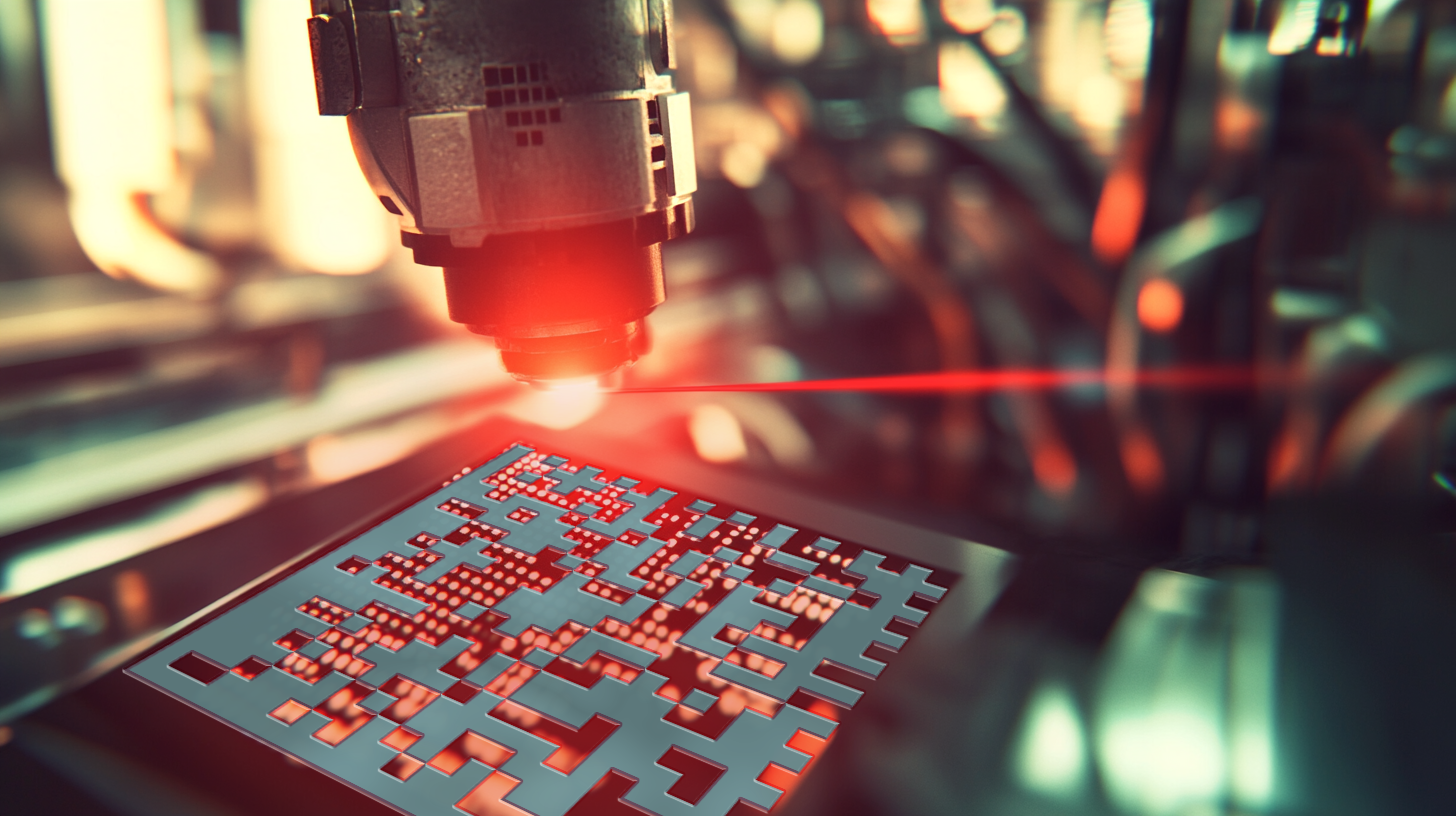
Sensors and measurement technology: How will the GS1 DataMatrix code change the sensor technology industry? – Image: Xpert.Digital
How will GS1's 2D matrix code change the sensor technology industry? What are the future predictions, which industries will it affect, and who will benefit the most?
The GS1 DataMatrix Code and the Future of Sensor Technology
The sensor technology industry is undergoing a transformation. The increasing digitalization and networking of production processes within the framework of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 necessitates new solutions for the unambiguous identification and traceability of components and products. The GS1 DataMatrix code offers enormous potential in this regard and will significantly influence the industry in the coming years. This report examines the functionality of the GS1 DataMatrix code, analyzes its impact on sensor technology, and provides an outlook on future developments and trends.
Suitable for:
What is the GS1 DataMatrix code?
The GS1 DataMatrix code is a variant of the DataMatrix symbology that conforms to GS1 specifications and has been publicly available since 1994. It is based on the ECC200 standard and differs from conventional DataMatrix codes in its use of FNC1, a special character for identifying GS1 data structures, and in its use of application identifiers (AIs) to define the data that follows. Application identifiers are short codes that precede the data record and indicate the type of information (e.g., serial number, batch number, expiration date). This allows the scanner to correctly interpret and assign the data. The GS1 DataMatrix code is compact, space-saving, and can store large amounts of data in a small area—up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters or 3,116 numbers. It consists of a finder pattern, which helps the scanner locate the symbol, and the encoded data record itself. The size of the symbol varies depending on the amount of data and can be either square or rectangular. Another important aspect of the GS1 DataMatrix code is its error-correcting capability. By using the Reed-Solomon error correction method, the code can still be read even with up to 30% damage. This increases the reliability and robustness of the code, especially in harsh environments.
The GS1 DataMatrix code can also be used to encode a GS1 Digital Link. A GS1 Digital Link is a special web URI that enables both product identification and a link to online materials that comply with the GS1 standard. This allows manufacturers and distributors to provide web-based product information to other businesses or consumers.
Current trends in sensor technology
The sensor technology industry is dynamic and innovative. Current trends include, among others:
- Miniaturization and integration: Sensors are becoming increasingly smaller and can be integrated into larger systems to simplify data acquisition and analysis.
- Improved accuracy and reliability: Sensors are delivering increasingly accurate and reliable data, which is crucial for many applications.
- Wireless connectivity: Sensors are increasingly being networked wirelessly to facilitate data transmission and integration.
- AI-supported data analysis: Artificial intelligence (AI) is used to analyze sensor data and gain valuable insights from it.
- Energy efficiency and sustainability: Sensors are becoming more energy-efficient and thus contribute to sustainability.
- Sensor fusion and edge computing: Sensor data is combined with other data sources and processed directly at the edge of the network to enable faster response times.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: Protecting sensor data from cyberattacks and safeguarding privacy are becoming increasingly important.
These trends show that the sensor technology industry is constantly evolving and adapting to the requirements of modern industry.
The sensor technology industry and its challenges
The sensor technology sector is an important component of modern industry and plays a crucial role in areas such as automation, robotics, medical technology, and environmental monitoring. Current challenges facing the sector include:
High costs
Developing and implementing sensor technology can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. This applies to both the purchase costs of the sensors themselves and the costs of integrating them into existing systems and developing software for data analysis.
Data management
Sensors generate large amounts of data, the management, processing, and analysis of which can be challenging. Storing, processing, and analyzing this data requires high-performance IT infrastructures and specialized expertise.
complexity
Sensor technology can be complex and difficult to implement, especially for manufacturers with limited technical expertise. Selecting the right sensors, integrating them into existing systems, and interpreting the sensor data require in-depth knowledge and experience.
integration
Integrating sensor technology into existing systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise. The compatibility of the sensors with the existing systems must be ensured, and the data must be integrated into existing processes and workflows.
Long ROI
The payback period for investments in sensor technology can be long, which hinders its adoption in various markets. Companies must weigh the long-term benefits of sensor technology against the initial investment costs.
Reliability and longevity
Sensors must function reliably in diverse environments and have a long service life. In industrial settings, sensors are often exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, vibrations, and other stresses.
Suitable for:
Impact of the GS1 DataMatrix code on sensor technology
The GS1 DataMatrix code has the potential to change the sensor technology industry in many ways:
Improved traceability
The unique identification of sensors and components with the GS1 DataMatrix code allows their path through the entire supply chain to be traced seamlessly. This enables better quality control, simplifies the tracking of errors, and supports the optimization of production processes. In the event of problems or recalls, the affected products can be identified quickly and precisely.
More efficient maintenance
Linking sensor data with the GS1 DataMatrix code enables predictive maintenance. By analyzing sensor data, maintenance intervals can be optimized and downtime minimized. Instead of maintaining sensors at fixed intervals, maintenance can be performed on demand when sensor data indicates an impending failure.
Integration into digital twins
The GS1 DataMatrix code can serve as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds, enabling the integration of sensors into digital twins. Digital twins are virtual representations of physical products or systems used for the simulation, analysis, and optimization of processes. By linking sensor data with the digital twin, processes can be monitored and optimized in real time.
Suitable for:
Increasing efficiency
By automating processes and reducing errors, the GS1 DataMatrix code contributes to increased efficiency in the sensor technology industry. Automatic data acquisition through code scanning minimizes manual intervention and thus reduces the likelihood of transmission errors.
Improved data security
The GS1 DataMatrix code offers higher data security compared to conventional barcodes because it has integrated error correction and remains readable even when damaged. This is particularly important in harsh environments where sensors are often exposed to extreme conditions.
Printing technologies
The GS1 DataMatrix code can be applied to products using various printing technologies. These include, among others:
- Direct Part Marking (DPM): The code is laser-etched or engraved directly onto the product.
- Labels: The code is printed on a label, which is then stuck onto the product.
- Inkjet printing: The code is printed onto the product using an inkjet printer.
The choice of printing technology depends on the requirements of the application, e.g. the size of the product, the material and the environment in which the sensor is used.
Developments in the sensor technology industry
The integration of the GS1 DataMatrix code into the sensor technology industry will continue to progress in the future. The following trends are emerging:
Increasing networking
The GS1 DataMatrix code will be increasingly linked with other technologies such as RFID and the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable even more comprehensive data collection and analysis. This will allow the development of intelligent and networked sensor networks that can collect and exchange data in real time.
Smart implants
In medical technology, smart implants could be equipped with a GS1 DataMatrix code to transmit information about their condition and function to a central system in real time. This enables continuous monitoring of the implant and early detection of problems.
Personalized medicine
The GS1 DataMatrix code will play a crucial role in personalized medicine by enabling the unique identification of medications and medical devices, thus supporting more individualized patient care. Linking patient data to the code allows treatments to be better tailored to individual patient needs.
Blockchain and AI
The GS1 DataMatrix code will also be integrated with new technologies such as blockchain and AI in the future. Blockchain can increase the security and transparency of supply chains, while AI can improve the analysis of sensor data and enable the development of new applications.
Industries and players
The introduction of the GS1 DataMatrix code in sensor technology will affect various industries. Among the most important are:
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, the GS1 DataMatrix code is used for component traceability and to ensure the long-term availability of information about the service life of aircraft and military equipment. The code can be used, for example, to identify engine parts, landing gear components, or avionics systems. Sensors play a crucial role in aerospace, for instance, in monitoring the structural integrity of aircraft, monitoring engines, and in navigation.
Medical technology
In medical technology, the GS1 DataMatrix code plays a central role in implementing Unique Device Identification (UDI). The UDI regulation aims to uniquely identify each medical device and track it throughout its entire lifecycle. The code contains the Device Identifier (UDI-DI), which identifies the manufacturer and the specific model of the medical device, as well as the Production Identifier (UDI-PI), which contains information such as the batch number, serial number, and manufacturing date. Sensors are used in a wide variety of medical applications, such as ventilators, infusion pumps, and dialysis machines.
pharmaceutical industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, the GS1 DataMatrix code is used to combat counterfeit medicines and optimize the supply chain. The code enables the unique identification of medications and assists pharmacists and healthcare professionals in verifying their authenticity. By coding batch numbers and expiration dates, medications can be better managed and recalls conducted more efficiently. The code also supports sustainability initiatives by reducing waste through improved inventory management. Sensors are used in the pharmaceutical industry to monitor environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity to ensure the quality of medications.
logistics
In the logistics industry, the GS1 DataMatrix code enables more efficient and secure management of goods flows. The code can be used to mark packages, pallets, and containers, and allows for the automatic collection of data at various points in the supply chain.
Healthcare
In healthcare, the GS1 DataMatrix code contributes to improved patient safety and increased efficiency. The code can be used to label medications, medical devices, and patient samples, enabling secure and efficient information management within hospitals.
Various stakeholders will benefit from the introduction of the GS1 DataMatrix code in sensor technology
Sensor manufacturer
Sensor manufacturers benefit from improved traceability of their products and more efficient management of their supply chains.
Sensor integrators
Sensor integrators can use the GS1 DataMatrix code to integrate sensors into digital twins and thus develop new services and business models.
End users of sensor technology
End users benefit from increased reliability and efficiency of their plants and systems.
Logistics provider
Logistics providers can use the GS1 DataMatrix code to optimize their processes and improve transparency in the supply chain.
Regulatory authorities
Regulatory authorities benefit from improved control over the supply chain and a more effective fight against product counterfeiting.
advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
The GS1 DataMatrix code offers numerous advantages for the sensor technology industry. Among the most important are:
- High data capacity: The GS1 DataMatrix code can store large amounts of data in a small area.
- Robustness: The code is robust against damage and can still be read even if partially destroyed.
- Versatility: The code can be printed in various sizes and shapes and is suitable for marking small and large products.
- Global standardization: The GS1 DataMatrix code is a global standard that ensures interoperability between different systems and stakeholders.
Disadvantages
Besides the advantages, there are also some challenges in implementing the GS1 DataMatrix code in sensor technology:
- Compatibility: Integrating the code into existing systems may involve compatibility issues.
- Training requirements: The introduction of the code requires training for employees to ensure correct application and handling.
- Costs: Implementing the code may involve initial costs for new scanners and software.
Suitable for:
Potential for process optimization
The GS1 DataMatrix code offers the sensor technology industry enormous potential for process optimization, improved traceability, and increased efficiency. The increasing digitalization and networking of production processes will further enhance the code's importance in the future. Various industries and stakeholders will benefit from the code's introduction, particularly sensor manufacturers, sensor integrators, end users, logistics providers, and regulatory authorities.
The GS1 DataMatrix Code addresses the specific challenges of the sensor technology industry, such as the traceability of components in complex supply chains and the need for efficient maintenance. By linking sensor data with unique product identifiers, the code enables the implementation of predictive maintenance and the integration of sensors into digital twins. Furthermore, the GS1 DataMatrix Code supports the trend toward personalized medicine by enabling the unique identification of medical devices and the tracking of patient-specific data.
Despite some challenges in its implementation, the advantages of the GS1 DataMatrix code outweigh the disadvantages, and it will significantly shape the sensor technology industry in the coming years.
Our recommendation: 🌍 Limitless reach 🔗 Networked 🌐 Multilingual 💪 Strong sales: 💡 Authentic with strategy 🚀 Innovation meets 🧠 Intuition
At a time when a company's digital presence determines its success, the challenge is how to make this presence authentic, individual and far-reaching. Xpert.Digital offers an innovative solution that positions itself as an intersection between an industry hub, a blog and a brand ambassador. It combines the advantages of communication and sales channels in a single platform and enables publication in 18 different languages. The cooperation with partner portals and the possibility of publishing articles on Google News and a press distribution list with around 8,000 journalists and readers maximize the reach and visibility of the content. This represents an essential factor in external sales & marketing (SMarketing).
More about it here:
We are there for you - advice - planning - implementation - project management
☑️ SME support in strategy, consulting, planning and implementation
☑️ Creation or realignment of the digital strategy and digitalization
☑️ Expansion and optimization of international sales processes
☑️ Global & Digital B2B trading platforms
☑️ Pioneer Business Development
I would be happy to serve as your personal advisor.
You can contact me by filling out the contact form below or simply call me on +49 89 89 674 804 (Munich) .
I'm looking forward to our joint project.
Xpert.Digital - Konrad Wolfenstein
Xpert.Digital is a hub for industry with a focus on digitalization, mechanical engineering, logistics/intralogistics and photovoltaics.
With our 360° business development solution, we support well-known companies from new business to after sales.
Market intelligence, smarketing, marketing automation, content development, PR, mail campaigns, personalized social media and lead nurturing are part of our digital tools.
You can find out more at: www.xpert.digital - www.xpert.solar - www.xpert.plus

