Digitalization is the infrastructure for the global economy and exports at the same time - Image: Xpert.Digital
🌐🔄 Political undesirable developments and the opportunities of digitalization for SMEs
🔎 Current situation in Germany
Undesirable political developments, often driven by ideology, are areas in which small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have only limited opportunities to exert influence. But one sector that offers wide open doors and enormous opportunities for these companies is digitalization. In this respect, Germany is currently in the middle of the European field, which at the same time leaves room for improvements and developments.
Suitable for:
🚀 Digitalization as an economic engine
Digitalization is much more than a buzzword; it is the infrastructure and the foundation of global economic success and also plays a central role in the area of exports. This opens up a field with immense untapped potential for SMEs. Through the targeted use and further development of digital possibilities, these companies can not only keep up, but also consolidate their position in the market and even develop and expand competitive advantages.
🔍 Germany as an export nation and digitalization
Let's start with the current situation: Germany is traditionally known as an export nation, but when it comes to digitalization it has a middle position in a European comparison. This shows that there is a need for action in the area of digital innovations and structures. Digitalization should be seen as an essential part of corporate strategy because it has the potential to revolutionize business models and open up new markets.
🏭 SMEs as drivers of innovation
SMEs provide the majority of German companies and are often referred to as the 'innovation engine' of the economy. As a rule, they are faster and more flexible than large corporations and can therefore adapt to new technologies faster. However, they also face special challenges: limited resources, less specialization in the areas of IT and digitization and a tendency to lower market power compared to large players.
Suitable for:
💡 Digitalization as an opportunity for SMEs
Digitalization offers SMEs the opportunity to meet these challenges. Tools to increase productivity, market research and customer acquisition, as well as platforms for exchange with other companies and for better visibility on international markets are just a few examples of the potential of digitalization.
🌐 Optimization of internal processes
Another added value of digitalization lies in the optimization of internal processes. Cloud solutions enable SMBs to securely store data and access it from anywhere. Communication tools promote collaboration within the team and with external partners, even across national borders. Intelligent software can help automate processes, increase efficiencies and reduce costs.
🏭 Technologies in production
In the area of production, for example, Industry 4.0 technologies can be used to make manufacturing processes more intelligent and flexible. By connecting physical and digital systems, production processes can be optimized in real time and adapted to changing market requirements.
📈 Digital customer access and marketing
Another key aspect is customer access. Digitalization enables SMEs to enter online markets and make their products and services available to a wider audience. You can use digital channels to interact with customers, conduct personalized marketing, and improve buyer experiences.
🔒 IT security for SMEs
The security of information technology is crucial because SMEs are increasingly becoming the target of cyber attacks. Robust IT security not only protects company data, but also customer trust.
💼 Rethink and invest in digital skills
However, digitalization also requires SMEs to rethink their approach. It is important that they are ready to adapt their business models and also invest in digital capabilities. This includes both technological infrastructure and employee training.
📚 Further training and qualifications
Further training and qualifications for the workforce are essential to ensure competitiveness. Employees must learn to deal with new technologies and use them effectively for their work processes.
💡 Strategic importance of digitalization
Commitment to digitalization is not just a reaction to competition, but should be seen as a strategic goal to secure future viability and open up new markets. SMEs that position themselves digitally at an early stage can enjoy first-mover advantages and thus maintain and expand their market position.
🏡 SMEs in rural regions
SMEs also play a key role in rural regions. Through digitalization, they can create jobs and contribute to strengthening the regional economy. They can help narrow the digital divide between urban and rural areas, thereby contributing to balanced economic growth.
🤝 Collaboration for digital transformation
Close cooperation between politics, educational institutions and business associations is necessary to improve the framework conditions for the digital transformation of SMEs. This is about creating an innovation-friendly climate with appropriate funding programs to support SMEs in digitalization.
🔍 Opportunity for digitalization
The challenges of digitalization and global integration for SMEs are great, but the opportunities far outweigh them. Targeted and strategically clever digitalization enables SMEs to tap new market potential, better meet customer needs and remain competitive in the long term. It is these small and medium-sized companies that can shape and drive the economy forward through their innovative strength and flexibility - and are therefore a decisive engine for economic growth in Germany and Europe.
📣 Similar topics
- 🚀 Digitalization opportunities for SMEs: How they can master digital transformation
- 🌐 SME as a “innovation engine”: the central role of digitization
- 🔧 Germany in the digital midfield: Need for action in digital innovations
- 🛠️ Challenges and potential: SMEs and the digitalization options
- ☁️ Cloud technology and international networking: Digital added value for SMEs
- 🏭 Industry 4.0: Revolution in manufacturing for German medium-sized companies
- 🛍️ Conquer online marketplaces: Digital customer access for SMEs
- 🔒 IT security: An investment in the future of SMEs
- 🎓 Strengthen skills: Further training as the key to digital competence
- 🏡 SMEs in rural regions: Digitalization as a growth engine
#️⃣ Hashtags: #DigitizationKMU #Innovationsmotor #Industrie40 #ITSecurity #DigitalEducation
🎯🎯🎯 Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, five-fold expertise in a comprehensive service package | BD, R&D, XR, PR & Digital Visibility Optimization
Benefit from Xpert.Digital's extensive, fivefold expertise in a comprehensive service package | R&D, XR, PR & Digital Visibility Optimization - Image: Xpert.Digital
Xpert.Digital has in-depth knowledge of various industries. This allows us to develop tailor-made strategies that are tailored precisely to the requirements and challenges of your specific market segment. By continually analyzing market trends and following industry developments, we can act with foresight and offer innovative solutions. Through the combination of experience and knowledge, we generate added value and give our customers a decisive competitive advantage.
More about it here:
🔍 Digitalization is fundamentally reshaping the foundations of the European economy and society
📈📊 Degree of digitalization of EU countries according to the DESI Index 2022
⚙️ The five dimensions of the DESI index
What this means for Germany becomes particularly clear when looking at the DESI index - an instrument of the European Commission that annually measures and compares the digital progress of the member states. In 2022, an index value of 52.9 was achieved for Germany, which marks an average place in the EU-wide comparison. Leaders such as Finland and Denmark show what high levels can already be achieved.
🌐 Connectivity in Germany
The heart of the DESI index consists of five dimensions: connectivity, digital skills, internet use by private individuals, integration of digital technology by companies and digital public services. These areas are essential for mapping and evaluating the transformation processes in a modern society. Germany shows both light and shadow in these categories.
💡 Digital skills
Connectivity in Germany has seen remarkable progress. Over 65 million people use the Internet, and almost 90 percent of households have a broadband connection. However, the speed and availability of broadband as well as the expansion of the ultra-fast fiber optic network and 5G technology are a major challenge. The international comparison indicates that there is a clear need to catch up in these areas.
👩🎓 Society and education in the digital age
Digital skills are another pillar of the digital society. Germany is investing in the population’s digital education and training. Schools are being equipped with digital devices and curricula are being adapted to prepare children and young people for a digital future. But here too, studies show a need for improvement – in the practical application of digital skills as well as in lifelong learning.
🌐 Internet usage of the population
In the category of Internet use by private individuals, things are looking quite positive, as a large part of the German population is actively online. Nevertheless, the wider use of e-government offerings or e-health services could further improve the quality of life and simplify processes.
🏭 Corporate digitalization
When it comes to companies integrating digital technology, there are both pioneers and laggards. Large corporations and start-ups are often already well digitized, but small and medium-sized companies in particular are lagging behind. This is particularly critical since they form the backbone of the German economy.
🏛️ Digital public services
Germany is making progress in digital public services. The introduction of digital administration and services such as electronic file management and digital administrative channels is progressing. But here, too, there is still a long way to go until there is a comprehensive and user-friendly offer.
♻️ Opportunities and risks of digitalization
Throughout this entire process, it should not be overlooked that digitalization presents both opportunities and challenges. From an economic perspective, it has the potential for innovation, competitiveness and ecological sustainability. Mobility is becoming more flexible through digital offerings and the issue of climate benefits from intelligent solutions for energy efficiency. Education can be enriched and made more accessible through digital media and methods.
