What advantages do heat pumps offer compared to other heating systems? – Image: Costazzurra|Shutterstock.com
Innovative heating solutions: How heat pumps reduce costs in the long term
Modern heating systems: Why heat pumps are the better choice
Heat pumps offer numerous advantages compared to other heating systems, making them an attractive option for modern and sustainable heating solutions. These advantages include not only energy efficiency and environmental friendliness, but also long-term costs and security of supply. The following section details the most important advantages of heat pumps over conventional heating systems such as oil, gas, and pellet boilers.
1. High energy efficiency
One of the biggest advantages of heat pumps is their impressive energy efficiency. While conventional heating systems like oil or gas boilers typically have an efficiency of 80 to 90 percent, heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of 300 to 500 percent. This means that they can generate three to five kilowatt-hours of heat from one kilowatt-hour of electricity by utilizing the heat stored in the ambient air, the ground, or groundwater.
Unlike fossil fuels, which generate energy through combustion and cause losses in the form of waste heat, heat pumps utilize existing environmental energy. This makes them particularly efficient and allows them to produce large amounts of heat with relatively little electricity. This high efficiency also results in lower operating costs compared to gas or oil heating systems.
2. Lower operating costs
Another advantage of heat pumps is their comparatively low operating costs. Since they draw most of the energy they need from the environment, they require only a small amount of electrical energy to operate the compressor. This means that, with a correctly sized heat pump, heating costs can be about a quarter lower than those of a gas heating system and even a third lower than those of an oil heating system.
In the long run, the higher initial costs of heat pumps are offset by savings in operating costs. Especially in times of rising prices for fossil fuels such as gas and oil, heat pumps offer a cost-effective and stable alternative.
3. Use of renewable and inexhaustible energy sources
Heat pumps utilize renewable energy sources such as air, soil, or groundwater, which are virtually inexhaustible. Unlike fossil fuels, these natural resources are not subject to economic or political fluctuations. This makes heat pumps particularly future-proof and independent of volatile energy market prices.
Furthermore, these energy sources are emission-free, meaning that heat pumps do not release harmful greenhouse gases during operation – provided they are powered by green electricity. As a result, they contribute significantly to reducing CO₂ emissions and are an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional heating systems.
4. Future security and independence from fossil fuels
Dependence on fossil fuels like oil and gas poses not only an economic risk but also an environmental problem. Fossil fuels are finite, and their prices are subject to strong fluctuations due to geopolitical developments. The Russian war of aggression against Ukraine, for example, has demonstrated how drastically gas and oil prices can rise.
Heat pumps, on the other hand, make households more independent of these developments, as they do not require fuel. They rely on electricity as their primary energy source, which increasingly comes from renewable sources. This ensures stable and predictable operating costs and offers long-term security of supply.
5. Low maintenance and longevity
An often overlooked advantage of heat pumps is their low maintenance compared to other heating systems. Since heat pumps do not use combustion processes, there are fewer wear parts and therefore less need for repairs. Unlike pellet or oil heating systems, for example, there is no need to clean combustion chambers or dispose of ash.
Heat pumps have a lifespan of over 20 years and operate largely maintenance-free during this time. Only regular system inspections are required to ensure optimal performance. This longevity makes heat pumps a reliable and cost-effective solution for long-term use.
6. Space-saving installation
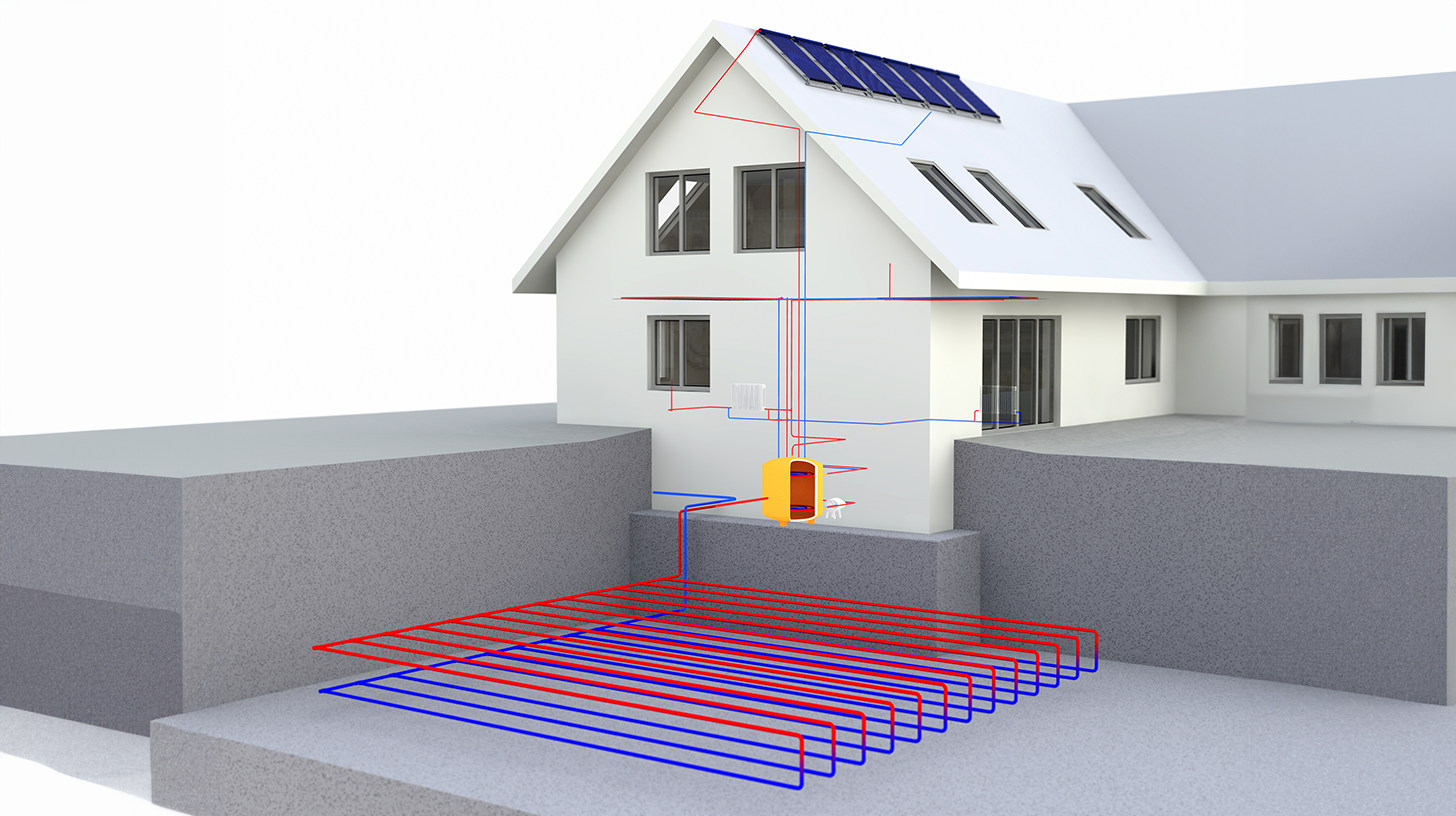
Compared to pellet heating systems or other systems that require fuel storage, heat pumps require significantly less space. There is no need for storage rooms for pellets or tanks for oil or gas. Especially in new buildings or well-insulated older buildings, an air-to-water heat pump can be installed in a space-saving manner.
Even though ground or water heat pumps require somewhat more construction work (e.g. drilling for ground probes), the overall space requirement remains more manageable than with systems that use fuel storage.
7. Versatile applications
Heat pumps are versatile: they can be used not only for heating buildings, but also for hot water production and cooling in summer (with appropriate equipment). Ground source heat pumps are particularly well-suited for this dual function, as they can both heat and cool.
Heat pumps can be operated even more efficiently when combined with other technologies such as photovoltaic systems. Using self-generated electricity from solar energy further reduces operating costs and minimizes CO₂ emissions.
8. Government subsidies
Another important advantage of heat pumps is the government subsidy available for their installation. Many countries offer generous grants for installing heat pump systems to encourage the switch to renewable energy. In Germany, for example, up to 70 percent of the investment costs can be covered by government subsidy programs.
These subsidies make switching to a heat pump more financially attractive and help the investment pay for itself faster.
The advantages clearly outweigh the disadvantages
Heat pumps offer numerous advantages over conventional heating systems:
- They are extremely energy efficient and offer lower operating costs.
- They use renewable energy sources from the environment and are therefore environmentally friendly.
- They make households independent of fossil fuels and their price fluctuations.
- They require little maintenance and have a long lifespan.
- They require less space than systems with fuel storage.
- They are versatile (heating, cooling) and can be easily combined with photovoltaic systems.
- Government funding programs provide financial support for the transition.
All these factors make heat pumps a future-proof solution for sustainable heating – both in new buildings and in well-insulated existing buildings.
Suitable for:
