A digital transformation is not so easily shaken from the sleeves. How should that work if you don't even know what, how and where should be "transformed". Where do you best start?
Most are luminaries in their field. But with digitalization it becomes so dizzying. All the terms like artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, Industry 4.0, smart factory, connectivity, global digital strategy and all the many other buzzwords.
Can you initiate digital transformation with traditional processes and simply adapt existing and long-successful business models? Where are the opportunities, where are the risks that it doesn't end up in chaos and worsening?
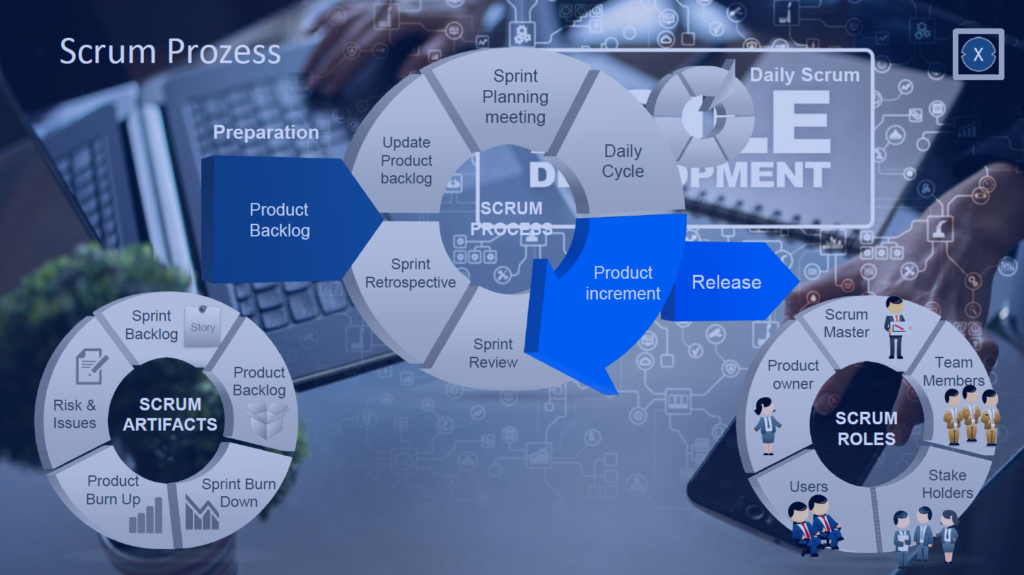
In addition to transformation and change management, the most important thing is the right project and product management.
Digital transformation is intended to improve processes. Here we present two management models: Kaizen and Six Sigma.
To download:
Design thinking is an approach that aims to solve problems and develop new ideas. The aim is to find solutions that are convincing from the user's point of view. In contrast to other innovation methods, design thinking can or is sometimes described not as a method or process, but as an approach that consists of the three equal basic principles of team, space and process.
Design thinking is based on the assumption that problems can be solved better when people from different disciplines work together in an environment that promotes creativity, develop a problem together, take people's needs and motivations into account and then develop concepts that are tested multiple times. The process is based on the work of designers, which is understood as a combination of understanding, observation, ideation, refinement, execution and learning.
Numerous international companies and organizations of all sizes use design thinking as a project, innovation, portfolio and/or development method. SAP SE in particular uses design thinking as an approach to how the development units work with customers and their end users. Other companies that use design thinking include Swisscom, Deutsche Bank, Volkswagen, Deutsche Bahn, Siemens, Airbnb, Pinterest, Francotyp-Postalia.
Thinking Hats – Six Thinking Hats is a creativity technique. It is a tool for group discussions and individual thinking. It includes six different colored “hats”. Parallel thinking linked to this method is intended to make thought processes more efficient, especially in groups.
A starting point of the method is the assumption that the brain thinks in different ways that can be controlled consciously and can therefore be used in a discussion at certain times. It is assumed that communication difficulties arise when, for example, one person expresses their feelings about something and then another person approaches the problem analytically.
The individual hats represent
- blue: organizing, moderating thinking: overview of the processes ('big picture': the blue sky)
- white: analytical thinking: concentration on facts, requirements and how they can be achieved (objectively: the blank slate)
- red: emotional thinking, feeling: concentration on feelings and opinions (subjective: fire and warmth)
- black: critical thinking: risk assessment, problems, skepticism, criticism and communicating fears (critical: black painting, devil's advocate)
- yellow: optimistic thinking: what is the best-case scenario (speculative: sunshine)
- green: creative, associative thinking: new ideas, creativity (constructive: growth)
This methodology is based on parallel thinking. This means that when working on a task, everyone involved always wears the same color hat and changes hats together, thus thinking in parallel. In this way, conflicts are avoided and all positions are still taken into account.
This method helps improve group communication.