Published on: November 22, 2024 / Updated on: November 22, 2024 – Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
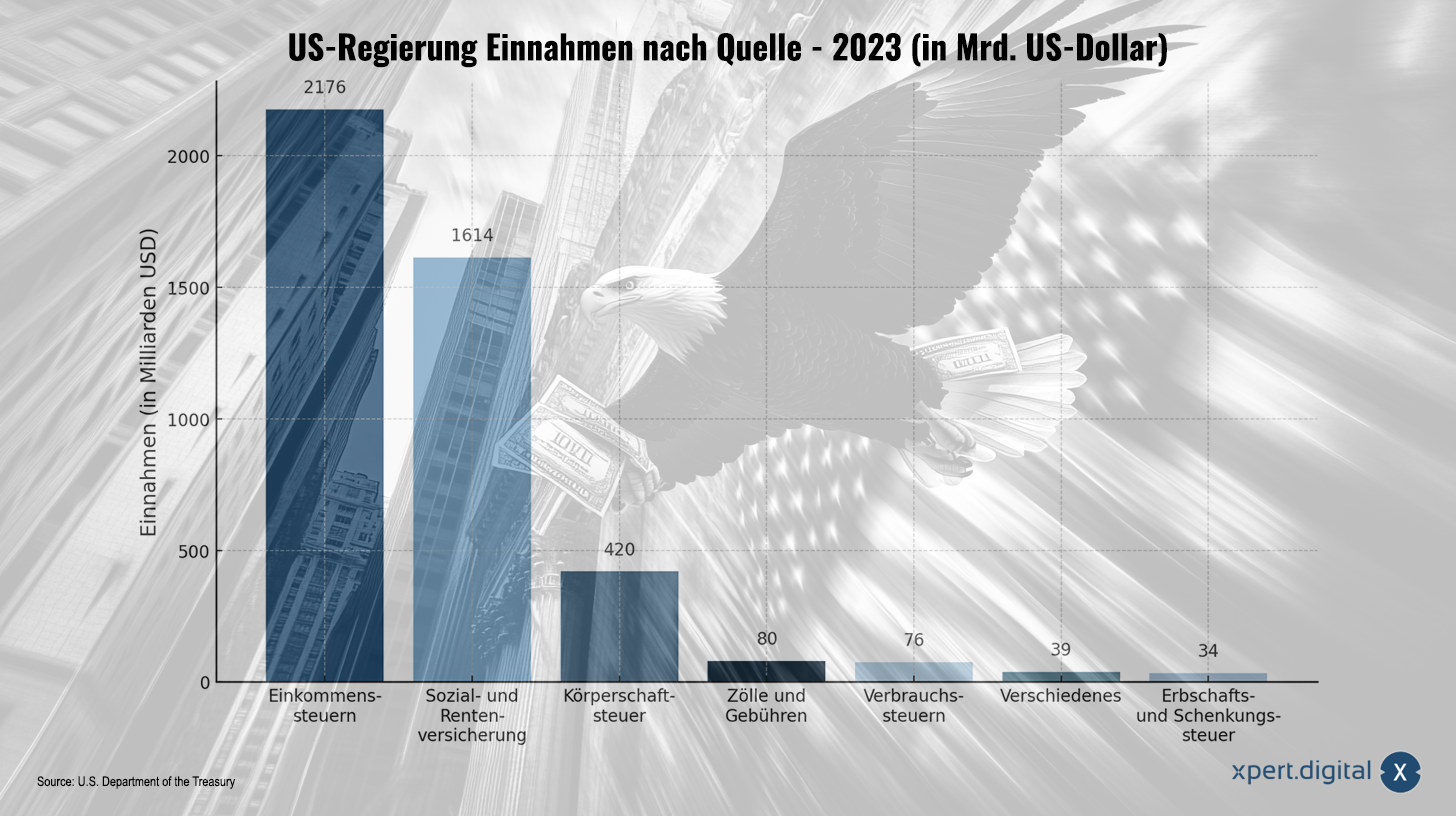
US government revenue in 2023 – Tariffs and their limits: How economically sound are they really? – Image: Xpert.Digital
Tariffs in the USA: How important are they really for the national budget?
Tariffs as a source of revenue for the US government: An analysis of their significance and impact
Tariffs play a minor role in the United States compared to other sources of government revenue. In 2023, revenue from tariffs and duties amounted to approximately $80 billion, representing only 1.8% of total US government revenue. By comparison, income tax generated roughly $2.2 trillion in the same year, accounting for about half of all government revenue. These figures illustrate that, despite their historical significance as a financing tool, tariffs now play only a marginal role in the US budget.
Trump's proposals and their feasibility
Throughout his political campaigns, Donald Trump repeatedly emphasized the importance of tariffs, highlighting them as a key economic and political tool. His proposals ranged from moderate adjustments to radical ideas. For example, he suggested using additional tariff revenue to finance tax cuts or debt reduction. In one particularly controversial proposal, he even floated the idea of replacing income tax entirely with tariffs.
This idea, however, met with widespread criticism from economists and financial experts. The reason lies in the sheer discrepancy between customs revenue and income tax revenue. To actually replace income tax, extremely high tariffs would be required – estimates suggest a universal tariff of around 58 to 70% on all imports would be necessary to reach the level of income tax revenue. Such a scenario is considered economically unsustainable, however, as it would have far-reaching negative consequences.
Firstly, such a high tariff would massively increase the prices of imported goods, significantly impacting consumers' purchasing power. Secondly, such tariffs could lead to a drastic decline in international trade, as both imports and exports would be severely restricted. This would not only reduce the potential revenue from the tariffs themselves but also stifle overall economic growth.
Economic impact of tariffs
Costs for consumers
Tariffs generally have a direct impact on consumers, as they lead to higher prices for imported goods. Companies that rely on imports often pass these additional costs on to end customers. A case in point is Trump's earlier tariffs on washing machines: studies show that this measure resulted in an average price increase of 12%. For US households, this meant an additional financial burden in their daily lives.
The effects of higher prices are particularly noticeable for low-income households, as they have to spend a larger share of their income on consumer goods. Thus, those population groups that are already economically disadvantaged bear the brunt of such measures.
Economic distortions
High tariffs can also lead to significant economic distortions. They generally reduce trade volume and decrease the quantity of imported goods. While this may boost sales of domestic products in the short term, it can have negative long-term consequences. Companies that rely on international supply chains could find their competitiveness hampered by higher import costs.
Furthermore, high tariffs could also lead companies to relocate their production facilities abroad to avoid the additional costs. This, in turn, could jeopardize jobs in the US and slow economic growth.
Retaliation and trade wars
"Retaliation" is an English term that literally means "retaliation" or "counterattack." It is frequently used, particularly in international trade law. It refers to a situation where one country (or an economic entity like the EU) imposes punitive measures—such as tariff increases or import bans—against another country in response to protectionism, unfair trade practices, or breaches of trade agreements.
For example, if one country unlawfully increases its import tariffs, the other country could retaliate by imposing tariffs on certain products of the first country.
Another risk of high tariffs lies in potential countermeasures from other countries. If a country raises its import tariffs, trading partners often respond with retaliatory tariffs on that country's exports. This can escalate into a trade war, resulting in economic losses for both sides.
A prominent example of this is the trade conflict between the US and China during Trump's presidency. Both countries imposed high tariffs on a wide range of products. The result was not only rising prices for consumers and businesses in both countries, but also a slowdown in global economic growth.
The limited role of tariffs as a source of revenue
The analysis clearly shows that tariffs are not a suitable alternative to income tax as the primary source of revenue for the US government. Their revenue is comparatively low and far from sufficient to cover the needs of the federal budget. Moreover, they are associated with significant economic side effects.
While Trump viewed tariffs as a central element of his economic policy, their actual effectiveness remains limited. Although they can serve as a steering instrument in certain situations—for example, to protect specific industries or to promote domestic production—their role as a reliable source of revenue is severely restricted.
Historical perspective: The development of customs policy
Tariffs have a long history in the United States and played a central role in financing the government, particularly in the 19th century. Before the introduction of income tax in 1913, they were even the primary source of revenue for the federal government. At that time, they served not only fiscal purposes but also to protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
With increasing globalization and the growth of international trade, the significance of tariffs has changed dramatically. Today, they often exist in a tension between economic efficiency and political objectives. While some politicians – like Trump – see them as a means of promoting national interests, economists frequently emphasize their negative impact on trade and prosperity.
Tariffs are a limited instrument
Tariffs are a complex economic instrument with limited potential as a source of revenue for modern economies like the US. Their introduction or increase should always be carefully considered, as they can have far-reaching consequences for consumers, businesses, and international trade.
Trump's idea of using tariffs as a replacement for income tax may seem politically popular, but it is neither practically nor economically sound. Instead, governments should seek balanced solutions that ensure fiscal stability while promoting economic growth – without creating unnecessary burdens for citizens and businesses.
In an increasingly globalized world, reconciling national interests with the demands of international trade remains a challenge for policymakers. The debate surrounding tariffs exemplifies the tensions inherent in modern economic policy: between protectionism and free trade, between short-term political gains and long-term economic prosperity.
Suitable for:

