets, reduce economic efficiency and can lead to welfare losses.
The USA and tariffs: a historical perspective
In their history, the United States has repeatedly used tariffs to pursue economic or strategic goals. However, such measures have often led to retaliatory measures of other countries, which resulted in commercial wars and global homes.
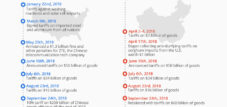
Some examples of previous US tariffs are the levies raised during the Trump government on solar cells, washing machines and steel (25 %) and aluminum (10 %). These measures aimed to boost US production and tackle unfair trading practices. The EU reacted to these tariffs with its own taxes to US goods such as Bourbon, Jeans and Harley-Davidson motorcycles.
Another historical example is the so-called “chicken tax” from the 1960s. This was imposed by the United States in response to tariffs from the European Economic Community to US chickens and, among other things, affected light commercial vehicles. It shows how long trade disputes can last.
The example of the Smoot-Hewley Tariff Act from 1930 is particularly deterrent. This protectionist act tightened the global economic crisis by massively disabling international trade. He illustrates that tariffs can trigger a downward spiral in times of crisis.
In contrast, there are international trade agreements that aim to facilitate trading by breaking down barriers and create favorable conditions. These agreements are based on the principle that free and fair trade benefits all countries involved.
The uncertainty as an additional burden
An important factor that is often underestimated is the uncertainty associated with the introduction of tariffs. Companies have to plan with many unknowns: How long will the tariffs apply? Are there any exceptions for certain products or countries? How will other countries react?
This uncertainty can slow down investments and slow down the overall business. Companies hesitate to make long -term decisions if they do not know how the trade conditions will develop in the future.
Suitable for:
- Globalization rethought: US experts asked – focus on expansion in the US market – production in the USA?
Global economic effects of US tariffs: a dark scenario
The introduction of a 20 percent US customs on German goods would have a number of negative effects on the global economy:
Detail of the commercial volume
By increasing imports, both the US and German exports would decrease. Other countries that are integrated into the supply chains would also be affected.
Lower economic growth
International trade is an important engine of global economic growth. When this engine gets stuttering, growth slows down. Some estimates assume that a flat-rate 20 percent customs could reduce US BIP growth by one percentage point.
Remanding measures and trade wars
It is very likely that Germany and the EU would take countermeasures in response to US tariffs. This could result in a trade war, in which the countries involved mutually occupy each other with ever higher tariffs.
Disruptions of the supply chains
Companies would try to avoid the higher costs caused by tariffs by shifting their supply chains. This could lead to inefficiencies and higher costs.
inflation
The higher import costs would be passed on to consumers, which could lead to increasing prices.
Most economists assume that increasing protectionism will have long -term harmful effects on the global economy. This would lead to slower growth, increased inflation and greater economic instability.
Effects on German industry: a sector -specific analysis
Germany is a strongly export -oriented economy. Almost ten percent of German exports go to the United States. This makes Germany particularly susceptible to trade barriers that are imposed by the USA.
A decline in German exports to the United States would significantly impair production levels in key industries. The following sectors in particular would be affected:
Automotive industry
The German automotive industry is very dependent on export to the United States. A 20 percent customs would consider German cars significantly in the United States and impair their competitiveness.
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is another important export sector for Germany. Here, too, tariffs would reduce the competitiveness of German products. However, direct customs load may be less than in the automotive industry.
Chemical and pharmaceutical industry
These sectors are also very export -oriented and would suffer from tariffs.
IT and marketing companies
These companies are not directly affected by tariffs to their services, but would indirectly suffer from general economic loss.
The proposed US tariffs represent a significant threat to the German economy. They could lead to a decline in exports, reduced industrial production, job losses and a decline in competitiveness in Germany on the important US market.
🎯🎯🎯 Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, fivefold expertise in a comprehensive service package | R&D, XR, PR & SEM

AI & XR 3D Rendering Machine: Fivefold expertise from Xpert.Digital in a comprehensive service package, R&D XR, PR & SEM - Image: Xpert.Digital
Xpert.Digital has in-depth knowledge of various industries. This allows us to develop tailor-made strategies that are tailored precisely to the requirements and challenges of your specific market segment. By continually analyzing market trends and following industry developments, we can act with foresight and offer innovative solutions. Through the combination of experience and knowledge, we generate added value and give our customers a decisive competitive advantage.
More about it here:
German products under pressure: The challenge of US tariffs
Competition disadvantage: German products on the US market
A 20 percent customs would increase the price of German goods that are sold in the USA by 20 percent. This makes them significantly more expensive for American consumers and companies.
This price increase would make domestic US goods relatively more competitive because they would not be subject to customs. German products would also be less competitive in comparison to goods that are imported from other countries and are not subject to the same 20 percent customs.
It is likely that US consumers will switch to cheaper alternatives, including domestic goods or imports from countries that are not subject to 20 percent customs to German goods.
The 20 percent customs would consider German products considerably on the US market and make it difficult for them to compete with domestic alternatives and imports from countries without such tariffs.
Suitable for:
- 25% “US criminal offenses” to all cars-the failure of politics, companies and consultants-misjudgments and dependencies
Coping with the challenges: Possible countermeasures and strategic reactions
In the past, the European Union has reacted to US tariffs with countermeasures. There is a possibility that the EU will reintroduce tariffs exposed to US goods that were originally imposed in response to previous US tariffs. There are new countermeasures from the EU that aims at a wider range of US products in order to meet the extended scope of potential US tariffs.
Germany and the EU are most likely to respond to the proposed US tariffs to German goods with their own tariffs to American products, which may lead to an escalating trade conflict that damages the economies on both sides of the Atlantic.
German companies have various proactive measures that they can take to reduce the negative effects of the US tariffs:
Diversification of the supply chains
Reduction of the dependence on exports to the USA by opening up alternative markets and covering materials from countries that are not affected by the tariffs.
Optimization of logistics
Exploration of alternative logistics routes and optimization of the supply chains for minimizing delays and costs.
Use of trade agreements
Use of existing trade agreements and examination of preferential customs treatments to reduce costs.
Tariff Engineering
Modification of products or their classification to possibly fall under lower customs categories.
Customs warehouse
Setup or use of customs bearings for duty -free storage of goods to need in a certain market.
New configuration of the procurement strategies
Consideration of which countries were to be obtained, raw materials and other materials.
Development of new business opportunities - Xpert.digital Business Development Focus on
Active search for new business opportunities and expansion of sales efforts in markets that are less affected by the US tariffs.
Restrict of supplier contracts
Optimization of production processes for the compensation of increased customs costs.
Evaluation and adaptation of tax strategies
Evaluation and adaptation of tax strategies, including the clearing price policy, is an essential part of ensuring efficient and legally compliant tax planning for companies. It is not just about checking current tax regulations, but also identifying possible risks and uncovering tax optimization potential.
Mastering market changes: A look at the challenges of the German economy
The broad industrial sector, including important industries such as automobile, chemistry and pharmace, will probably experience the greatest direct effects due to the high export volumes in the USA and potentially higher customs sets depending on the specific goods. The automotive sector in particular could be severely affected.
Mechanical engineering may see itself under a reciprocal scenario only a low direct increase (about 1 %), but is nevertheless susceptible to the general slowdown of world trade and the increased competition in non-US markets.
The IT and marketing sectors will probably experience more indirect effects through general economic weakening, reduced customer expenditure and potential disorders in the supply chain for IT hardware.
The biggest challenges and potential opportunities for every sector are diverse:
General industry
The challenge is to keep market shares and profitability in the United States despite the 20 percent increase in price. The opportunity lies in the development and expansion to new markets outside the USA, the strengthening of domestic demand and potential efficiency increases in the partial absorption of customs costs.
mechanical engineering
The challenge is the increased competition in non-US markets and a potential slowdown of global investments that affect the demand for machines. Chance lies in the use of the Ruf of Germany for high -quality engineering and focus on specialized, high -quality products in which the sensitivity to be sensitivity is possibly lower.
IT/marketing
The challenge is in potential reductions in customer budgets due to economic uncertainty and higher costs for IT hardware. The opportunity lies in the development of solutions and services that help German companies master the challenges of the new trade environment, such as: B. market analyzes, tools to optimize the supply chain and digital marketing strategies that aim at new markets.
Suitable Dazi:
- Things worth knowing about Trump Tariffs 2.0 & America First: From Surplus to Deficit – Why Trump is targeting the trade balance
Strategies against US tariffs: ways to strengthen German companies
The analysis of the potential effects of a 20 percent US custom on German goods indicates significant negative consequences for the German economy and global trade.
In view of these potential challenges, the following recommendations are given:
diplomacy
The German government should actively act in diplomatic negotiations with the US government in order to prevent the introduction of tariffs or to achieve exceptions and reductions.
coordination
A close coordination with the European Union to coordinate a strong and uniform reaction, including potential countermeasures, is crucial to maximize the pressure to negotiate.
Support measures
National measures should be taken to support the German companies affected by the tariffs, such as: B. the provision of financial aid, export promotion programs for alternative markets and incentives for innovation and efficiency increases.
Diversification
Strengthening trade relationships with other important global partners to diversify the export markets and to reduce dependency on the USA is also of great importance.
Risk management
German companies should carry out a thorough assessment of their current and potential threats from the US tariffs and develop detailed risk management strategies.
Market development
The active exploration of possibilities for diversifying your export markets beyond the United States, with a focus on regions with strong growth potential and favorable trade conditions, is essential.
Supply chain optimization
The review and optimization of your supply chains for the identification of potential cost savings and alternative procurement options that are less affected by the US tariffs should be a priority.
innovation
Investments in innovation and product differentiation are crucial in order to obtain a competitive advantage with the additional customs costs.
Cooperation
Cooperation with industry associations and government agencies is important in order to remain informed about the latest developments in trade policy and to represent their interests.
Protection against protectionism: strategies for Germany in commercial crises
It is important to emphasize that the effects shown here are based on a number of assumptions. The actual consequences of the US tariffs could vary depending on the concrete details of the implementation, the reactions of other countries and the adaptation skills of German companies.
Nevertheless, it is undeniable that a 20 percent customs on German goods would be a significant challenge for the German economy. It is all the more important that the German government and German companies actively act in order to minimize the negative effects and to use the opportunities offering.
In addition, German politics should emphasize the importance of the multilateral trading system and work for the reduction of trade barriers. Only through close international cooperation can the global economy be preserved from the harmful consequences of protectionism and trade wars.
Your global marketing and business development partner
☑️ Our business language is English or German
☑️ NEW: Correspondence in your national language!
I would be happy to serve you and my team as a personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) . My email address is: wolfenstein ∂ xpert.digital
I'm looking forward to our joint project.