🚧 Career change and cybersecurity
But the digital changes are not only positive. The automation and digitalization of work processes endanger traditional jobs and pose questions that threaten the existence of certain professions. This requires a society that is ready for career change and offers the appropriate support for retraining and upskilling.
🔒 The importance of cybersecurity in the digital age
Another issue in the digital age is cybersecurity. As connectivity increases, the risk of cyberattacks also increases. Here, Germany, like many other countries, must continue to invest in order to protect critical infrastructure and ensure the privacy of its citizens.
🛣️ Future prospects for digital transformation in Germany
Germany has already set many course on the path to a digital future, but there are still significant steps to be taken. Politics, business and every single person are called upon to actively shape this change. Digitalization should not just be seen as a technical process, but rather as a comprehensive social development that ushers in a new era. The future will show how quickly and successfully Germany will overcome these challenges.
📣 Similar topics
- 1️⃣ 🌐 GERMANY IN DIGITAL CHANGE: Challenges & Opportunities
- 2️⃣ 📶 DESI INDEX: An EU comparison of digital connectivity
- 3️⃣ 🎓 INVESTING IN THE FUTURE: Germany's path to digital competence
- 4️⃣ 🏡 BROADBAND & FIBER EXPANSION: Germany's infrastructure in comparison to the EU
- 5️⃣ 💡 INNOVATION THROUGH DIGITALIZATION: New opportunities for Germany's economy
- 6️⃣ 📚 EDUCATION IN THE DIGITAL AGE: Adaptation of curricula and equipment in schools
- 7️⃣ 👥 INDIVIDUAL INTERNET USE: Online behavior in Germany
- 8️⃣ 🏢 SMEs AND DIGITAL CHANGE: Challenges for the backbone of the German economy
- 9️⃣ 📱 PUBLIC SERVICES: The progress of digital administration in Germany
- 🔟 🛡️ CYBER SECURITY: The key to protection in digital Germany
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Digitalization #GermanyDigital #DESIIndex #DigitalEducation #DigitalInfrastructure
📈📊 Read more ➡️ Numbers: Degree of digitalization of EU countries according to the DESI Index 2022
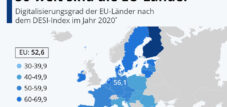
With an index value of 52.9, Germany was in the middle of the EU countries in the European comparison of the digital economy and society in 2022. The Scandinavian countries Finland and Denmark are leading the way. The European Commission annually publishes the Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI), which tracks Member States' progress in five key areas
Degree of digitalization of the EU countries according to the DESI index
- Finland – 69.60
- Denmark – 69.33
- Netherlands – 67.37
- Sweden – 65.22
- Ireland – 62.74
- Malta – 60.88
- Spain – 60.77
- Luxembourg – 58.85
- Estonia – 56.51
- Austria – 54.68
- Slovenia – 53.37
- France – 53.33
- Germany – 52.88
- Lithuania – 52.71
- EU – 52.28
- Portugal – 50.76
- Belgium – 50.31
- Latvia – 49.71
- Italy – 49.25
- Czech Republic – 49.14
- Cyprus – 48.35
- Croatia – 47.55
- Hungary – 43.76
- Slovakia – 43.45
- Poland – 40.55
- Greece – 38.93
- Bulgaria – 37.68
- Romania – 30.58
🌐 The digital age and Europe's economy 🛠️
📈📊 Level of digitalization of EU countries according to the Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI)
Degree of digitization of EU countries according to the Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI) – Image: Xpert.Digital
🌐 The digital age and the European Union
The digital age is increasingly shaping European societies and their economies, with the degree of digitalization varying from country to country. The European Union, as an association of member states with the aim of forming an ever closer union, is intensively addressing digital development and transformation in order to improve the competitiveness and quality of life of its citizens.
🔍 Digital Economy and Society Index ”(Desi)
One of the key instruments for measuring and comparing digital progress is the “Digital Economy and Society Index” (DESI), an index that aggregates important indicators of Europe's digital performance. The DESI provides an insight into the overall development of the EU member states in five central dimensions: connectivity, human capital, integration of digital technology, digital public services and internet use by private individuals and companies.
📊 DESI ranking and Germany
In 2022, DESI will show how different the EU countries are digitally positioned. Germany, for example, achieved 52.9 points this year, placing it in 13th place in a European comparison. This position highlights the country's state of digital transformation, but also indicates that there is still significant catching up to do, especially when compared to leading Scandinavian nations such as Finland and Denmark.
💡 Digital pioneers Scandinavia
The Scandinavian countries, often seen as beacons of digitalization in Europe, are characterized by a combination of high investments in digital infrastructures, a strong focus on education in the field of information technologies and a deep anchoring of digital services in public administration. Their top positions in DESI reflect the success of these approaches.
🔎 Detailed view of the DESI
📡 Connectivity
Connectivity as the first dimension measures the degree of expansion and quality of broadband infrastructure. This dimension is very important for optical broadband connections and 5G networks, because high-performance connectivity is the backbone of digital activities and a prerequisite for a modern digital economy.
🧠 Human capital
The human capital dimension is about digital skills and the availability of IT specialists. While Germany has made progress in this regard, the IT skills shortage remains a significant challenge that needs to be addressed. Especially in a direct comparison with the Nordic countries, it becomes clear that there is still great potential for training and further education in the digital sector.
🛠️ Integration of digital technology
Digital technology integration assesses how companies adopt and use new digital technologies. The digital transformation of the economy is crucial for growth and innovation. Germany certainly shows strengths in the middle field here, but with the prospect that more consistent digitalization could further increase the efficiency and innovative capacity of German companies.
🏛️ Digital public services
Digital public services are the fourth main dimension of DESI. This will identify how digital technologies are integrated into the public sector and contribute to more effective and user-friendly administrative processes. Countries like Estonia have shown examples of how administration can be made more efficient and closer to citizens through consistent digitalization.
🌐 Internet use
Finally, there is internet usage, which shows the extent to which people use digital content and are active online. Germany records widespread use here, but the intensity and diversity of online activities could certainly be increased compared to other European countries.
🚀 Germany's measures and strategies
So what does Germany have to do to catch up compared to other European countries? A main starting point is training and further education. It is not enough to simply expand the infrastructure; At the same time, people must be empowered to use and design them sensibly. Government initiatives and educational programs that promote digital skills from elementary school onwards and enable lifelong learning are crucial to ranking better on the DESI in the future.
💰 Investments and infrastructure
Furthermore, it is of central importance for Germany to strengthen the structure and extent of investments in digital innovations. There must be progress, particularly in the area of digital infrastructure, such as the expansion of fiber optic and 5G networks, so that digital services can be offered across the board and in high quality.
🏢 Promoting SMEs
In the corporate sector, the focus should be particularly on supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These form the backbone of the German economy and their digitalization is crucial for increasing productivity and maintaining international competitiveness.
📜 Digital management services
The German administration should also further digitize and simplify its processes for digital public services in order to speed up and make access easier for citizens.
🔧 Implementation of a digital strategy
A visionary digital strategy that combines all of these aspects and defines concrete, measurable goals is the key for Germany to rise internationally and take a leading role in Europe's digital economy and society.
🔮 DESI – A valuable orientation
The progress and challenges of DESI provide valuable guidance. It shows where measures have been successful and where there is an urgent need for action, thereby providing a basis for goal-oriented political control in an increasingly digital world. Digital transformation is no longer a marginal issue – it is a central pillar of every future-oriented society and economy. It will therefore be exciting to see how Germany's position in the DESI ranking will develop in the coming years and what steps will be taken to shape and improve the country's digital landscape.
📣 Similar topics
- 🌐 The dynamics of digital: Europe's path to digital excellence
- 📊 DESI 2022: A look at Germany's digital challenges
- 🏆 Scandinavian pioneers: lessons in digitalization
- 💻 Germany and IT: Ways to overcome the shortage of skilled workers
- 🛰️ Connectivity as a foundation: Europe's broadband and 5G expansion
- 🏭 Digital change in the economy: Germany's position and potential
- 📲 E-Government: Best practices for digitalizing administration
- 🕹️ Internet usage in European comparison: Where does Germany stand?
- 🎓 Education as a digital driver: The future of educational strategies
- 📡 Strengthen Germany digitally: Investments and innovations are key
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Digitalization #DESI2022 #Digital Competence #European Union #Educational Strategy
📈📊 Read more ➡️ Numbers: Degree of digitalization of EU countries by points in 2022
The “Digital Economy and Society Index” (DESI) is a composite index that summarizes relevant indicators of Europe's digital performance and pursues the development of the EU member states in five main dimensions. The DESI-Old Invex is calculated as a weighted average of the four main dimensions: 1. Connectivity, 2nd human capital, 3. Integration of digital technology and 4. Digital public service.
Germany ranks 13th in the European comparison of the digital economy and society in 2022 and has a total score of 52.9 points. The Scandinavian countries Finland and Denmark are leading the way. The European Commission annually publishes the Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI), which tracks Member States' progress in the five key areas of connectivity, digital skills, internet use by individuals, digital integration by businesses and digital public services.
Connectivity
- Finland – 15.14
- Denmark – 19.27
- Netherlands – 17.53
- Sweden – 15.06
- Ireland – 15.38
- Malta – 13.25
- Spain – 17.43
- Luxembourg – 14.83
- Estonia – 11.11
- Austria – 14.11
- Slovenia – 14.97
- France – 16.05
- Germany – 16.83
- Lithuania – 12.34
- EU – 14.98
- Portugal – 12.90
- Belgium – 9.96
- Latvia – 12.52
- Italy – 15.31
- Czech Republic – 13.17
- Cyprus – 14.69
- Croatia – 12.01
- Hungary – 14.40
- Slovakia – 12.46
- Poland – 11.63
- Greece – 12.39
- Bulgaria – 12.68
- Romania – 13.81
Human capital
- Finland – 17.85
- Denmark – 14.80
- Netherlands – 15.78
- Sweden – 15.49
- Ireland – 15.66
- Malta – 14.15
- Spain – 12.83
- Luxembourg – 14.44
- Estonia – 13.49
- Austria – 12.74
- Slovenia – 11.06
- France – 12.47
- Germany – 11.24
- Lithuania – 10.61
- EU – 11.44
- Portugal – 11.49
- Belgium – 12.17
- Latvia – 11.03
- Italy – 9.14
- Czech Republic – 11.40
- Cyprus – 10.44
- Croatia – 12.96
- Hungary – 9.61
- Slovakia – 11.03
- Poland – 9.26
- Greece – 10.03
- Bulgaria – 8.15
- Romania – 7.73
Integration of digital technology
- Finland – 14.77
- Denmark – 14.50
- Netherlands – 13.02
- Sweden – 14.06
- Ireland – 10.83
- Malta – 12.03
- Spain – 9.63
- Luxembourg – 8.74
- Estonia – 9.12
- Austria – 9.79
- Slovenia – 9.96
- France – 7.98
- Germany – 8.96
- Lithuania – 9.31
- EU – 9.02
- Portugal – 9.40
- Belgium – 12
- Latvia – 6.46
- Italy – 10.19
- Czech Republic – 8.46
- Cyprus – 8.84
- Croatia – 9.18
- Hungary – 5.40
- Slovakia – 6.96
- Poland – 5.72
- Greece – 6.66
- Bulgaria – 3.88
- Romania – 3.79
Digital public administration
- Finland – 21.84
- Denmark – 20.77
- Netherlands – 21.05
- Sweden – 20.61
- Ireland – 20.86
- Malta – 21.45
- Spain – 20.88
- Luxembourg – 20.84
- Estonia – 22.79
- Austria – 18.03
- Slovenia – 17.37
- France – 16.84
- Germany – 15.85
- Lithuania – 20.45
- EU – 16.84
- Portugal – 16.98
- Belgium – 16.19
- Latvia – 19.70
- Italy – 14.62
- Czech Republic – 16.11
- Cyprus – 14.38
- Croatia – 13.39
- Hungary – 14.35
- Slovakia – 13
- Poland – 13.94
- Greece – 9.85
- Bulgaria – 12.97
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Smart City & Factory: Industry expert for energetic 5G buildings and halls as well as advice and installation of solar systems
☑️ Xpert.Plus - logistics consulting and logistics optimization
☑️ Industry expert, here with his own Xpert.Digital Industry Hub with over 1,500 specialist articles
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus