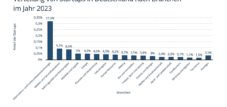
Startups sources of financing 2023 – Financing for start-ups in Germany developed positively in 2024
Language selection 📢
Published on: October 1, 2024 / update from: October 1, 2024 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
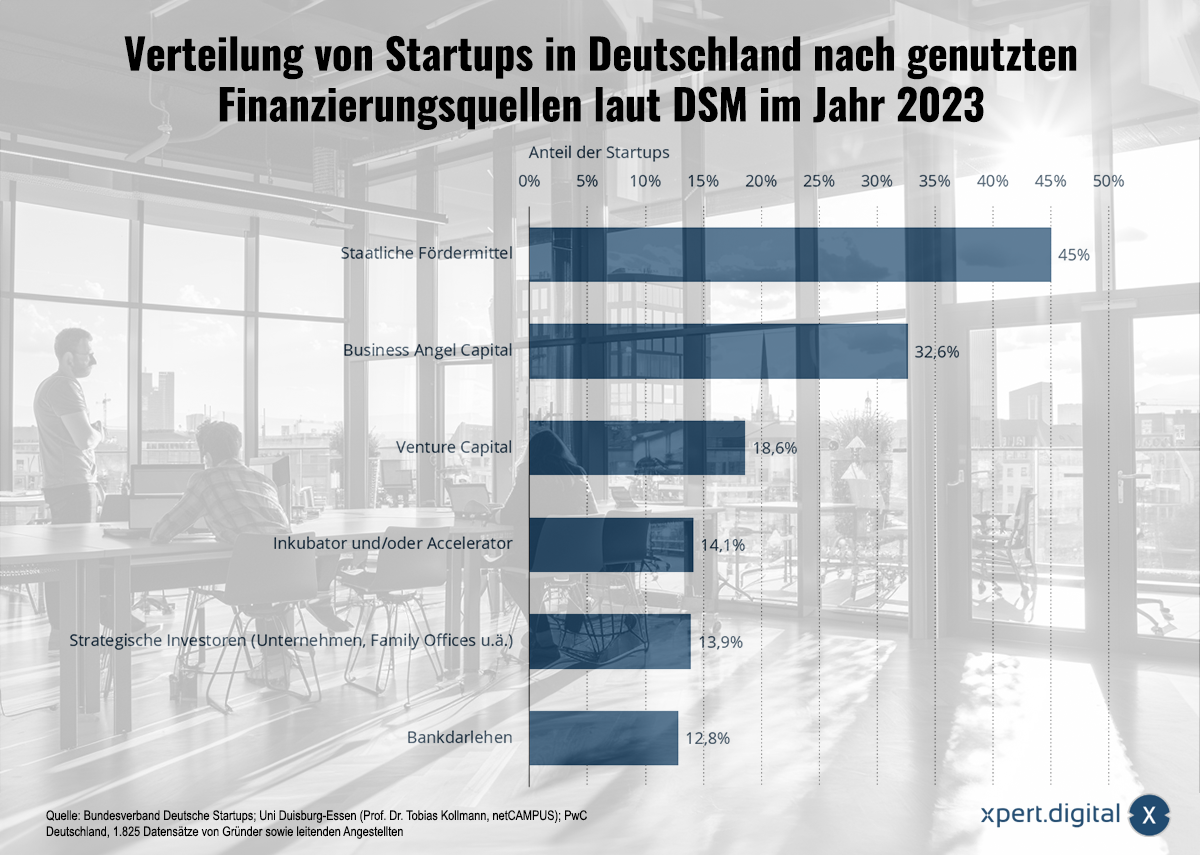
Startups sources of financing 2023 - Financing for start-ups in Germany developed positively in 2024 - Image: Xpert.Digital
🚀💡📊 Financing for start-ups in Germany developed positively in 2024
📈✨ Financing for start-ups in Germany developed positively in 2024, although challenges remain. Here are the key aspects of the current situation:
📈 Investment volumes and trends
In the first half of 2024, the volume of venture capital investments in German start-ups increased by 12% to a total of 3.4 billion euros compared to the same period last year. This marks a turnaround after a decline in 2022 and 2023.
Despite the increase in investment volume, the number of financing rounds fell by 19%, indicating a concentration on larger deals.
Particularly noteworthy is the increase in investments in start-ups from North Rhine-Westphalia, which received significantly more capital of 822 million euros in the first half of 2024 than in the previous year.
💼 Government initiatives and support
The German government has launched several initiatives to support start-ups, including the WIN initiative, which plans to invest at least 12 billion euros in venture capital by 2030.
The future fund will provide ten billion euros for investments by the end of 2030 in order to strengthen venture capital financing.
The High-Tech Gründerfonds (HTGF) Opportunity was launched in June 2024 with a volume of 660 million euros to support growth financing.
⚠️Challenges
Despite the positive developments, financing remains a key challenge for start-ups, especially in the growth phase.
The market for venture capital in Germany is smaller compared to other countries, which continues to be an obstacle.
Overall, there is a positive trend in the financing of start-ups in Germany, supported by government initiatives and a recovery in the venture capital market. However, securing sufficient funding remains a challenge, particularly for small and medium-sized financing rounds.
📣 Similar topics
- 💡 Venture Capital Market Recovery: Causes and Effects
- 📈 Growth in venture capital investments in German start-ups in 2024
- 🎯 Focus on larger deals: Analysis of current investment trends
- 🏅 Investments in North Rhine-Westphalia's start-ups: A look at the numbers
- 💼 Government initiatives: Support for German start-ups until 2030
- 🔍 The future fund: potential and prospects for venture capital
- 🚀 The High-Tech Gründerfonds (HTGF) Opportunity: New ways of financing growth
- ⚠️ Challenges of start-up financing in the growth phase
- 🌍 Germany in international comparison: The market for venture capital
- 🔧 Solutions for financing small and medium-sized financing rounds
#️⃣ Hashtags: #Startups2024 #Risk Capital #Government Initiatives #Growth Financing #Germany
💡🚀 Germany's startup financing 2023: Diverse sources for growth
🚀💡📊 The German startup market will be more diversified than ever in terms of financing options in 2023. The variety of financing methods not only reflects the growing need for capital by young companies, but also the structural support from various actors. Both government funding and private investors, from business angels to strategic investors, play a key role in the development of the startup landscape in Germany.
1️⃣💰 State funding as a central pillar of financing
With 45% of startups using government funding as a source of financing, these are clearly the focus of startup financing in Germany. Government funding programs, such as the Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (KfW) or regional development banks, offer startups grants, loans or other support. These programs are designed to promote the innovative power of the economy and reduce entrepreneurial risk, especially in early phases when startups often have difficulty convincing private investors.
Another advantage of government funding is their wide availability for a wide range of industries. Technological innovations, sustainability projects or startups in the area of digitalization particularly benefit from these offers. Funding often has the advantage that it is cheaper than private investments and sometimes does not have to be paid back, which reduces the startups' willingness to take risks. In addition, government programs also offer coaching, advice and networks, which go far beyond pure financing.
2️⃣👼 Business Angels: Private investors with a strategic function
Around 32.6% of startups in Germany rely on business angel capital. Business angels are usually wealthy private individuals who not only bring capital, but also their expertise and networks into a company. Business angels can be crucial, especially in the early phases of a startup, when products and services are not yet fully established on the market. Their investments are often more flexible than traditional venture capital funds, and they are willing to take greater risks to support innovative business ideas.
However, the role of business angels goes far beyond providing capital. They offer mentoring and strategic advice and are often long-term companions to startups. Through their close relationship with the company and their deep insight into the industry, they can give valuable advice and open doors to other investors or business partners. For many startups, business angels are the bridge between the founding phase and later rounds of financing, be it from venture capital or strategic investors.
3️⃣📈 Venture Capital: Growth through institutional capital
With 18.6% of startups using venture capital (VC), this form of financing remains an important pillar in the German startup ecosystem. VC funds invest primarily in startups with high growth potential. In contrast to business angels, venture capitalists bring in larger sums of money and often have stricter requirements for the scalability and market size of a company.
VC funds usually expect a significant return within a certain period of time and therefore play a crucial role in the internationalization and expansion of startups. VC funds are particularly indispensable in technology-intensive industries such as IT, biotechnology or artificial intelligence. They not only offer capital for growth, but also strategic support, access to global networks and expertise in scaling business models.
VC financing is often used in the later phases of a startup, when the business model has already been validated and the next stage of growth is to be reached. The relationship between startup and VC is often very close, as investors have a significant influence on strategic direction and operational decisions.
4️⃣🏠 Incubators and Accelerators: Support for young startups
With 14.1% of startups relying on incubators or accelerators, these programs have established themselves as a fixture in the German startup ecosystem. Incubators often offer comprehensive support for very young companies that are still in the ideation or prototype phase. They provide startups with space, infrastructure and consulting services and help to sharpen the business model and prepare it for the market.
Accelerators, on the other hand, are designed to accelerate the growth of startups. They usually offer an intensive, time-limited program in which startups are specifically prepared for growth and market entry. In addition to financial support, accelerators often offer training, workshops and access to networks and investors. Well-known accelerator programs in Germany include the TechFounders Accelerator or the Airbus BizLab.
These programs are particularly interesting for startups that want to benefit from experienced mentors and established companies. Incubators and accelerators often have a strong focus on specific industries or technologies, which allows participating startups to receive targeted support.
5️⃣🤝 Strategic investors: Growth through partnerships
Around 13.9% of startups in Germany will have strategic investors on board in 2023. Strategic investors are usually larger companies that want to gain access to innovative technologies or business models through investments in startups. Unlike investors who are purely financially motivated, strategic investments often focus on synergies and long-term cooperation.
An example of this are corporate venture capital units (CVC), which were created specifically to make strategic investments in innovative startups. Large corporations such as Siemens, Bosch or Deutsche Telekom have their own CVC units that specifically look for startups that can complement their existing business areas or open up new markets.
This type of financing not only offers startups capital, but also the opportunity to benefit from the resources, know-how and networks of the strategic investor. However, it also carries the risk that a startup will become too tied to the interests of the strategic investor and thereby lose its own flexibility and innovative strength.
6️⃣🏦 Bank loans: Classic financing remains relevant
Despite the variety of modern financing methods, 12.8% of startups continue to rely on traditional bank loans. Although this type of financing does not offer access to networks or strategic know-how as is the case with business angels or venture capital, it does have the advantage that the founders retain full control of their company.
Banks typically require collateral for their loans, making it more difficult for startups to take advantage of this source of funding, especially if they are not yet generating significant revenue. Nevertheless, bank loans can be a useful addition for startups in later phases to cover short-term liquidity needs or to invest in further growth.
📊🔍 What is DSM?
The DSM (German Startup Monitor) is one of the most comprehensive and important studies that provides a detailed insight into the German startup landscape every year. The DSM has been carried out by the Federal Association of German Startups eV (BVDS) in cooperation with other partners since 2013 and offers current data and trends on a variety of topics relating to startups in Germany, including financing. The study regularly surveys thousands of startups, founders and players in the ecosystem and provides valuable insights into challenges, opportunities and developments in the scene.
The results of the DSM are equally relevant for politics, business and science, as they serve as a basis for decisions and measures to promote startup culture. The monitor also highlights the regional differences within Germany, analyzes start-up behavior in various industries and shows how the framework conditions for startups in Germany have developed over the years.
Financing startups in Germany is based on a wide range of options. Government funding, private investors and strategic partnerships also play an important role. It is this variety of financing options that allows startups to grow flexibly and scalably, and at the same time makes the German startup ecosystem so dynamic and successful.
📣 Similar topics
- 📣 Diversified financing in Germany's startup market
- 📊 Government funding: backbone of startup financing
- 👼 Business Angels: The strategic supporters
- 🚀 Venture Capital: Growth through large capital
- 🚅 Incubators and accelerators: start-up help for young companies
- 🤝 Strategic Investors: Partnerships for Innovation
- 🏦 Bank loan: The traditional financing option
- 📈 DSM: The German Startup Monitor at a glance
- 🌍 Internationalization through venture capital
- 🧑🏫 Coaching and advice through government programs
#️⃣ Hashtags: #StartupFinancing #BusinessAngels #VentureCapital #Incubators #StrategicInvestors
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Start-up and industry expert, here with its own Xpert.Digital industry hub with over 2,500 specialist articles
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus