The demand for heat pumps as an alternative to oil or gas heating is currently high – Image: Xpert.Digital / SKT Studio|Shutterstock.com
The use of heat pumps as a replacement for oil or gas heaters is currently in great demand in Germany. With the help of heat pumps, the stored heat heat from the environment (water, air or earth) can be removed and brought to a temperature that can be used for heating purposes, hot water preparation and even cooling. The graphic, see below “This is how a heat pump works”, illustrates this process schematically. Heat pumps are therefore an environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to conventional heating systems. It is important to note that the choice of heat pump technology depends on various factors, such as the size of the building, the type of heat requirement and the available resources. Detailed advice and planning by a specialist is therefore essential.
Advice and tips for your heat pump heating
A heat pump heater is an efficient and environmentally friendly type of heating, but it also has a few things to consider. One of the most important points is the location of the heat pump. It is recommended that the installation location should not be in the immediate vicinity of bedrooms or neighboring buildings and that a minimum distance of three to four meters is advisable. In addition, the individual manufacturer's information on noise emissions should also be observed.
Another important thing about heat pump heating systems is that they should ideally be installed in modernly insulated new buildings with central ventilation control. Heating systems with a lower flow temperature such as underfloor or wall heating are also recommended. However, if the area is large enough, normal radiators can also be used.
There are also some general things to consider when using heat pump heaters. For example, heat pumps should be regularly maintained and cleaned to maximize their efficiency. In addition, the heat pumps should only be installed and maintained by professionals to avoid problems or damage.
It is important to do your research and seek expert advice if necessary to ensure the best possible efficiency and performance from the heat pump.
A heat pump heater is an environmentally friendly heating system
A heat pump heater is an environmentally friendly heating system that recovers energy from the environment (e.g. from the air, the ground or groundwater) and uses it to generate heat in buildings. In contrast to conventional heating systems, which burn fossil fuels and therefore emit pollutants and greenhouse gases, a heat pump uses energy from the environment and is therefore low-emission and cost-efficient. There are different types of heat pumps, which vary depending on the type and availability of the energy source. An important consideration when installing a heat pump heater is the location of the system, as an adequate supply of air or water is required. The location should also not be in the immediate vicinity of bedrooms or neighboring buildings. When choosing a heat pump, you should also pay attention to the individual manufacturer's information on noise emissions. A heat pump is particularly effective in combination with a low flow temperature, for example with underfloor heating or wall heating, and is therefore particularly recommended for modernly insulated new buildings with central ventilation control.
What types of heat pumps are there?
There are different types of heat pumps, which differ mainly based on the heat source they use. The types of heat pumps common for single- and two-family homes are the air/water heat pump, groundwater/water heat pump and geothermal heat pump, also known as brine heat pump or brine/water heat pump. In comparison, the consumer advice center differentiates between air heat pumps, groundwater heat pumps and geothermal heat pumps. But there are also types of heat pumps that can utilize high media temperatures, for example to use industrial waste heat. Overall, the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of heat pumps depend on various factors such as individual needs and structural conditions, so thorough advice from experts is recommended.
How a heat pump works
A heat pump is a heat engine that absorbs thermal energy from a reservoir with a lower temperature and - together with the drive energy - transfers it as useful heat at a higher temperature to a system to be heated.
The refrigeration cycle process is a central part of how the heat pump works and takes place in four steps:
- Evaporate
- Compressing a gas
- Condense
- Relax
This process is constantly repeated. Heat pumps can generate heat from various sources such as ambient air, groundwater or soil and use renewable energy. However, this use alone does not make a system climate-friendly, as the energy consumption during production and operation must also be taken into account.
In principle, the heat pump works like a refrigerator, but in reverse. The heat pump extracts heat from the outside air, the ground or the groundwater, raises it to a higher temperature level and then releases it into the heating and/or shower water. It works reliably and requires no special maintenance. Similar to the refrigerator, the heat pump releases heat through a heat exchanger. While the refrigerator uses the evaporation process to cool the interior, the heat pump uses the heat gained during liquefaction in the heat exchanger for heating purposes. Strictly speaking, all households have a refrigerator with a heat pump that cools the interior by moving heat out.
The heat pump is an energy-efficient technology
The heat pump is an energy-efficient technology for space heating and hot water supply based on the principle of heat transfer. The ambient air is used as a heat source and the temperature is increased through compression before the heat is transferred to the heating and service water.
To maximize the efficiency of the heat pump, it is best if the temperature difference between the ambient heat and the target temperature of the room is as small as possible. In this way, the heat pump has to work less and uses less energy.
There are different types of heat pumps, such as air-to-water heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps and water-to-water heat pumps, each with different advantages and disadvantages and should be selected depending on the location and requirements.
An important factor when choosing a heat pump is its efficiency, which is measured by the so-called COP (Coefficient of Performance). A higher COP value means higher efficiency and therefore lower operating costs.
It is also important to maintain the heat pump regularly to maximize its efficiency and lifespan. Regular maintenance can also help identify problems early and fix them before they lead to expensive repairs.
The heat pump is a promising technology for reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions in building technology, especially in conjunction with renewable energies such as solar or photovoltaic systems.
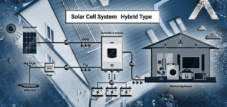
Combination of heat pump and solar system
Combining a heat pump with a solar system is considered one of the most effective ways to heat a building while reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
While the heat pump requires electricity as a heat source, more and more electricity suppliers are offering special electricity tariffs for heat pumps, which are referred to as heating electricity. These tariffs are tailored to the needs of heat pumps and can help reduce operating costs.
Changing your heating electricity provider is usually straightforward and can be carried out in a similar way to changing your household electricity provider. However, it is important to carefully review the contract terms and tariff details to ensure that the tariff chosen meets the heat pump's requirements and makes economic sense.
The price for heat pump electricity is currently in the middle range of consumer prices for heating fuels in Germany and amounts to around 11.15 cents per kilowatt hour. However, it should be noted that the actual operating costs of a heat pump depend on various factors, such as the efficiency of the heat pump, the size of the building and the heating habits of the residents.
The combination of heat pump and solar system is a sustainable and effective way to heat buildings, which can become even more economical through the use of special heating electricity tariffs.
Solar thermal energy, heat pump and solar system
Combining a heat pump with a solar system makes sense, but whether this combination is efficient depends on various factors.
A combination with a solar thermal system makes little sense because both devices perform the same task. Instead, it is recommended to consider a combination of a heat pump and a photovoltaic system in order to use the electricity generated by the photovoltaic system to operate the heat pump. Such a combination can be efficient because the heat pump can operate at low flow temperatures, as is the case with underfloor heating. This means that the heat pump only requires a small amount of electrical energy.
It is also possible to combine a heat pump with solar thermal energy and photovoltaics at the same time. Because solar thermal energy is very efficient, it requires less space than photovoltaics and therefore has little impact on the amount of electricity generated by the photovoltaic system. However, it is important to consider that such a combination may result in higher installation costs.
Overall, the usefulness and efficiency of combining a heat pump with a solar system depends on many factors, such as the size of the systems, the existing infrastructure, the installation costs and the specific requirements of the building. It is therefore advisable to seek advice from a qualified installer to find the best solution for your individual building.
- Plan photovoltaics for warehouses, commercial halls and industrial halls
- Industrial plant: Plan a photovoltaic open-air system or open-space system
- Plan solar systems with photovoltaic solutions for freight forwarding and contract logistics
- B2B solar systems and photovoltaic solutions & advice
Technical advice from Xpert.Solar
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital – Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital – www.xpert.solar – www.xpert.plus