Published on: February 12, 2025 / update from: February 12, 2025 - Author: Konrad Wolfenstein
Future technology robotics: opportunities, risks and ethical questions in the focus - background analysis
AI meets robotics: how advanced technologies transform our lives
Intelligent machines are no longer just a vision of science fiction films. More and more industries are relying on advanced robots that are becoming increasingly efficient thanks to sophisticated technologies and artificial intelligence (AI). They relieve people of monotonous or dangerous work, increase productivity and at the same time bring a variety of new challenges, for example in terms of labor market, ethics and data protection. Nevertheless, the market for robotics is more dynamic than ever: estimates could be achieved in a few years in a few years that reach the three -digit billion dollar sector. An average annual growth rate is forecast, which is clearly in the double -digit percentage range. Europe plays a central role in this and is increasingly confident. In the following, a comprehensive overview of the most important developments, areas of application and trends in robotics is given, supplemented by interesting facts and considerations on opportunities and risks.
Economic growth and market potential
The global robotics market is often assessed by experts as an extremely promising field of activity for companies, investors and research institutions. With a view to the period until 2030, estimates are circulating that the entire volume could increase in the range of over $ 180 billion, with an average growth rate between 20 and 25 percent per year. Numerous factors are fueling this development: growing demands on automation in industry, rising wage costs in many countries, but also technological breakthroughs in the field of artificial intelligence and sensors.
A central feature of this boom is that robots are increasingly being used in areas that have so far been firmly in human hands. While industrial robots in automotive production or heavy industry have been used in the past decades, the manufacturers are now opening up to numerous new business areas. This includes the logistics industry, healthcare, retail, gastronomy, agriculture and service areas of all kinds.
Suitable for:
Europe at the center of development
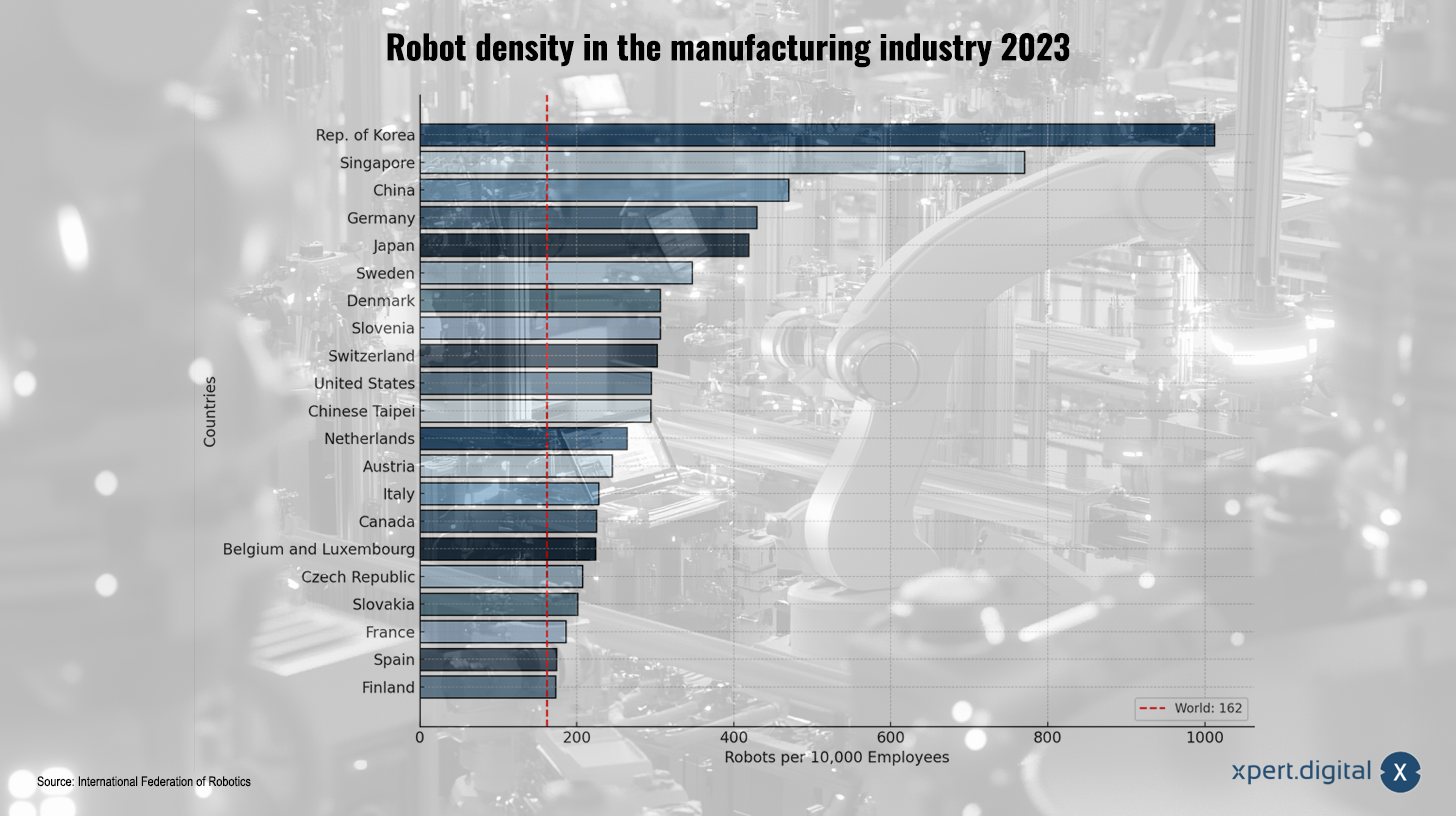
In international comparison, Europe has long played an important role in robotics-from research in top institutions to the production of highly innovative companies to an active start-up scene. In many countries of the European Union, funding programs exist that are particularly geared towards new technologies for industrial automation. At the same time, increasing demands on production quality and speed ensure that companies are increasingly investing in robotics solutions.
"More and more European countries recognize the strategic importance of robotics for their economy," one could summarize, and accordingly, in numerous initiatives and networks that act both nationally and across bodies, are looking for new solutions for a wide variety of industries. While in the past Asia and North America were often considered a pioneer, Europe is now becoming more important when it comes to future -proof technologies.
Particularly noteworthy are some European companies that have managed to secure significant market shares despite the great worldwide competition. Established companies that specialize in the production of industrial robots are worth mentioning, as well as young players who develop innovative service robots for everyday applications. One example is the takeover of a European robotic branch by a larger group, which expands the range of humanoids and collaborative robots in the region. Such mergers increase competitiveness, strengthen innovative strength and ensure an ever greater presence of "intelligent machines" in companies and in public space.
Growth opportunities in South America
Not only Europe, but also regions such as South America, increasingly benefit from the global wave of automation. Countries with a strong production and automation base as well as an active assembly industry- especially Mexico- are moving into the spotlight here. By founding a trade association with a focus on robotics, companies in this region have a solid platform to exchange ideas about innovations and best practice. In view of increasing wage costs and the need for precise, secure manufacturing processes, industrial branches are increasingly rising on robots, which further boosts global needs.
Large players in the robotics market
Although there are a variety of medium -sized and small companies that often develop very specialized robotic solutions, the global market is listed by some major players. Among them are companies with a long tradition in drive and automation technology that are known worldwide. These focus on continuously expanding your customer base and use strategic cooperation to consolidate your market shares and increase your profit.
Some of these companies specialize in delivering turnkey robotics systems for industrial applications. Others rely on service robots, for example in care or gastronomy. A large robotic company recently introduced its smallest industrial robot, which is suitable for sensitive assembly work and particularly tight production environments. With such innovations, manufacturers react to the fact that electronics and other branches of industry produce increasingly finer and more complex products in which millimeter work is required.
Different types of robots
Over time, a wide range of robot types has developed, which differ in terms of their construction, its application and their skills. Instead of a short table shape, it is worth taking a closer look at the most important categories:
1. Industrial robot
These robots are traditionally used in production and take on tasks such as welding, painting, assembling and handling materials. They are often designed for high precision and speed. Modern industrial robots can now be equipped with advanced sensors to perceive their surroundings. As a result, they are much more flexible than their predecessors and can be more easily adjusted to new requirements and product variants.
2. Service robot
Service robots support in the service sector. You can serve food and drinks in gastronomy, in the hotel industry you could take on cleaning tasks and in logistics you support you in picking and transport. There are also more and more service robots in healthcare, for example as assistance systems for nursing staff. Through AI-controlled speech recognition, gesture and facial expressions, some service robots even become reasonably empathetic companions, which in some cases can also take on social tasks.
3. Medical robot
In medicine, robots are used in surgical interventions, rehabilitation or patient care. Surgical robots enable minimally invasive operations and increase the prospects of success in complicated interventions through high -precision movements. Rehabilitation robots help patients to recover mobility by monitoring and customizing the healing process. The further the technology progresses, the more the entire health system will benefit from robots, relieve the nursing staff and at the same time enable higher quality of care.
4. Autonomous mobile robot (AMR)
Autonomous mobile robots can independently orientate themselves in their surroundings by using sensors and using algorithms for navigation and obstacle detection. Unlike so -called driverless transport systems, Amrs do not follow a fixed route, but plan their paths dynamically and adapt to changed conditions. In camps or production halls, they are able to transport goods between different stations autonomously. Thanks to artificial intelligence and machine learning, they are becoming more and more flexible, which makes stronger individualization and higher efficiency in logistics possible.
5. Driverless transport systems (AGV)
Driverless transport systems are suitable for clearly structured environments in which they run a fixed route. They are more limited in their movement patterns than AMRS, but their reliability makes them indispensable in many industrial areas. Such transport systems perform important services in particular where people and machines are separated, for example in automated high -beam bearings.
6.
Gelecrobots have several movable axles that allow you a large radius of action and a highly flexible handling. Typical applications can be found in production and assembly, where a wide range of movements are required, for example when assembling electronic components or when welding larger metal parts. Thanks to advanced tax and control technology, joint crowds can be dosed very finely and can carry out precise forces.
7. Humanoid robots
Humanoid robots are designed in such a way that they resemble humans in appearance or behavior. They often have two legs, two arms and a head area in which sensors, cameras or microphones are installed. These robots serve, among other things, research, entertainment or in some cases in nursing. They can be suitable as a platform for a variety of AI experiments because they act in human environments thanks to human-like anatomy and motor skills. Humanoid robots that provide simple information in department stores or at trade fairs are exemplary.
8. Cobots (collaborative robot)
Collaborative robots are created to work closely with people without the need for extensive safety charges. They have sensitive sensors that react immediately to resistors and can automatically stop when touched in order not to cause any injuries. Cobots are used in companies where man and machine work hand in hand on a production line, for example when installing parts that require precision, while humans make more complex cognitive decisions.
9. Hybrid systems
Hybrid robots combine several of these robot types in one system. An example would be an autonomous mobile robot with an integrated joint arm, which only moves independently in a production hall, then absorbs components or placed. Such multifunctional systems are becoming more important because they are particularly flexible and versatile.
Artificial intelligence as a key technology
AI gives robots the ability to adapt to changed environmental conditions, to learn from experience and to make decisions independently. As a result, robots are increasingly more than mere execution machines whose radius of action is limited by permanently programmed routines. AI algorithms enable them to cope with complex tasks that were originally reserved for human cognitive abilities.
For navigation, for example, many robots use methods of mechanical seeing that allow them to recognize objects or people and to adapt to them situational. In manufacturing systems, a AI-based robot can learn to grab workpieces more and more precisely or to adapt to new models without being completely re-programmed. AI is also indispensable in robotics control: Complicated movement patterns can be created using deep neuronal networks, which are adapted to external influences in real time.
The diverse fields of application show that artificial intelligence gives the robots a real "brain", which increases not only their technical but also their economic importance. However, this also makes it clear that robots and AI are closely interlinked and that it is accordingly important to think about both fields strategically.
Suitable for:
New skills through continuous learning
A significant advantage of AI-controlled robots lies in their ability to learn. You can record, analyze and implement data from the surrounding area. This opens up numerous applications that were previously unthinkable. In production, this means that robots not only perform simple, repeatable activities, but also learn in real time and adapt to new products, materials or assembly steps.
Thanks to methods of mechanical learning and re -forcement learning, a robot can recognize errors, optimize its movement and benefit from any run in order to act faster and more precisely in the future. This continuous learning can also be simulated via digital twins in which virtual robots are trained in a simulation environment before using them in the real production environment.
Effects on different industries
The progressive automation through robot has enormous effects on numerous industries. Robots have been present in the manufacturing industry, especially in automotive construction, but now there are always more demanding applications, for example in the area of e-mobility and battery cell production. High-precision assembly and test processes are required there, which can be implemented well by the high repeatability of robots.
In logistics, driverless transport systems and autonomous mobile robots take over storage work such as picking, goods transport and inventory. This reduces delivery times and companies can make just-in-time production more efficient. In the healthcare system, medical robots enable more precise interventions and relieve doctors for routine tasks, which frees human resources free for more intensive patient contacts.
Service robots in the hotel and catering business are trendy. They serve meals, mix cocktails or clean floors. It is not always just about pure efficiency: some guest also feels such robots as an original attraction. In hospitals or nursing homes, service robots support the staff, bring medication or meals, measure vital parameters or help patients training in the rehabilitation area.
Challenges and hurdles
Despite all the positive growth prospects, robotics and users face various challenges that need to be mastered:
Shortage of skilled workers
The development, programming and maintenance of robots requires highly specialized staff. The lack of qualified specialists in these areas can slow down growth dynamics. Companies and educational institutions must therefore invest in training and further education in order to secure enough experts for the future.
Suitable for:
High costs
Despite falling prices for certain components such as sensors or processors, the purchase and integration of robots for some companies remains expensive. In addition, there are costs for retrofits, software licenses and, if necessary, conversions in production halls. Small and medium -sized companies in particular have to carefully consider when an investment in robotics pays off.
Interoperability
There are grown, heterogeneous systems in many companies. The connection of new robots to existing production management and IT systems is a task that requires comprehensive planning and technical expertise. The respective communication protocols, controls and interfaces must harmonize so that a smooth process is guaranteed.
Ethical and legal aspects
With the use of AI-controlled robots, numerous ethical questions arise. For example, who is liable when an autonomous machine causes damage? How are data protection and privacy preserved when robots collect and analyze data about your environment? What tasks can you entrust robots at all, and which should remain in a human hand to ensure empathy and social responsibility?
acceptance in society
New technologies often cause skepticism, especially when they intervene as deeply into everyday life and work as the robotics. Employers, unions, associations and political decision -makers must therefore develop solutions together that ensure socially acceptable use of robots and strengthen trust in these technologies.
Catalysts: KI, 5G and IoT
The progressive spread of high -speed networks such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) open up new dimensions of robotics. Robots can access cloud -based computing power in real time, evaluate large amounts of data and cooperate with other machines. In a networked factory, robots constantly exchange information about production processes, faults or maintenance intervals, which makes the processes much more efficient and flexible.
The use of edge computing, in which part of the data processing takes place directly at the scene, also makes it easier and reliably to react to events quickly and reliably. Latz reduction through EDGE computing can be decisive in particular in security-critical areas if robots act in direct cooperation with people, for example, or navigate through tight terrain.
Ethical implications and social responsibility
The growing robotic use raises a number of ethical questions. In particular, concern for jobs is a sensitive topic: How many manual activities will be taken over by machines in the future, and in which areas is human staff still needed? In the past, technological upheavals have often caused new job profiles to develop while old people disappeared. Nevertheless, a high degree of further training and retraining is required so that people in an automated world can continue to find meaningful and qualified employment.
Another important point is data protection: service robots with cameras and microphones can quickly penetrate personal areas. Whether in the nursing home or in private households - if robots collect data on health, habits or conversations, it is essential to ensure that it remains protected. Technologies such as anonymization and encryption play a central role here.
The question also arises. If a robot makes decisions independently, who is liable if these decisions are wrong and cause damage? Manufacturers, programmers, users or even the robot themselves? Since legal framework conditions in many countries are not yet fully adapted to the new technical possibilities, there is a need for action here. "Legislators and manufacturers are asked to formulate and maintain clear rules to prevent abuse and undesirable developments," one could demand.
The human factor
Despite all the automation, people remain irreplaceable in many ways. Complex creativity, empathy, moral judgment and the ability to intuitively behave in crisis situations are strengths that, according to today, cannot cover the robots to the same extent. The trend is closer to a closer cooperation between man and machine: While robots fully exploit their strengths in precision and endurance, humans can contribute their skills to solve problem and communication.
An example of this is collaborative jobs in modern factories. There, Cobot's side stand by side with the employees at a assembly line. The robot is enough, screw or solder, while humans take the more complex or creative steps. However, this close interaction presupposes that the robots used are safe and intuitive.
Passenend to this:
Outlook for future developments
The robotic is and remains a dynamic field in which a lot can change in a short time. There are several trends that are expected to become more important in the coming years:
1. Further development of humanoid robots
The desire to make robots as human-like as possible is not just a gimmick for science fiction fans. Humanoid robots could work in environments that are designed for humans - without complex conversions. You could operate door handles, climb stairs or use tools that are already designed for human ergonomics. The closer the robotics approaches the human anatomy, the greater the application spectrum, provided the technical hurdles can be solved in the event of balance, energy supply and control.
2. Robotics in agriculture
Agriculture also benefits from increasingly intelligent robots. Whether on automatic sowing and harvesting, watering, weeds or monitoring plant growth - the possibilities are diverse. Precision agriculture, in which drones and floor robots collect data and use fertilizers or crop protection in a targeted manner, protects resources and increases the yield. This trend is likely to accelerate in the coming years, especially in regions where specialists for field work are rare.
3. Robotics in care
In view of the aging population, the demand for supportive technologies in the nursing sector will increase. Robots can take on physically exhausting tasks, such as lifting and surrounding patients. You can help people with restrictions to cope with their everyday life, be it through assistance when dressing or gripping objects. In addition, there could also be social robots who do the elderly company or remind them of taking medication.
4. Robotics and climate protection
Robots can be used in environmental protection projects, for example for waste disposal in water or for monitoring nature reserves. Robots will also become more important in the energy sector when it comes to waiting and monitoring solar or wind turbines. Since such systems are often installed in hard -to -reach places, robots can do inspections and repairs more efficiently and safely.
5. Coordination and standardization
In order for robots to be able to interact smoothly with other systems and people, standards and norms are needed that make compatibility easier. Numerous organizations work on guidelines for safe and efficient robotics application. In the future, it can be expected that even more value will be placed on interoperability and easy usability in order to reduce the hurdles for companies when entering robotics.
6. Connection to quantum computing
In the future, quantum computing could play a role in highly complex calculations and optimization tasks that are relevant for autonomous robots. Due to the considerably faster processing of certain mathematical problems, intelligent algorithms could be developed that enable movements, environmental analyzes or resource planning at a new level of complexity. Quantum computing is still in an early phase, but the robotics community observes the progress very closely.
The robotics are in a phase in which economic opportunities and technological innovations go hand in hand
With rapid growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation, robots can be found in more and more industries and reliably perform their services there. Companies worldwide react to this development by making extensive investments in research and development.
At the same time, experts and political decision -makers agree that social, ethical and legal questions are associated with the triumphal march of intelligent machines. Framework conditions must be created that ensure a fair distribution of the advantages and cushioned disadvantages for the labor market and society. If this succeeds, the robotics can make an important contribution to create more prosperity, to automate dangerous or monotonous activities and focus on people of demanding and creative activities.
Europe has the potential to take on a leading role if it is possible to promote innovation and at the same time value data protection and social responsibility. Initiatives that are carried together by public institutions and private companies can help research, development and standard application go hand in hand.
While many industries have just discovered the potential in the use of intelligent machines, other already extensive experience with robot solutions. In the future we will probably see even more how robots change our living and working world. The skills for interaction and collaboration with people will continue to mature and thus enable new working models in which the strengths of people and machine complement each other perfectly.
Robots could become an integral part of everyday life in the near future: be it that they support older people, make it easier to cook or help us in disaster areas. From automatic delivery bots in large cities to high-tech assistants in hospitals and factories-"the future belongs to the robot assistants", one could say in reprint. It is crucial to make this change responsible and make clever decisions in order to use the technology in such a way that it serves as much as possible.
In view of these developments, it remains to be seen whether the considerable growth potential actually develops fully. In contrast to some of the past, there is a lot of indications that the robotics and AI have long since arrived in the real world and provide tangible added value. Increasing speed, precision and ability to learn from robots create a solid foundation that goes far beyond pure experimental fields.
For the next few years, it can be refrained from that new robot generations will come onto the market with improved sensors, refined AI algorithms and a higher adaptability. There are also collaborative approaches in which people continue to play a crucial role. The question is less whether robots are integrated into everyday life, but rather how quickly and to what extent this happens.
Robotics harbors huge opportunities: It can help to make urgently needed products more efficient, relieve the shortage of skilled workers and to make relief in many areas of life. At the same time, one should not ignore possible risks and have to actively tackle them. Responsible politics, forward -looking regulation and an open social debate are essential to ensure that the development goes in a direction that uses everyone.
Ultimately, it turns out that intelligent machines are in conquering the entire globe. It is shown whether the market volume in the coming years will actually reach or even surpass the forecast billions. However, the signs suggest that the robotics will be one of the central technologies of the 21st century. Anyone who relies on this future today and brings up the courage to invest in research, development and training in good time will benefit tomorrow. And it is precisely in this interface from an economic opportunity and social responsibility the key to exploit the enormous potential of robots sensibly and sustainably.
Suitable for: