The silent revolution for Great Britain: Why the future of food lies in automated cold storage facilities – Image: Xpert.Digital
Food security in the UK: How automation strengthens the supply chain and creates resilience
Why has food security become a critical issue in the United Kingdom?
Food security has become one of the United Kingdom's most pressing strategic challenges in recent years. With a self-sufficiency rate of just 62% for food and only 75% for domestically produced goods, the country is increasingly reliant on international supply chains. These figures are particularly alarming given that forty years ago the UK produced over 75% of its own food.
This dramatic decline in self-sufficiency is the result of a combination of structural changes and recent political and economic upheavals. Population growth, changing consumer preferences, and the increasing demand for a diverse diet, including produce that cannot be grown in the UK climate, have all contributed to this development. Of particular concern is the fall in self-sufficiency for fresh vegetables to just 53% – the lowest level since records began in 1988.
What external factors have destabilized British food security?
Brexit has proven to be one of the most impactful factors on British agriculture and food security. Leaving the European Union not only ended free trade with its main trading partner for agricultural products, but also created significant bureaucratic hurdles. Farmers now face complex documentation requirements, permit procedures, and unforeseen delays, leading to food waste and lost revenue. The EU remains the main supplier of British food, accounting for 24.2% of imports in 2023, but this share has fallen considerably since 2018.
The EU's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which shaped British agricultural policy for decades, has been replaced by a new system focused on public goods and environmental services. While this realignment could have positive long-term effects, the transition process is causing considerable uncertainty for farmers. Direct payments to farmers are being phased out, putting many farms under enormous financial pressure.
The war in Ukraine has dramatically exposed the vulnerability of global food supply chains. Russia and Ukraine together account for 36% of global wheat exports and significant shares of other staple foods. The conflict has led to dramatic price increases for energy, fertilizers, and animal feed. British farmers experienced a 50% rise in feed costs within a year, significantly increasing production costs and threatening the economic viability of many farms.
How do budget cuts affect British agriculture?
The British government has made significant cuts to agricultural support in recent years. Since 2015, subsidies for farmers have fallen by 20% in real terms, representing a loss of £722 million in public funding. These cuts are continuing: the Labour government has announced a further annual reduction of £100 million to England's agricultural budget.
These cuts come at a time when British agriculture is already under enormous pressure. In 2023, 8,100 farms closed their doors – almost one in every 25 farms in the country. The combination of reduced subsidies, rising production costs, and extreme weather events has led to a collapse of confidence in the agricultural community. A survey by the Country Land and Business Association found that 88% of farmers would have to revert to intensive farming methods if funding for sustainable programs were cut.
Why is automation in the cold chain crucial for food safety?
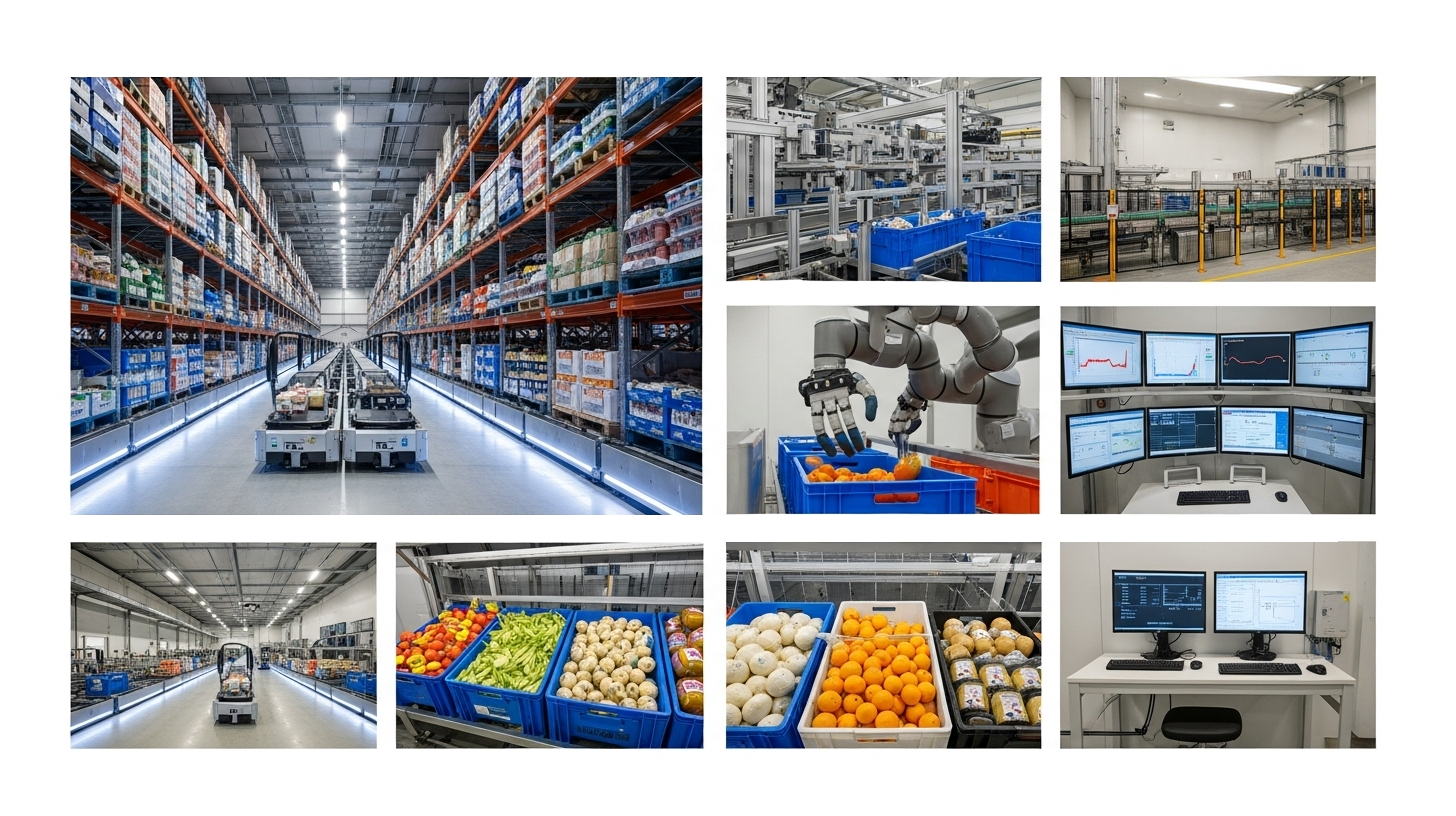
Automating the cold chain is a critical component in strengthening food security. Given the UK's increasing reliance on imports – particularly for 84% of its fresh tomatoes and significant shares of other perishable goods – efficient management of buffer stocks is becoming a strategic necessity. Automated systems make it possible to absorb fluctuations in supply and ensure a continuous availability of food.
The challenges of cold chain logistics are multifaceted: precise temperature control, strict inventory management, and rapid order fulfillment are essential to ensure quality and safety. Traditionally, cold storage facilities relied on manual labor for tasks such as order picking, packing, and inventory management. However, this approach often resulted in inefficiencies, increased labor costs, and a higher risk of errors.
Automated storage systems and transport vehicles (AS/RS and STVs) have proven to be transformative solutions. These systems can move goods between storage racks and picking stations with minimal human intervention. The flexibility of STVs enables faster retrieval times and a smoother workflow, while also allowing them to operate in temperature-controlled areas where employees can work in more comfortable conditions.
How do buffer systems contribute to the resilience of the supply chain?
Buffer systems play a crucial role in building resilience in the food supply chain. They act as a strategic reserve that can compensate for fluctuations in production and demand. In a volatile global environment where supply disruptions can occur due to geopolitical events, extreme weather, or pandemics, automated buffer systems offer the flexibility needed to maintain supply.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the fragility of global food systems. Sudden spikes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and labor shortages led to shortages on supermarket shelves. Automated systems proved more resilient to these disruptions, as they are less dependent on human labor and can operate around the clock.
Modern buffer systems utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to make proactive decisions for optimal system automation. These systems can predict demand patterns, automate inventory rotation, and optimize warehouse efficiency through precise inventory management. Particularly in the area of the cold chain, they enable the management of goods according to expiration dates and best-before information – a continuous flow of pallet storage, retrieval, and picking based on specific requirements.
How can automation help manage supply fluctuations?
Automation offers several mechanisms for managing supply fluctuations, which are crucial for food security. First, automated systems enable precise inventory management through real-time monitoring and tracking of products. Warehouse Control Software (WCS) and Warehouse Execution Software (WES) can manage inventory based on FEFO (First-Expiry-First-Out) and FIFO principles, thereby minimizing food waste and maintaining product quality.
The systems can continuously monitor temperatures in different zones of the cold storage facility to ensure products are stored within the correct temperature range. They can also monitor how long products are exposed to temperatures outside the desired range and send alerts based on user-defined time limits. This functionality is crucial for maintaining product integrity during supply interruptions.
A key aspect of automation is the ability to anticipate and respond to fluctuations in demand. Modern systems use predictive analytics and artificial intelligence to identify demand patterns and optimize inventory accordingly. This allows companies to build strategic reserves while avoiding overstocking.
Automation also reduces reliance on human labor, which is particularly important in times of crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how labor shortages can impact food supplies. Automated systems can operate around the clock without interruption, thus ensuring continuity of supply even with limited staff availability.
What is the significance of temperature control for food safety?
Temperature control is a fundamental aspect of food safety that goes beyond mere storage and encompasses the entire cold chain from production to consumer. Precise temperature control is crucial to preventing spoilage, protecting consumers, and avoiding costly product recalls. At a time when the UK is heavily reliant on imports, the integrity of the cold chain is becoming a matter of national strategic interest.
Automated refrigeration systems offer significant advantages over manual approaches. They can maintain constant temperatures across different zones while using energy more efficiently. An automated storage and retrieval (AS/RS) system requires less roof space than conventional racking systems and can achieve energy savings of 35-50%. This is particularly important given rising energy costs, exacerbated by the war in Ukraine and other geopolitical factors.
The systems can also maintain detailed logs and audit trails for all temperature measurements, inventory movements, and user actions to simplify compliance reporting and provide reports for audits. This documentation is crucial for traceability and quality assurance in an increasingly regulated food industry.
Xpert partner in warehouse planning and construction
Automation in cold chains: Improved safety and more efficient food supply
How does digitalization contribute to the resilience of the cold chain?
Digitizing the cold chain is a crucial factor in building resilience against disruptions. Internet of Things (IoT) services enable real-time information, online deliveries, and market-based demand forecasts. In an environment where the majority of shops and markets were closed due to COVID-19 restrictions, digital services proved to be a lifesaver.
A cold chain with a robust digital manufacturing system enables standardized work to meet consumer demand, allows workers to keep their jobs, and reduces the pressure of relying on specific experts or individuals for smooth operations. Digitalization also enables real-time data exchange between businesses and governments, closes communication gaps, and facilitates timely decision-making to manage crises.
Advanced temperature tracking and reporting are key technologies increasingly being used in food supply chains worldwide. They provide valuable temperature visibility across the entire supply chain, enable rapid action in case of problems, and deliver data that can contribute to improved transport efficiency, safety, and temperature control.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cold chain automation enables systems to make proactive and dynamic decisions for optimal system automation. These technologies can predict demand patterns, detect anomalies, and initiate preventive maintenance measures before problems occur.
What challenges exist when implementing automation in the cold chain?
Implementing automation in refrigerated environments presents unique technical and operational challenges. Extreme temperature conditions place specific demands on materials and technology. Forklift trucks must be equipped with specialized components, cables, and a particular grade of steel to function reliably in environments as low as -25°C. Pallet shuttles have similar requirements and utilize low-viscosity lubricants, heated controllers, and capacitors instead of lithium-ion batteries.
The conditions that are so stressful for people can also pose challenges for automation systems not specifically designed for low temperatures. This necessitates specialized equipment and expertise, which can increase investment costs. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced workload, improved safety, and increased efficiency, outweigh these initial costs.
Another obstacle is the complexity of integrating different systems. Modern cold chain solutions must seamlessly integrate AS/RS systems, conveyor systems, automated guided vehicles, and warehouse management software. This integration requires specialized expertise and careful planning to ensure that all components work together harmoniously.
Training staff and adapting to new workflows can also present challenges. While automation reduces repetitive and physically demanding tasks, it requires employees to develop new skills in system monitoring and maintenance.
How does automation affect working conditions in the cold chain industry?
Automation has a transformative impact on working conditions in the cold chain industry, with significant improvements in employee safety and well-being. Traditionally, cold storage operations required personnel to work in extreme conditions as low as -25°C, which not only impacted productivity but also posed safety risks. Automation significantly minimizes the need for manual labor in these hazardous environments.
The implementation of automated systems allows order picking tasks to be carried out in well-lit, safe areas with comfortable temperatures between -5°C and +5°C. This improvement in working conditions leads to increased employee well-being, satisfaction, and more productive operations. STVs can deliver goods to operators, enabling tasks to be performed outside of extreme cold environments.
Automation also reduces physical strain and repetitive movements that can lead to workplace accidents and long-term health problems. Automated systems take over heavy lifting, repetitive movements, and precise positioning, significantly reducing the risk of injury for employees. This results in lower insurance costs, reduced employee turnover, and improved morale.
While some fear that automation will lead to job losses, reality paints a more nuanced picture. Automation often shifts the nature of work required from physically demanding, repetitive tasks to more technical roles in system monitoring, maintenance, and optimization. This can lead to better career opportunities and higher wages for skilled workers.
What impact does automation have on food quality and safety?
Automation plays a crucial role in improving food quality and safety by reducing human error and ensuring consistent processes. Automated systems eliminate many of the variables that can lead to quality and safety issues, such as inconsistent temperature control, improper handling, and cross-contamination.
Precise inventory rotation is a critical aspect of food safety that is significantly improved through automation. Warehouse control software can automatically manage products based on expiration dates and best-before information, ensuring that older stock is used first. This reduces food waste and minimizes the risk of spoiled products reaching consumers.
The continuous monitoring and documentation provided by automated systems are crucial for traceability. If a food safety issue arises, automated systems can quickly identify the affected product batches and track their path through the supply chain. This capability is essential for effective recalls and minimizing the impact of safety problems.
Automated systems also use food-safe lubricants and materials specifically designed for food contact. This ensures that the automation itself does not pose a source of contamination. Furthermore, automated systems reduce manual product handling, thereby minimizing the risk of contamination through human contact.
How can automated systems contribute to the long-term sustainability of the food supply?
Automated systems contribute to the long-term sustainability of the food supply in several ways. First, they optimize energy efficiency through precise temperature control and reduced energy waste. AS/RS systems can achieve energy savings of 35-50% compared to conventional storage systems, which is particularly important given rising energy costs and environmental concerns.
Reducing food waste is another critical aspect of sustainability. Through precise inventory management, optimized stock rotation, and improved quality control, automated systems can significantly reduce the amount of food that spoils before reaching consumers. This is particularly important given that an estimated one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted.
Automated systems also enable better space utilization through vertical storage and compact system designs. This means that more inventory can be stored in fewer square meters, reducing the need for expanding the facility's footprint. This efficient use of space is crucial in a world of increasing urbanization and limited available land.
The longevity and reliability of automated systems also contribute to sustainability. Well-designed automation systems can operate for decades with minimal maintenance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and their associated environmental impact. Furthermore, these systems enable more precise planning and forecasting, thereby reducing overproduction and the associated waste of resources.
The ability of automated systems to operate around the clock also maximizes the efficiency of existing infrastructure. Instead of building new facilities, companies can utilize their existing ones more intensively, thereby reducing the overall footprint of food logistics. This is particularly important for the sustainability of the global food supply.
What role do automated systems play in addressing future challenges?
The role of automated systems in addressing future food supply challenges cannot be overstated. With projected population growth, increasing urbanization, and the intensification of climate change, the demands on food systems will rise exponentially. Automated systems offer the scalability and flexibility needed to meet these growing demands.
Climate change poses particular challenges for food production and distribution. Extreme weather events, altered precipitation patterns, and rising temperatures are already impacting agricultural production worldwide. Automated cold chain systems can help mitigate these effects by creating a more reliable and controlled environment for the storage and transport of temperature-sensitive foods.
The ability of automated systems to collect and analyze large amounts of data will also be crucial for optimizing global food distribution. By integrating IoT sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, these systems can predict demand patterns, anticipate supply chain disruptions, and take proactive measures to maintain supply.
The modular nature of modern automation systems also allows them to grow and adapt to changing needs. Companies can gradually expand their automation capabilities as demand grows, ensuring that investments remain flexible and aligned with evolving business requirements.
Ultimately, automated systems will play a crucial role in creating resilient local and regional food systems. By enabling efficient, small-scale production and distribution facilities, these systems can help reduce reliance on long, vulnerable supply chains while strengthening local food security.
Investing in automated cold chain technologies is therefore not only a response to current challenges, but also a strategic preparation for a future in which food security, sustainability, and resilience will be crucial. For the United Kingdom, which already faces a critical self-sufficiency deficit, comprehensive cold chain automation could be the key to securing its long-term food security.
Xpert.Plus warehouse optimization - high-bay warehouses such as pallet warehouses consulting and planning
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ Our business language is English or German
☑️ NEW: Correspondence in your national language!
I would be happy to serve you and my team as a personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) . My email address is: wolfenstein ∂ xpert.digital
I'm looking forward to our joint project.